
25 serological study by using the elisa technique to identification of
... This study also in agreement with the earlier works of (Lue et al., 1993; Arathy et al., 2001) who showed that the reason for outbreaks in vaccinated chickens may be due to the tendency of the virus to undergo continuous genomic drift and shift which led to emerge of new serotypes differences from v ...
... This study also in agreement with the earlier works of (Lue et al., 1993; Arathy et al., 2001) who showed that the reason for outbreaks in vaccinated chickens may be due to the tendency of the virus to undergo continuous genomic drift and shift which led to emerge of new serotypes differences from v ...
Hepatitis viruses - University of Yeditepe Faculty of Medicine, 2011
... HGV is also known as hepatitis-GB virus (HGBV) (so named after the initials of the patient from whom the virus was isolated). There is considerable homology between HGV and HGBV. Three different viruses were isolated and designated GBV-A, GBV-B, and GBV-C. The role of HGV and GBV-C in human disease, ...
... HGV is also known as hepatitis-GB virus (HGBV) (so named after the initials of the patient from whom the virus was isolated). There is considerable homology between HGV and HGBV. Three different viruses were isolated and designated GBV-A, GBV-B, and GBV-C. The role of HGV and GBV-C in human disease, ...
12-11-13 The Central Nervous System fections
... • Marked fibrous thickening of the meninges • The entire brain surface is involved, with the basal meninges more severely affected in cases of tuberculosis. • The causative agent may be identified in tissue sections specially stained for acid-fast bacilli and fungi ...
... • Marked fibrous thickening of the meninges • The entire brain surface is involved, with the basal meninges more severely affected in cases of tuberculosis. • The causative agent may be identified in tissue sections specially stained for acid-fast bacilli and fungi ...
Natural HPV immunity and vaccination strategies
... immune responses compared to low risk type infections. Li et al. (1999) have also demonstrated the HPV18 E6 binds to Tyk2 and so prevents Tyk2 from binding to the IFNa receptor 1. This leads to the breakdown of the IFNa Jak-STAT pathway. The binding of E6 to Tyk2 is viral type dependent, with the HP ...
... immune responses compared to low risk type infections. Li et al. (1999) have also demonstrated the HPV18 E6 binds to Tyk2 and so prevents Tyk2 from binding to the IFNa receptor 1. This leads to the breakdown of the IFNa Jak-STAT pathway. The binding of E6 to Tyk2 is viral type dependent, with the HP ...
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
... that are present in human blood and can infect and cause disease in people who are exposed to blood containing the pathogen. These microorganisms can be transmitted through contact with contaminated blood and body fluids. ...
... that are present in human blood and can infect and cause disease in people who are exposed to blood containing the pathogen. These microorganisms can be transmitted through contact with contaminated blood and body fluids. ...
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
... MRSA infections are found in the community, as well as in health care settings. ■ Over the years the bacteria has become more resistant to antibiotics. ...
... MRSA infections are found in the community, as well as in health care settings. ■ Over the years the bacteria has become more resistant to antibiotics. ...
Sialadenitis Inflammation of the salivary glands is known as
... bacterial infections, allergic reactions and systemic diseases are the major causes for sialadenitis. It may be acute or chronic. Viral Infections Mumps (epidemic parotitis) is the most common viral infection at feeling the salivary glands; which is caused by a paramyxo virus. It is an acute, contag ...
... bacterial infections, allergic reactions and systemic diseases are the major causes for sialadenitis. It may be acute or chronic. Viral Infections Mumps (epidemic parotitis) is the most common viral infection at feeling the salivary glands; which is caused by a paramyxo virus. It is an acute, contag ...
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
... l HIV is passed from one person to another through blood-to-blood and sexual contact. l HIV+ women can pass the virus to their unborn child during pregnancy or delivery, and through breast feeding. ...
... l HIV is passed from one person to another through blood-to-blood and sexual contact. l HIV+ women can pass the virus to their unborn child during pregnancy or delivery, and through breast feeding. ...
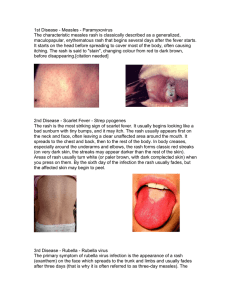
1st Disease - Measles
... comprises cardiac, cerebral, ophthalmic and auditory defects.[7] It may also cause prematurity, low birth weight, and neonatal thrombocytopenia, anaemia and hepatitis. The risk of major defects or organogenesis is highest for infection in the first trimester. CRS is the main reason a vaccine for rub ...
... comprises cardiac, cerebral, ophthalmic and auditory defects.[7] It may also cause prematurity, low birth weight, and neonatal thrombocytopenia, anaemia and hepatitis. The risk of major defects or organogenesis is highest for infection in the first trimester. CRS is the main reason a vaccine for rub ...
Aplastic Anemia [PPT]
... Hematopoietic growth factors Limited usefulness Stem cell transplantation This is the best therapy for the younger patient with a fully ...
... Hematopoietic growth factors Limited usefulness Stem cell transplantation This is the best therapy for the younger patient with a fully ...
Viruses as a cause of foodborne diseases: a review of the literature
... Ninety-two of the 97 cases identified were confirmed as having consumed raw oysters within three days prior to developing the illness. Kirkland et al. (1996) reported that the risk of illness increased with the number of oysters eaten and the even steaming oysters was not adequate to inactivate thes ...
... Ninety-two of the 97 cases identified were confirmed as having consumed raw oysters within three days prior to developing the illness. Kirkland et al. (1996) reported that the risk of illness increased with the number of oysters eaten and the even steaming oysters was not adequate to inactivate thes ...
Biofilms role in chronic infections.
... Cystic Fibrosis is caused by infection of the alveoli of the lungs with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The alveoli slowly fill with mucous and damage is caused to the lung tissue which cause labored breathing and eventually death. Cystic Fibrosis is now believed to form biofilms in the alveoli from neutrop ...
... Cystic Fibrosis is caused by infection of the alveoli of the lungs with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The alveoli slowly fill with mucous and damage is caused to the lung tissue which cause labored breathing and eventually death. Cystic Fibrosis is now believed to form biofilms in the alveoli from neutrop ...
Approach to Sore Throat, Depression and Acne
... GERD: history of sore throat that is accompanied by dyspepsia and waterbrash. Symptoms usually occur following meals, at night and early in the morning. Sore throat is relieved following several days’ use of antacids and histamine-2 blockers. IM and GABHS look similar in a teenager but IM usually pr ...
... GERD: history of sore throat that is accompanied by dyspepsia and waterbrash. Symptoms usually occur following meals, at night and early in the morning. Sore throat is relieved following several days’ use of antacids and histamine-2 blockers. IM and GABHS look similar in a teenager but IM usually pr ...
SMALLPOX - the chris hobbs site
... disease and vaccination, the global population is significantly more susceptible. Some experts have estimated today's rate of transmission to be more on the order of 10 new infections per infected person. ...
... disease and vaccination, the global population is significantly more susceptible. Some experts have estimated today's rate of transmission to be more on the order of 10 new infections per infected person. ...
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) - Region of Waterloo Public Health
... How is it spread and what are the symptoms of HPV? HPV is commonly spread during sexual activity by skin to skin contact with an infected person. Most people never develop symptoms and do not know that they have been infected with HPV. They can still however carry the virus and infect others. Many H ...
... How is it spread and what are the symptoms of HPV? HPV is commonly spread during sexual activity by skin to skin contact with an infected person. Most people never develop symptoms and do not know that they have been infected with HPV. They can still however carry the virus and infect others. Many H ...
antibiotic prophylaxis - Stark County Dental Society
... previous cardiac valve surgery. Control subjects were more likely to have undergone a dental procedure than those with cases of IE. Conclusion: dental treatment was not a risk factor for IE even in patients with valvular heart disease. Few cases of IE could be prevented with prophylaxis even if it w ...
... previous cardiac valve surgery. Control subjects were more likely to have undergone a dental procedure than those with cases of IE. Conclusion: dental treatment was not a risk factor for IE even in patients with valvular heart disease. Few cases of IE could be prevented with prophylaxis even if it w ...
18.1 Studying Viruses and Prokaryotes
... of single-stranded RNA. – causes disease in plants – passed through seeds or pollen ...
... of single-stranded RNA. – causes disease in plants – passed through seeds or pollen ...
Smallpox
... and vaccination, the global population is significantly more susceptible. Some experts have estimated today's rate of transmission to be more on the order of 10 new infections per infected person. ...
... and vaccination, the global population is significantly more susceptible. Some experts have estimated today's rate of transmission to be more on the order of 10 new infections per infected person. ...
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: a
... used for virus culture [51]. Cell culture can detect only high virus concentration and only useful during first five days of disease. Generally the virus produces no or little cytopathic effects so it can be identified by immunofluorescence assay using specific monoclonal antibodies [4]. The traditi ...
... used for virus culture [51]. Cell culture can detect only high virus concentration and only useful during first five days of disease. Generally the virus produces no or little cytopathic effects so it can be identified by immunofluorescence assay using specific monoclonal antibodies [4]. The traditi ...
Human cytomegalovirus

Human cytomegalovirus is a species of the Cytomegalovirus genus of viruses, which in turn is a member of the viral family known as Herpesviridae or herpesviruses. It is typically abbreviated as HCMV or, commonly but more ambiguously, as CMV. It is also known as human herpesvirus-5 (HHV-5). Within Herpesviridae, HCMV belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, which also includes cytomegaloviruses from other mammals.Although they may be found throughout the body, HCMV infections are frequently associated with the salivary glands. HCMV infection is typically unnoticed in healthy people, but can be life-threatening for the immunocompromised, such as HIV-infected persons, organ transplant recipients, or newborn infants. After infection, HCMV remains latent within the body throughout life and can be reactivated at any time. Eventually, it may cause mucoepidermoid carcinoma and possibly other malignancies such as prostate cancer.HCMV is found throughout all geographic locations and socioeconomic groups, and infects between 60% and 70% of adults in industrialized countries and almost 100% in emerging countries.Of all herpes viruses, HCMV harbors the most genes dedicated to altering (evading) innate and adaptive immunity in the host and represents a life-long burden of antigenic T cell surveillance and immune dysfunction.Commonly it is indicated by the presence of antibodies in the general population. Seroprevalence is age-dependent: 58.9% of individuals aged 6 and older are infected with CMV while 90.8% of individuals aged 80 and older are positive for HCMV. HCMV is also the virus most frequently transmitted to a developing fetus.HCMV infection is more widespread in developing countries and in communities with lower socioeconomic status and represents the most significant viral cause of birth defects in industrialized countries. Congenital HCMV is the leading infectious cause of deafness, learning disabilities, and intellectual disability in childrenCMV also ""seems to have a large impact on immune parameters in later life and may contribute to increased morbidity and eventual mortality.""











![Aplastic Anemia [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000248384_1-5c39883593ffaaa864ec61d1eb51b312-300x300.png)










