Introduction
... Are not useful for predicting the temperature changes observed during the 20th century. Show that volcanic eruptions and changes in sunlight are responsible for most of the changes observed over the 20th century. Can predict the 20th century observed temperature changes with natural factors only. Ca ...
... Are not useful for predicting the temperature changes observed during the 20th century. Show that volcanic eruptions and changes in sunlight are responsible for most of the changes observed over the 20th century. Can predict the 20th century observed temperature changes with natural factors only. Ca ...
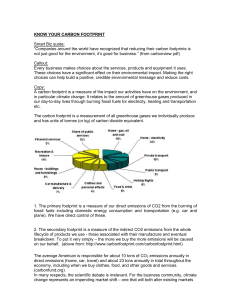
Know your carbon footprint
... lifecycle of products we use - those associated with their manufacture and eventual breakdown. To put it very simply – the more we buy the more emissions will be caused on our behalf. (above from: http://www.carbonfootprint.com/carbonfootprint.html) The average American is responsible for about 10 t ...
... lifecycle of products we use - those associated with their manufacture and eventual breakdown. To put it very simply – the more we buy the more emissions will be caused on our behalf. (above from: http://www.carbonfootprint.com/carbonfootprint.html) The average American is responsible for about 10 t ...
Radiation: Most? Least?
... encourage plants to grow, followed by long periods of drought, during which they will burn. We can already see this in Florida," - Meinrat Andreae, Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, August 2001. ...
... encourage plants to grow, followed by long periods of drought, during which they will burn. We can already see this in Florida," - Meinrat Andreae, Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, August 2001. ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... Mauna Loa observations, the concentration of carbon dioxide appears to be increasing over time. ...
... Mauna Loa observations, the concentration of carbon dioxide appears to be increasing over time. ...
Climate Control and Ozone Depletion
... Biodiversity will decrease NPP will decrease Dry climate ecosystems will increase Positive feedback-accelerate global warming and climate change= more drought ...
... Biodiversity will decrease NPP will decrease Dry climate ecosystems will increase Positive feedback-accelerate global warming and climate change= more drought ...
Document
... Why should we care if snow and ice are melting? • Arctic ice regulates the temperature and precipitation of regions to the south (North America, Europe) • Mountain glaciers play a vital role in the water cycle and the availability of fresh water for hundreds of millions of people. ...
... Why should we care if snow and ice are melting? • Arctic ice regulates the temperature and precipitation of regions to the south (North America, Europe) • Mountain glaciers play a vital role in the water cycle and the availability of fresh water for hundreds of millions of people. ...
2014 Was the Warmest Year Ever Recorded on Earth
... “Since the end of the 20th century, the temperature hasn’t done much,” Dr. Christy said. “It’s on this kind of warmish plateau.” NASA and the other American agency that maintains long-term temperature records, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, issued separate data compilations on ...
... “Since the end of the 20th century, the temperature hasn’t done much,” Dr. Christy said. “It’s on this kind of warmish plateau.” NASA and the other American agency that maintains long-term temperature records, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, issued separate data compilations on ...
(Abstract)
... Research Applications Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Thursday, November 4, 2010 3:00 PM – 4:00 PM 282 J. Wayne Reitz Union Co-Host: Florida Climate Institute Title: Helping Water Utilities consider climate change and other uncertainties in their planning process Abstract The wat ...
... Research Applications Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Thursday, November 4, 2010 3:00 PM – 4:00 PM 282 J. Wayne Reitz Union Co-Host: Florida Climate Institute Title: Helping Water Utilities consider climate change and other uncertainties in their planning process Abstract The wat ...
Contrarian views on Climate Change
... human-caused warming of the Earth’s atmosphere, is seen by many as the foremost threat facing our world today. The UN has convened scientific experts from around the world to research, measure and gauge possible responses to what many warn as significant global changes due to warming of the planet’s ...
... human-caused warming of the Earth’s atmosphere, is seen by many as the foremost threat facing our world today. The UN has convened scientific experts from around the world to research, measure and gauge possible responses to what many warn as significant global changes due to warming of the planet’s ...
Definitions
... greenhouse gas emissions. Climate change scenarios are produced by the UK Climate Impacts Programme every 6 years. These are based on various scenarios depending on whether greenhouse gas emissions are reduced, stay the same or increased. Go to the UKCIP website for more information: http://www.ukci ...
... greenhouse gas emissions. Climate change scenarios are produced by the UK Climate Impacts Programme every 6 years. These are based on various scenarios depending on whether greenhouse gas emissions are reduced, stay the same or increased. Go to the UKCIP website for more information: http://www.ukci ...
Science of climate change
... The atmosphere is not behaving as models would predict. Climate is mainly influenced by the sun. A carbon dioxide rise has always come after a temperature increase not before. 8. Long-term data on hurricanes and arctic ice is too poor to assess trends. 9. Water vapour is the major greenhouse gas; co ...
... The atmosphere is not behaving as models would predict. Climate is mainly influenced by the sun. A carbon dioxide rise has always come after a temperature increase not before. 8. Long-term data on hurricanes and arctic ice is too poor to assess trends. 9. Water vapour is the major greenhouse gas; co ...
Sum Tipping Point Feb 06
... Hurricanes are powerful heat engines. Fortune magazine (“The High Cost of Climate Change,” 2 September 2005) explains, “Hurricanes suck energy from warm waters to drive their winds. So as sea-surface temperatures rise, the storms absorb more energy that gets pumped out in the form of high-speed wind ...
... Hurricanes are powerful heat engines. Fortune magazine (“The High Cost of Climate Change,” 2 September 2005) explains, “Hurricanes suck energy from warm waters to drive their winds. So as sea-surface temperatures rise, the storms absorb more energy that gets pumped out in the form of high-speed wind ...
Chapter 19 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
... • 90–99% likely that lower atmosphere is warming • Especially since 1960 • Mostly from human-caused increases in greenhouse gases • Earth’s climate is now changing from increased greenhouse gases • Increased greenhouse gas concentrations will likely trigger significant climate disruption this centur ...
... • 90–99% likely that lower atmosphere is warming • Especially since 1960 • Mostly from human-caused increases in greenhouse gases • Earth’s climate is now changing from increased greenhouse gases • Increased greenhouse gas concentrations will likely trigger significant climate disruption this centur ...
Unit 1 - Climate and Change
... closer to the sun, and therefore received more radiation making temperatures warmer. At other times earth is further away, receives less radiation, and temperatures are therefore cooler. 2.2 What challenges might our future climate present us with? a The climate of the UK appears to be changing as a ...
... closer to the sun, and therefore received more radiation making temperatures warmer. At other times earth is further away, receives less radiation, and temperatures are therefore cooler. 2.2 What challenges might our future climate present us with? a The climate of the UK appears to be changing as a ...
2 - ISDC
... – Surface temperature increase without feedbacks: 1.2 K – Surface temperature increase with feedbacks: 2-5 K, according to the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) – Most of the uncertainty comes from how clouds will respond ...
... – Surface temperature increase without feedbacks: 1.2 K – Surface temperature increase with feedbacks: 2-5 K, according to the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) – Most of the uncertainty comes from how clouds will respond ...
Equilibrium response of a climate model when feedbacks are
... The Union of Concerned Scientists recently published an assessment of climate change in California. They based their assessment on the results from two global climate models, one with a relatively low sensitivity to CO2 doubling (PCM), and the other with a relatively high sensitivity (HADCM3). They ...
... The Union of Concerned Scientists recently published an assessment of climate change in California. They based their assessment on the results from two global climate models, one with a relatively low sensitivity to CO2 doubling (PCM), and the other with a relatively high sensitivity (HADCM3). They ...
Chapter 7.2 Revision Answers
... Allow up to [2] for more than 3 effects and then up to [2] for each category. Candidates are asked to review so there should be an overview of most effects not emphasis on one or two. Carbon dioxide increases → global warming → climate change → sea levels rise/disruption of ocean currents (e.g. in ...
... Allow up to [2] for more than 3 effects and then up to [2] for each category. Candidates are asked to review so there should be an overview of most effects not emphasis on one or two. Carbon dioxide increases → global warming → climate change → sea levels rise/disruption of ocean currents (e.g. in ...
Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate
... 1750 has been one of warming, with a radiative forcing of 1.6 Wm-2” (IPCC 2007). • Mean g global CO2 concentrations are now at 386ppm pp (2008 mean) which is 30% greater than at anytime in the past 800,000 years, while the rate of increase is 200 times faster than at any time over the same period. p ...
... 1750 has been one of warming, with a radiative forcing of 1.6 Wm-2” (IPCC 2007). • Mean g global CO2 concentrations are now at 386ppm pp (2008 mean) which is 30% greater than at anytime in the past 800,000 years, while the rate of increase is 200 times faster than at any time over the same period. p ...
CHAPTER II DISCUSSION 2.1 Definition of Global Warming
... Global warming is a process of increasing the average temperature of the atmosphere, ocean, and land earth. Global average temperature at the earth's surface has risen 0.74 + 0,180C (1.33 + 0,320F) during the last hundred. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes that "Most of the ...
... Global warming is a process of increasing the average temperature of the atmosphere, ocean, and land earth. Global average temperature at the earth's surface has risen 0.74 + 0,180C (1.33 + 0,320F) during the last hundred. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes that "Most of the ...
Yeomans Letter 11
... dioxide out of the air. Fundamentally that’s what rich soil humus is made of. Fixing soil is totally feasible and so terribly necessary For the oil and other fossil fuel producers and for the agrochemical companies, these are not options they happily support. Logically they would never graciously pe ...
... dioxide out of the air. Fundamentally that’s what rich soil humus is made of. Fixing soil is totally feasible and so terribly necessary For the oil and other fossil fuel producers and for the agrochemical companies, these are not options they happily support. Logically they would never graciously pe ...
Document
... A change in the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing infrared radiation. Without any radiative forcing, solar radiation coming to the Earth would continue to be approximately equal to the infrared radiation emitted from the Earth. ...
... A change in the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing infrared radiation. Without any radiative forcing, solar radiation coming to the Earth would continue to be approximately equal to the infrared radiation emitted from the Earth. ...
Global Climate Change Fact Sheet - Minnesota Pollution Control
... are released through human activity every year. CO2 added today remains in the atmosphere for 100 years or more, which means that the atmosphere is thrown more and more out of balance each year. Since scientists say that CO2 is responsible for three-fourths of any predicted warming, ...
... are released through human activity every year. CO2 added today remains in the atmosphere for 100 years or more, which means that the atmosphere is thrown more and more out of balance each year. Since scientists say that CO2 is responsible for three-fourths of any predicted warming, ...
Climate change feedback

Climate change feedback is important in the understanding of global warming because feedback processes may amplify or diminish the effect of each climate forcing, and so play an important part in determining the climate sensitivity and future climate state. Feedback in general is the process in which changing one quantity changes a second quantity, and the change in the second quantity in turn changes the first. Positive feedback amplifies the change in the first quantity while negative feedback reduces it.The term ""forcing"" means a change which may ""push"" the climate system in the direction of warming or cooling. An example of a climate forcing is increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases. By definition, forcings are external to the climate system while feedbacks are internal; in essence, feedbacks represent the internal processes of the system. Some feedbacks may act in relative isolation to the rest of the climate system; others may be tightly coupled; hence it may be difficult to tell just how much a particular process contributes. Forcings, feedbacks and the dynamics of the climate system determine how much and how fast the climate changes. The main positive feedback in global warming is the tendency of warming to increase the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, which in turn leads to further warming. The main negative feedback comes from the Stefan–Boltzmann law, the amount of heat radiated from the Earth into space changes with the fourth power of the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere.Some observed and potential effects of global warming are positive feedbacks, which contribute directly to further global warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report states that ""Anthropogenic warming could lead to some effects that are abrupt or irreversible, depending upon the rate and magnitude of the climate change.""