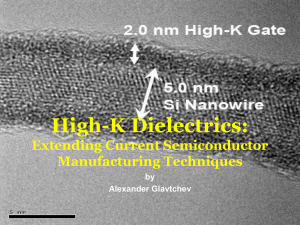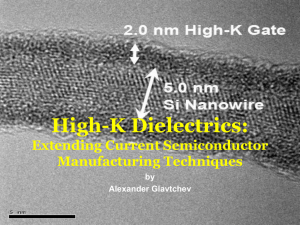
Extending Current Lithography
... Since the 1960’s semiconductor industry has used polySilicon gate with a Silicon dioxide gate dielectric layer. Continuing miniaturization has thinned the SiO2 gate dielectric layer to ~5 atomic layers, or less than 2nm in thickness. Electron tunneling is a major concern at this level as it co ...
... Since the 1960’s semiconductor industry has used polySilicon gate with a Silicon dioxide gate dielectric layer. Continuing miniaturization has thinned the SiO2 gate dielectric layer to ~5 atomic layers, or less than 2nm in thickness. Electron tunneling is a major concern at this level as it co ...
Dielectric
... We just saw that the energy is reduced by the introduction of a dielectric. Since systems want to reduce their energy, the dielectric will be sucked into the capacitor. Alternatively, since opposing charges are induced on the dielectric surfaces close to the plates, the attraction between these will ...
... We just saw that the energy is reduced by the introduction of a dielectric. Since systems want to reduce their energy, the dielectric will be sucked into the capacitor. Alternatively, since opposing charges are induced on the dielectric surfaces close to the plates, the attraction between these will ...
2.7 Ceramic Capacitors Improvements
... Trade-offs occur for selecting these families. The Y5 & Z5 give large capacitance values up to 100 uF in a small package, but the capacitance varies greatly (+22% to -82%) with temperature and applied voltage. The X5 & X7 family varies less with temperature (±15%) and applied voltage, but are limite ...
... Trade-offs occur for selecting these families. The Y5 & Z5 give large capacitance values up to 100 uF in a small package, but the capacitance varies greatly (+22% to -82%) with temperature and applied voltage. The X5 & X7 family varies less with temperature (±15%) and applied voltage, but are limite ...
Activity: A Pyroelectric Smart Sensor
... mated to microelectronics. In this activity we will use metal coated PVDF films as our sensor system and a computer will take the place of the microelectronics. The system used in this activity is not engineered to minimize size and power consumption but clearly those would be goals in any widely ...
... mated to microelectronics. In this activity we will use metal coated PVDF films as our sensor system and a computer will take the place of the microelectronics. The system used in this activity is not engineered to minimize size and power consumption but clearly those would be goals in any widely ...
CP PHYSICS
... 20. Why is it safe to touch a charged balloon which has a very high voltage? 21. A positive charge of 3.2 x 10-5 C is located 0.85 m away from another positive charge of 7.4 x 10-6 C. What is the electric force between the two charges? 22. Two identical charges of 1.78 x 10-6 C are separated by a di ...
... 20. Why is it safe to touch a charged balloon which has a very high voltage? 21. A positive charge of 3.2 x 10-5 C is located 0.85 m away from another positive charge of 7.4 x 10-6 C. What is the electric force between the two charges? 22. Two identical charges of 1.78 x 10-6 C are separated by a di ...
Introductory Electricity - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 4. Now, we will compare this velocity with the drift velocity. Suppose we connect the two plates by a straight copper wire with resistivity of ρ = 1.68 × 10−8 Ω m. Find the drift velocity of this electron according to the Drude model of conductivity. 5. Compare the drift velocity of the electron wit ...
... 4. Now, we will compare this velocity with the drift velocity. Suppose we connect the two plates by a straight copper wire with resistivity of ρ = 1.68 × 10−8 Ω m. Find the drift velocity of this electron according to the Drude model of conductivity. 5. Compare the drift velocity of the electron wit ...
Monday, Feb. 13, 2006
... charged, the battery is disconnected. The plates have area A=4.0m2, and are separated by d=4.0mm. (a) Find the capacitance, the charge on the capacitor, the electric field strength, and the energy stored in the capacitor. (b) The dielectric is carefully removed, without ...
... charged, the battery is disconnected. The plates have area A=4.0m2, and are separated by d=4.0mm. (a) Find the capacitance, the charge on the capacitor, the electric field strength, and the energy stored in the capacitor. (b) The dielectric is carefully removed, without ...
Selecting Dielectric Materials
... key element for optimizing performance in your application.The dielectric is a proprietary polymer/ceramic blend that gives Thermal Clad its excellent electrical isolation properties and low thermal impedance. ...
... key element for optimizing performance in your application.The dielectric is a proprietary polymer/ceramic blend that gives Thermal Clad its excellent electrical isolation properties and low thermal impedance. ...
INSULATING MATERIALS
... SILICONE: Silicone foams provide excellent vibration damping characteristics and excellent high temperature performance and chemical resistance. VINYL: Vinyl foam has very little "spring" and is useful for vibration damping. LAMINATES: Various foams are often laminated with a heavy center layer to c ...
... SILICONE: Silicone foams provide excellent vibration damping characteristics and excellent high temperature performance and chemical resistance. VINYL: Vinyl foam has very little "spring" and is useful for vibration damping. LAMINATES: Various foams are often laminated with a heavy center layer to c ...
17.1 Electric Potential and Potential Difference
... charge. Electric potential is defined as the potential energy per unit charge. The symbol for electric potential (or simply, potential) is V. Suppose a point charge has electric potential energy PE(a) at point a, then the electric potential (the potential energy per unit charge), or V, is ...
... charge. Electric potential is defined as the potential energy per unit charge. The symbol for electric potential (or simply, potential) is V. Suppose a point charge has electric potential energy PE(a) at point a, then the electric potential (the potential energy per unit charge), or V, is ...
PX-13 - ADI Global Distribution
... Technology generating a dry contact N.O. pulse simply by the touch of a finger, with no physical movement or moving parts. The PX-13 features virtually unlimited lifespan of over 20 Million uses, which is the ideal benefit of piezoelectric technology, and tested to work in harsh conditions of -40°C ...
... Technology generating a dry contact N.O. pulse simply by the touch of a finger, with no physical movement or moving parts. The PX-13 features virtually unlimited lifespan of over 20 Million uses, which is the ideal benefit of piezoelectric technology, and tested to work in harsh conditions of -40°C ...
EM 3 Section 3: Gauss` Law 3. 1. Conductors and Insulators A
... 3. 1. Conductors and Insulators A conductor is a material in which charges can move about freely. Therefore any electric field forces the charges to rearrange themselves until a static equilibrium is reached. This in turn means that • Inside a conductor E=0 everywhere, ρ = 0 and any free charges mus ...
... 3. 1. Conductors and Insulators A conductor is a material in which charges can move about freely. Therefore any electric field forces the charges to rearrange themselves until a static equilibrium is reached. This in turn means that • Inside a conductor E=0 everywhere, ρ = 0 and any free charges mus ...
Work done by external force on charge q
... A ball in gravitational field is pushed up by external/applied force against gravitational field. ◊ The work done by applied force is stored as change in gravitational potential energy in the object . ...
... A ball in gravitational field is pushed up by external/applied force against gravitational field. ◊ The work done by applied force is stored as change in gravitational potential energy in the object . ...
Carbon based materials for electronic bio-sensing
... Bio-sensing represents one of the most attractive applications of carbon material based electronic devices; nevertheless, the complete integration of bioactive transducing elements still represents a major challenge, particularly in terms of preserving biological function and specificity while maint ...
... Bio-sensing represents one of the most attractive applications of carbon material based electronic devices; nevertheless, the complete integration of bioactive transducing elements still represents a major challenge, particularly in terms of preserving biological function and specificity while maint ...
Communication BVI-3 Une nouvelle methode pour !`analyse par
... transmission line configurations. The initial distribution of charge density n at the finite-element nodes is obtained by exploiting the way in which the mesh is constructed. As mentioned above, the mesh is generated by tracing, approximately, the electrostatic field lines starting from the conducto ...
... transmission line configurations. The initial distribution of charge density n at the finite-element nodes is obtained by exploiting the way in which the mesh is constructed. As mentioned above, the mesh is generated by tracing, approximately, the electrostatic field lines starting from the conducto ...
Electroactive polymers

Electroactive polymers, or EAPs, are polymers that exhibit a change in size or shape when stimulated by an electric field. The most common applications of this type of material are in actuators and sensors. A typical characteristic property of an EAP is that they will undergo a large amount of deformation while sustaining large forces.The majority of historic actuators are made of ceramic piezoelectric materials. While these materials are able to withstand large forces, they commonly will only deform a fraction of a percent. In the late 1990s, it has been demonstrated that some EAPs can exhibit up to a 380% strain, which is much more than any ceramic actuator. One of the most common applications for EAPs is in the field of robotics in the development of artificial muscles; thus, an electroactive polymer is often referred to as an artificial muscle.