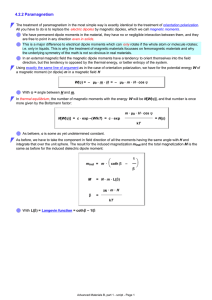
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... associated with the atoms of the material, is of no (electro)technical consequence . It is, however, important for analytical purposes called "Electron spin resonance" (ESR) techniques. There are other types of paramagnetism, too. Most important is, e.g., the paramagnetism of the free electron gas. ...
... associated with the atoms of the material, is of no (electro)technical consequence . It is, however, important for analytical purposes called "Electron spin resonance" (ESR) techniques. There are other types of paramagnetism, too. Most important is, e.g., the paramagnetism of the free electron gas. ...
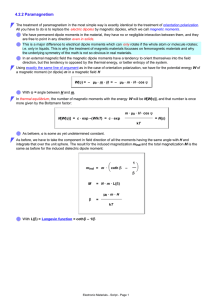
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... associated with the atoms of the material, is of no (electro)technical consequence . It is, however, important for analytical purposes called "Electron spin resonance" (ESR) techniques. There are other types of paramagnetism, too. Most important is, e.g., the paramagnetism of the free electron gas. ...
... associated with the atoms of the material, is of no (electro)technical consequence . It is, however, important for analytical purposes called "Electron spin resonance" (ESR) techniques. There are other types of paramagnetism, too. Most important is, e.g., the paramagnetism of the free electron gas. ...
Magnetism - Mr. Treon
... apply an invisible force on objects around them. • The space around an electric charge, in which an electric force can be exerted, is called an electric field. • The space around a magnet, in which a magnetic force is exerted, is filled with a magnetic field. • If we place another magnet or a small ...
... apply an invisible force on objects around them. • The space around an electric charge, in which an electric force can be exerted, is called an electric field. • The space around a magnet, in which a magnetic force is exerted, is filled with a magnetic field. • If we place another magnet or a small ...
Electromagnetism William Gilbert (15401603) Hans Christian
... Right Hand Rule # 1 Grasp the straight conductor with your right hand. The thumb points in the direction of the conventional current (positive to negative). The curved fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
... Right Hand Rule # 1 Grasp the straight conductor with your right hand. The thumb points in the direction of the conventional current (positive to negative). The curved fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
Magnetism - Little Miami Schools
... o The fields from _______________ poles _________________ each other forming a ________________________ between the magnets. o The fields from two ______________ poles ____________ each other. ...
... o The fields from _______________ poles _________________ each other forming a ________________________ between the magnets. o The fields from two ______________ poles ____________ each other. ...
Magnetism
... • If a material is magnetic, it has the ability to exert forces on magnets or other magnetic materials. • A permanent magnet is a material that keeps its magnetic properties even when it is NOT close to other magnets. ...
... • If a material is magnetic, it has the ability to exert forces on magnets or other magnetic materials. • A permanent magnet is a material that keeps its magnetic properties even when it is NOT close to other magnets. ...
Attention Graduate Students Introduction to Plasma Physics Physics
... time to circle the Earth--a few minutes. View from North Pole ...
... time to circle the Earth--a few minutes. View from North Pole ...
Magnetic Activity
... There are many stars that exhibit magnetic activity, some are much stronger than the sun Usually because they are rotating faster ...
... There are many stars that exhibit magnetic activity, some are much stronger than the sun Usually because they are rotating faster ...
Mass extinctions-Superchrons draft June 2010
... their demise. The hypothesis draws upon evolutionary pressure, unstable behavior of the earth's magnetic field and the presence in all species of animals since the Precambrian of an organelle that responds to the earth's magnetic field for local and long distance navigation, orientation and homing, ...
... their demise. The hypothesis draws upon evolutionary pressure, unstable behavior of the earth's magnetic field and the presence in all species of animals since the Precambrian of an organelle that responds to the earth's magnetic field for local and long distance navigation, orientation and homing, ...
Magnetic Earth - Earth Learning Idea
... by movements within the liquid iron-rich part of the outer core of the Earth and NOT by a bar magnet inside it. • When some rocks (particularly lavas) cool, they can retain the direction of the Earth’s magnetisation at that location and at that time. This is called ‘remanent magnetisation’. This inf ...
... by movements within the liquid iron-rich part of the outer core of the Earth and NOT by a bar magnet inside it. • When some rocks (particularly lavas) cool, they can retain the direction of the Earth’s magnetisation at that location and at that time. This is called ‘remanent magnetisation’. This inf ...
Figure 23-1 Magnetic Induction
... The polarity of the induced emf in a loop is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux through the loop. That is, the induced current is in a direction such that the induced magnetic field attempts to maintain the original flux through the loop. ...
... The polarity of the induced emf in a loop is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux through the loop. That is, the induced current is in a direction such that the induced magnetic field attempts to maintain the original flux through the loop. ...
Diapositiva 1
... produced by a magnet has similar pattern to the electric field lines produced by an electric dipole. The main difference is that the magnetic field lines are closed loop (they have no origin and no ending point) while electric field lines always originate from positive charges and end on negative ch ...
... produced by a magnet has similar pattern to the electric field lines produced by an electric dipole. The main difference is that the magnetic field lines are closed loop (they have no origin and no ending point) while electric field lines always originate from positive charges and end on negative ch ...
The Measurement of a Magnetic Field in Fundamental Units
... a magnetic field. If the balance is so aligned that the end of the U-shaped metal loop is perpendicular to the field while the sides are parallel to it only the end will be subject to a force from the field. We can measure the force on the end of the loop by balancing it with a known weight hung fro ...
... a magnetic field. If the balance is so aligned that the end of the U-shaped metal loop is perpendicular to the field while the sides are parallel to it only the end will be subject to a force from the field. We can measure the force on the end of the loop by balancing it with a known weight hung fro ...
Ch 7 Magnetism and Its Uses
... What do magnetic field lines represent. In what direction do they point? How do they indicate the strength of the magnetic field? Where, on a magnet, are the magnetic fields the strongest? What happens to the magnetic field of two magnets when they are brought close to each other? See fig 4 p 204. I ...
... What do magnetic field lines represent. In what direction do they point? How do they indicate the strength of the magnetic field? Where, on a magnet, are the magnetic fields the strongest? What happens to the magnetic field of two magnets when they are brought close to each other? See fig 4 p 204. I ...
the nature of magnetism 19.1
... • 2 ( a north pole and a south pole) • Two north poles or two south poles = alike poles • One north pole and one south pole = unlike or opposite poles ...
... • 2 ( a north pole and a south pole) • Two north poles or two south poles = alike poles • One north pole and one south pole = unlike or opposite poles ...
Magnetism Activity Write-up
... 1. Students will be able to describe how magnetic forces affect objects on Earth 2. Recognize patters of magnetic fields ...
... 1. Students will be able to describe how magnetic forces affect objects on Earth 2. Recognize patters of magnetic fields ...
Continental Drift Continental Drift Continental Drift
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
Edward Sabine

General Sir Edward Sabine KCB FRS (14 October 1788 – 26 June 1883) was an Irish astronomer, geophysicist, ornithologist,explorer, soldier and the 30th President of the Royal Society.Two branches of Sabine's work are notable: Determination of the length of the seconds pendulum, a simple pendulum whose time period on the surface of the Earth is two seconds, that is, one second in each direction; and his research on the Earth's magnetic field. He led the effort to establish a system of magnetic observatories in various parts of British territory all over the globe, and much of his life was devoted to their direction, and to analyzing their observations.While most of his research bears on the subjects just mentioned, other research deals with the birds of Greenland (Sabine's gull is named for him), ocean temperatures, the Gulf Stream, barometric measurement of heights, arc of the meridian, glacial transport of rocks, the volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands, and various points of meteorology.