Why Magnets may Repel Mosquitoes and other Predatory
... Mosquitoes are literally wired for hunting. These predators are equipped with a special sense known as Electroreception which allows them to home in on their prey with precise accuracy. Other members of the Mosquito family also share this trait but the Common Mosquitoes Electroreception (Electrorece ...
... Mosquitoes are literally wired for hunting. These predators are equipped with a special sense known as Electroreception which allows them to home in on their prey with precise accuracy. Other members of the Mosquito family also share this trait but the Common Mosquitoes Electroreception (Electrorece ...
Electric charge
... dissimilar electric fields. Similarly, two similar electric fields (lines of force between them are in opposite directions), placed nearby but farther than certain distance, reduce distortion-density between them. Higher distortion-density on outer sides, while being transferred inwards, moves 3D ma ...
... dissimilar electric fields. Similarly, two similar electric fields (lines of force between them are in opposite directions), placed nearby but farther than certain distance, reduce distortion-density between them. Higher distortion-density on outer sides, while being transferred inwards, moves 3D ma ...
Lecture 20
... So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor. Conductors, as we know are substances which have free electrons, which would move around the material if we applied electric field. Under equilibrium conditions, the electric field inside is zero and free charges, if t ...
... So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor. Conductors, as we know are substances which have free electrons, which would move around the material if we applied electric field. Under equilibrium conditions, the electric field inside is zero and free charges, if t ...
2731-AQA Physics P3.3 SoW Keeping things moving
... Vp / np = Vs / ns h) If transformers are assumed to be 100% efficient,the electrical power output would equal the electrical power input. Vp x Ip = Vs x Is i) Switch mode transformers operate at a high frequency, often between 50 kHz and 200 kHz. j) Switch mode transformers are much lighter and smal ...
... Vp / np = Vs / ns h) If transformers are assumed to be 100% efficient,the electrical power output would equal the electrical power input. Vp x Ip = Vs x Is i) Switch mode transformers operate at a high frequency, often between 50 kHz and 200 kHz. j) Switch mode transformers are much lighter and smal ...
Phys11U_Unit 5_Ch13_transmittal_July12
... current will produce a magnetic field, so it would be logical to assume the opposite—that a constant magnetic field will produce an electric current in a conductor sitting in that constant magnetic field. It does not. Faraday discovered hat in order to produce an electric current the magnetic field ...
... current will produce a magnetic field, so it would be logical to assume the opposite—that a constant magnetic field will produce an electric current in a conductor sitting in that constant magnetic field. It does not. Faraday discovered hat in order to produce an electric current the magnetic field ...
+Q - Purdue Physics
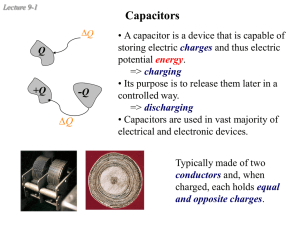
... storing electric charges and thus electric potential energy. => charging • Its purpose is to release them later in a controlled way. => discharging • Capacitors are used in vast majority of electrical and electronic devices. Typically made of two conductors and, when charged, each holds equal and op ...
... storing electric charges and thus electric potential energy. => charging • Its purpose is to release them later in a controlled way. => discharging • Capacitors are used in vast majority of electrical and electronic devices. Typically made of two conductors and, when charged, each holds equal and op ...
Insulator (electricity)

An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and therefore make it impossible to conduct an electric current under the influence of an electric field. This contrasts with other materials, semiconductors and conductors, which conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. A perfect insulator does not exist, because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and Teflon, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivity, are still good enough to prevent significant current from flowing at normally used voltages, and thus are employed as insulation for electrical wiring and cables. Examples include rubber-like polymers and most plastics.Insulators are used in electrical equipment to support and separate electrical conductors without allowing current through themselves. An insulating material used in bulk to wrap electrical cables or other equipment is called insulation. The term insulator is also used more specifically to refer to insulating supports used to attach electric power distribution or transmission lines to utility poles and transmission towers. They support the weight of the suspended wires without allowing the current to flow through the tower to ground.