Practice Exam for 3 rd Astronomy Exam
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
Abstract - chara - Georgia State University
... jovian and terrestrial. Low mass stars and brown dwarfs are very cool and faint and are therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrared surveys are detecting a large number of these objects, which, due to magnitude limits, mostly turn out to be nearby. In the local stellar neighborhood they tend ...
... jovian and terrestrial. Low mass stars and brown dwarfs are very cool and faint and are therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrared surveys are detecting a large number of these objects, which, due to magnitude limits, mostly turn out to be nearby. In the local stellar neighborhood they tend ...
Evolution of Warm Debris Around Sun-like Stars: Clues to Terrestrial
... our photospheric model fits as a function of distance. Three things can be easily discerned from this plot: 1) there is a small systematic offset between the models and the data for nearly all sources in that the observations are in excess of the model predictions: 2) the scatter in the photometry i ...
... our photospheric model fits as a function of distance. Three things can be easily discerned from this plot: 1) there is a small systematic offset between the models and the data for nearly all sources in that the observations are in excess of the model predictions: 2) the scatter in the photometry i ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 19 Notes: The Stellar
... measure the PDMF, and then try to extrapolate back to an IMF based on an understanding of mass loss and stellar lifetimes as a function of mass. This is tricky because we only understand those things at a rough level. The great advantage of the method is that it gives us an absolutely immense number ...
... measure the PDMF, and then try to extrapolate back to an IMF based on an understanding of mass loss and stellar lifetimes as a function of mass. This is tricky because we only understand those things at a rough level. The great advantage of the method is that it gives us an absolutely immense number ...
May
... M64 is a type Sb spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices (KOH-mah bera-NEE-seez,). Popularly known as the Black Eye Galaxy, this object has a diameter of about 51,000 LY. Steady seeing will offer viewers a bright irregular shape with uneven brightness and texture. This is as a result of an ...
... M64 is a type Sb spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices (KOH-mah bera-NEE-seez,). Popularly known as the Black Eye Galaxy, this object has a diameter of about 51,000 LY. Steady seeing will offer viewers a bright irregular shape with uneven brightness and texture. This is as a result of an ...
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations
... with their mythological stories, which were in turn adopted from even older Babylonian constellations. Southern constellation (32) were formed in the 19th century. ...
... with their mythological stories, which were in turn adopted from even older Babylonian constellations. Southern constellation (32) were formed in the 19th century. ...
15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... Irregular galaxies are galaxies that have no definite shape. The smallest irregular galaxies have only about 10 million stars. The largest irregular galaxies can contain several billion stars. Galaxies contain not only stars and planetary systems. Large features, such as gas clouds and star clusters ...
... Irregular galaxies are galaxies that have no definite shape. The smallest irregular galaxies have only about 10 million stars. The largest irregular galaxies can contain several billion stars. Galaxies contain not only stars and planetary systems. Large features, such as gas clouds and star clusters ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... Combine parallax and brightness Canopus has twice the parallax of Spica. Since distance α 1 / parallax, Spica must be at twice the distance of Canopus. (The numbers are 100 pc and 200 pc, but you don’t need to know that.) The more distant star (Spica) appears fainter. Since it is twice as distant a ...
... Combine parallax and brightness Canopus has twice the parallax of Spica. Since distance α 1 / parallax, Spica must be at twice the distance of Canopus. (The numbers are 100 pc and 200 pc, but you don’t need to know that.) The more distant star (Spica) appears fainter. Since it is twice as distant a ...
The Sky Tonight - Northern Stars Planetarium
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
The Lifecycle of the Stars
... The leftover core of a star is so dense that it causes the gravitational collapse. Lifecycle of a star notes. >Once a star (or anything for that matter) falls into the black hole it will never be able to excape its gravitational ...
... The leftover core of a star is so dense that it causes the gravitational collapse. Lifecycle of a star notes. >Once a star (or anything for that matter) falls into the black hole it will never be able to excape its gravitational ...
14. The Milky Way Galaxy: A Spiral in Space
... • Galactic rotation curve shows large amounts of undetectable mass at large radii, called dark matter. • Activity near Galactic center suggests presence of a 3.7 million-solar-mass black hole. ...
... • Galactic rotation curve shows large amounts of undetectable mass at large radii, called dark matter. • Activity near Galactic center suggests presence of a 3.7 million-solar-mass black hole. ...
Star Light, Star Bright
... universe consists of all the galaxies and all the other matter and space around them. Draw Figure 20-3 on the board to help students visualize the relationship between the universe, the galaxies, the stars, the planets, and the moons. ...
... universe consists of all the galaxies and all the other matter and space around them. Draw Figure 20-3 on the board to help students visualize the relationship between the universe, the galaxies, the stars, the planets, and the moons. ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... Test your eyesight from a dark site by counting the number of naked eye stars that are visible. Seven should readily be seen. Keen vision will lead you into double figures. A test for moderate apertures is the nebulosity around some of the other brighter stars of the group, especially Merope. Nebula ...
... Test your eyesight from a dark site by counting the number of naked eye stars that are visible. Seven should readily be seen. Keen vision will lead you into double figures. A test for moderate apertures is the nebulosity around some of the other brighter stars of the group, especially Merope. Nebula ...
US - Real Science
... its 'real' center, around which it rotates, does not coincide with the central bar. So its rotation is out of kilter. But strangely enough NGC 1313 is an isolated galaxy. It is not part of a group and has no near neighbors. It is not clear whether it may have swallowed a small companion in its past ...
... its 'real' center, around which it rotates, does not coincide with the central bar. So its rotation is out of kilter. But strangely enough NGC 1313 is an isolated galaxy. It is not part of a group and has no near neighbors. It is not clear whether it may have swallowed a small companion in its past ...
EF Eri: Its White Dwarf Primary and L Dwarf Secondary
... Stars are high state SED Filled dots are observed points and dotted line is a 9500K white dwarf (BB) model Open squares are WD subtracted SED and L6 spectrum is shown Note J band is transition region WD/M2 ...
... Stars are high state SED Filled dots are observed points and dotted line is a 9500K white dwarf (BB) model Open squares are WD subtracted SED and L6 spectrum is shown Note J band is transition region WD/M2 ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... relative to the local standard of rest (LSR), while: ...
... relative to the local standard of rest (LSR), while: ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... relative to the local standard of rest (LSR), while: ...
... relative to the local standard of rest (LSR), while: ...
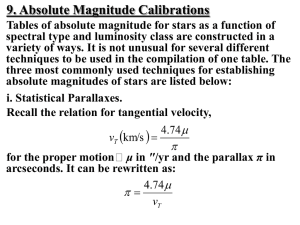
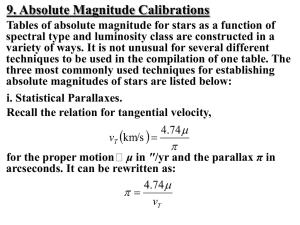
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.