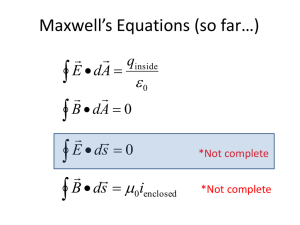Lecture 13 ELEC 3105 NEW
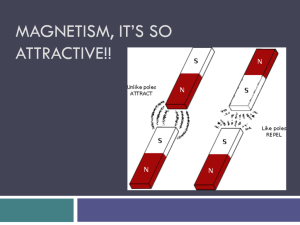
... of repulsion is very weak (a hundred thousand times weaker than the ferromagnetic force of attraction). Water, the main component of grapes, is diamagnetic. When an electric charge moves, a magnetic field is created. Every electron is therefore a very tiny magnet, because electrons carry charge and ...
... of repulsion is very weak (a hundred thousand times weaker than the ferromagnetic force of attraction). Water, the main component of grapes, is diamagnetic. When an electric charge moves, a magnetic field is created. Every electron is therefore a very tiny magnet, because electrons carry charge and ...
Magnets and the Magnetic field Part 1: The magnetic field of a
... minimal (or even absent)? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 4. Using your text as a reference, explain how RHR-1 explain ...
... minimal (or even absent)? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 4. Using your text as a reference, explain how RHR-1 explain ...
* Magnetic Scalar Potential * Magnetic Vector Potential
... The magnetic scalar potential is useful only in the region of space away from free currents. If J=0, then only magnetic flux density can be computed from the magnetic scalar potential The potential function which overcomes this limitation and is useful to compute B in region where J is present is ...
... The magnetic scalar potential is useful only in the region of space away from free currents. If J=0, then only magnetic flux density can be computed from the magnetic scalar potential The potential function which overcomes this limitation and is useful to compute B in region where J is present is ...
The electric field
... Gauss’s Law can be used to solve three types of problems: 1. Finding the total charge in a region when you know the electric field outside that region 2. Finding the total flux out of a region when the charge is known a) It can also be used to find the flux out of one side in symmetrical problems b) ...
... Gauss’s Law can be used to solve three types of problems: 1. Finding the total charge in a region when you know the electric field outside that region 2. Finding the total flux out of a region when the charge is known a) It can also be used to find the flux out of one side in symmetrical problems b) ...
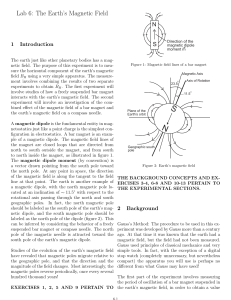
Permanent Magnet
... molten core. These currents are hundreds of miles wide and flow at thousands of miles per hour as the earth rotates. The powerful magnetic field passes out through the core of the earth, passes through the crust and enters space. This picture was created by a computer from a mathematical model, show ...
... molten core. These currents are hundreds of miles wide and flow at thousands of miles per hour as the earth rotates. The powerful magnetic field passes out through the core of the earth, passes through the crust and enters space. This picture was created by a computer from a mathematical model, show ...
On electromagnetic induction Contents
... 2. The first two - grouped under square brackets for underlining their common H ~ whose ~ · dl, mathematical and physical origin - come from the line integral l E value is controlled by Maxwell equation (2) through equation (5). Accordingly, their sum must be zero when the magnetic eld does not dep ...
... 2. The first two - grouped under square brackets for underlining their common H ~ whose ~ · dl, mathematical and physical origin - come from the line integral l E value is controlled by Maxwell equation (2) through equation (5). Accordingly, their sum must be zero when the magnetic eld does not dep ...