NASA FUSE Satellite Solves the Case of the Missing Deuterium
... -2 In 2003, Bruce Draine of Princeton University, a co-author on the new result, developed computer models that showed how deuterium, compared to hydrogen, might preferentially bind to interstellar dust grains, changing from an easily detectable gaseous form to an unobservable solid form. The new F ...
... -2 In 2003, Bruce Draine of Princeton University, a co-author on the new result, developed computer models that showed how deuterium, compared to hydrogen, might preferentially bind to interstellar dust grains, changing from an easily detectable gaseous form to an unobservable solid form. The new F ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
The surface composition of Beta Pictoris
... listed in Tab. 1. Figure 1 illustrates the case of Cr II; error limits shown are estimates based on the fit of observed and synthetic spectrum. Ti II and Fe II look similar, but the spread is somewhat larger. We suppose that the Cr II gf -values have the highest internal accuracy. The slight residua ...
... listed in Tab. 1. Figure 1 illustrates the case of Cr II; error limits shown are estimates based on the fit of observed and synthetic spectrum. Ti II and Fe II look similar, but the spread is somewhat larger. We suppose that the Cr II gf -values have the highest internal accuracy. The slight residua ...
Dubhe
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s ...
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... Because of its position in the sky, the Alpha Centauri system is not easily visible in much of the Northern Hemisphere. An observer must be at latitudes south of 28 degrees north (or roughly from Naples, Florida and locations further south) to see the closest stellar system to us. The two brighter c ...
... Because of its position in the sky, the Alpha Centauri system is not easily visible in much of the Northern Hemisphere. An observer must be at latitudes south of 28 degrees north (or roughly from Naples, Florida and locations further south) to see the closest stellar system to us. The two brighter c ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
Document
... space (narrow lines translates into wide features in the Fourier domain), the Fourier transform is a sensitive measure of subtle shapes in the line profile. It is also good for measuring rotation ...
... space (narrow lines translates into wide features in the Fourier domain), the Fourier transform is a sensitive measure of subtle shapes in the line profile. It is also good for measuring rotation ...
The Galaxies
... studying how the stars in our galaxy move, we can tell that most of the galaxy’s mass is in the corona, in a form that doesn’t give off light. ► It is called dark matter. ► We’re not sure what it is, although there are several very good ideas. ...
... studying how the stars in our galaxy move, we can tell that most of the galaxy’s mass is in the corona, in a form that doesn’t give off light. ► It is called dark matter. ► We’re not sure what it is, although there are several very good ideas. ...
How Marius Was Right and Galileo Was Wrong Even Though
... but as the telescopic data suggests that the stars are essentially identical suns scattered through space, such a pairing must be a line-of-sight alignment of a nearer and farther star. ...
... but as the telescopic data suggests that the stars are essentially identical suns scattered through space, such a pairing must be a line-of-sight alignment of a nearer and farther star. ...
18 Throughout history people around the world have looked up at
... might not be as accurate as our current scientific knowledge, they can be interesting to share with your classes. The stories provide an opportunity not only to discuss the rotation of the Earth on its axis and its revolution around the Sun, but also to enjoy literature from different cultures. I us ...
... might not be as accurate as our current scientific knowledge, they can be interesting to share with your classes. The stories provide an opportunity not only to discuss the rotation of the Earth on its axis and its revolution around the Sun, but also to enjoy literature from different cultures. I us ...
Neutron Stars PowerPoint
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
AMNH_colloquium_2May07_v7b
... broadened, shifted, and asymmetric as the wind-shock scenario predicts But the degree of asymmetry requires significantly lower wind optical depths than are expected in these stars Clumping and the associated porosity can, in principle, alleviate this problem, but only if the degree of clumping is u ...
... broadened, shifted, and asymmetric as the wind-shock scenario predicts But the degree of asymmetry requires significantly lower wind optical depths than are expected in these stars Clumping and the associated porosity can, in principle, alleviate this problem, but only if the degree of clumping is u ...
Neutron Stars PowerPoint
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
Week 3
... along the horizon is fastest around the equinoxes, and slowest around the solstices Around the equinoxes, the declination (distance from the celestial equator) will change by 0.5° per day Near the solstices, it will stay fixed for almost a week ...
... along the horizon is fastest around the equinoxes, and slowest around the solstices Around the equinoxes, the declination (distance from the celestial equator) will change by 0.5° per day Near the solstices, it will stay fixed for almost a week ...
memphis astronomical society short course in astronomy 2015
... Part 1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FzSW4_w6Cfc Part 2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e_epJ_LwJik Questions: Be able to distinguish between the various types of nebulae – dark, emission, reflection, planetary – and their roles in the modern theory of stellar evolution; give examples of each. U ...
... Part 1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FzSW4_w6Cfc Part 2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e_epJ_LwJik Questions: Be able to distinguish between the various types of nebulae – dark, emission, reflection, planetary – and their roles in the modern theory of stellar evolution; give examples of each. U ...
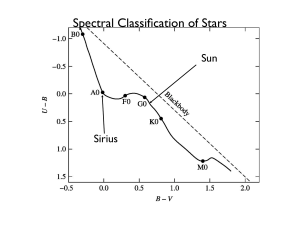
Astronomical Spectra
... by the Saha and Boltzman equations, and photon distribution is black body Hydrostatic Equilibrium – No dynamically significant mass loss – The photosphere is not undergoing large scale accelerations comparable to surface gravity – No pulsations or large scale flows Plane Parallel Atmosphere – Only o ...
... by the Saha and Boltzman equations, and photon distribution is black body Hydrostatic Equilibrium – No dynamically significant mass loss – The photosphere is not undergoing large scale accelerations comparable to surface gravity – No pulsations or large scale flows Plane Parallel Atmosphere – Only o ...
Chapter 15
... • Early in the history of the universe, hydrogen and helium (and other forms of matter) clumped together by gravitational attraction to form countless trillions of stars. Billions of galaxies, each a cluster of billions of stars, now form most of the visible mass in the universe. ...
... • Early in the history of the universe, hydrogen and helium (and other forms of matter) clumped together by gravitational attraction to form countless trillions of stars. Billions of galaxies, each a cluster of billions of stars, now form most of the visible mass in the universe. ...
For stars
... The Twelve constellations (some say thirteen) that the Sun moves through during the year are called the zodiac; The view of the night sky changes as Earth moves in its orbit about the Sun. As drawn here, the night side of Earth faces a different set of constellations at different times of the year. ...
... The Twelve constellations (some say thirteen) that the Sun moves through during the year are called the zodiac; The view of the night sky changes as Earth moves in its orbit about the Sun. As drawn here, the night side of Earth faces a different set of constellations at different times of the year. ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.