TRADE OF HEAVY VEHICLE MECHANIC
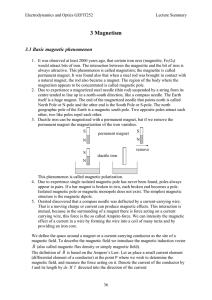
... Some materials such as soft iron become magnetised more easily than other materials, but they also lose their magnetism easily, so magnets of soft iron are called temporary magnets. When we consider materials simply as either magnetic or non-magnetic, this division is really based on the strong magn ...
... Some materials such as soft iron become magnetised more easily than other materials, but they also lose their magnetism easily, so magnets of soft iron are called temporary magnets. When we consider materials simply as either magnetic or non-magnetic, this division is really based on the strong magn ...
NGSS High School Domains - Frontera`s Physics Chomp!
... o PS3.A: Energy is quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter and radiation within that system. That there is a single quantity called energy is due to the fact that system’s total energy is conserved, even as, within the system, energy is continually tra ...
... o PS3.A: Energy is quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter and radiation within that system. That there is a single quantity called energy is due to the fact that system’s total energy is conserved, even as, within the system, energy is continually tra ...
Lesson Plan
... Figure 1. A needle is normally not a magnet because its magnetic domains are not aligned (left). When a needle contacts a permanent magnet for an extended time (or is rubbed along a permanent magnet), its magnet domains align in the same direction, forming a temporary magnet with a magnetic field ( ...
... Figure 1. A needle is normally not a magnet because its magnetic domains are not aligned (left). When a needle contacts a permanent magnet for an extended time (or is rubbed along a permanent magnet), its magnet domains align in the same direction, forming a temporary magnet with a magnetic field ( ...
Magnetic Field Sensor
... range (marked low amplification in an earlier version of this sensor) is used to measure relatively strong magnetic fields around permanent magnets and electromagnets. Each volt represents 32 gauss (3.2 × 10-3 tesla). The range of the sensor is ±64 gauss or ±6.4 × 10-3 tesla. The 0.3 mT range (marke ...
... range (marked low amplification in an earlier version of this sensor) is used to measure relatively strong magnetic fields around permanent magnets and electromagnets. Each volt represents 32 gauss (3.2 × 10-3 tesla). The range of the sensor is ±64 gauss or ±6.4 × 10-3 tesla. The 0.3 mT range (marke ...
A rotating coil - Collins.co.uk.
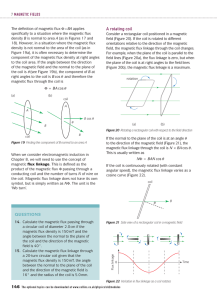
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...