Science Olympiad Circuit Lab
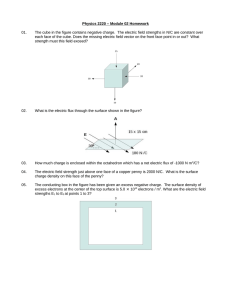
... Internal Resistance (Ri ) – the resistance associated with an EMF. Part of the potential drop produced by the EMF must be used to cause current in the circuit to also flow through the EMF. The actual potential drop available to the circuit outside the EMF is called the Terminal Voltage (VT) is calcu ...
... Internal Resistance (Ri ) – the resistance associated with an EMF. Part of the potential drop produced by the EMF must be used to cause current in the circuit to also flow through the EMF. The actual potential drop available to the circuit outside the EMF is called the Terminal Voltage (VT) is calcu ...
Department of Natural Sciences
... Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a certain distance R. If the magnitudes of the charges are doubled, and their separation is halved, then what happens to the electrical force between these charges? a. It increases by a factor of 16. b. It increases by a factor of 8. c. It is doubled. d. It r ...
... Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a certain distance R. If the magnitudes of the charges are doubled, and their separation is halved, then what happens to the electrical force between these charges? a. It increases by a factor of 16. b. It increases by a factor of 8. c. It is doubled. d. It r ...
Electricity - WordPress.com
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
Insulator (electricity)

An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and therefore make it impossible to conduct an electric current under the influence of an electric field. This contrasts with other materials, semiconductors and conductors, which conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. A perfect insulator does not exist, because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and Teflon, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivity, are still good enough to prevent significant current from flowing at normally used voltages, and thus are employed as insulation for electrical wiring and cables. Examples include rubber-like polymers and most plastics.Insulators are used in electrical equipment to support and separate electrical conductors without allowing current through themselves. An insulating material used in bulk to wrap electrical cables or other equipment is called insulation. The term insulator is also used more specifically to refer to insulating supports used to attach electric power distribution or transmission lines to utility poles and transmission towers. They support the weight of the suspended wires without allowing the current to flow through the tower to ground.