Stars in the night Sky - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... astronomical texts aster was often used for a combination of stars rather than for single stars. Aster could also refer to a planet, or to a particular configuration of planets or a conjunction of planets and stars. This usage might be implicit in Matthew's description of the Star (aster) of Bethleh ...
... astronomical texts aster was often used for a combination of stars rather than for single stars. Aster could also refer to a planet, or to a particular configuration of planets or a conjunction of planets and stars. This usage might be implicit in Matthew's description of the Star (aster) of Bethleh ...
Searching for the oldest, most metal-poor stars in the SkyMapper Survey
... In the first minutes after the Big Bang, apart from traces of lithium, hydrogen and helium were the only elements that were present. Hydrogen consisted of ∼ 0.75 of the matter by mass fraction, helium was ∼ 0.25, and lithium was ∼ 2 × 10−9 . The first generation of stars, termed Population III stars ...
... In the first minutes after the Big Bang, apart from traces of lithium, hydrogen and helium were the only elements that were present. Hydrogen consisted of ∼ 0.75 of the matter by mass fraction, helium was ∼ 0.25, and lithium was ∼ 2 × 10−9 . The first generation of stars, termed Population III stars ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
Entropy Production of Main-Sequence Stars
... and generalize gravitation theories, etc. (see, e.g., [6–10]). The majority of the papers, being strictly theoretical, place principal emphasis on functional relations between variables established through the analysis of entropy and its production. There are almost no quantitative calculations of e ...
... and generalize gravitation theories, etc. (see, e.g., [6–10]). The majority of the papers, being strictly theoretical, place principal emphasis on functional relations between variables established through the analysis of entropy and its production. There are almost no quantitative calculations of e ...
Galaxies - cloudfront.net
... _____ 1. There are a total of about 5 million galaxies in the universe. _____ 2. Star clusters contain greater numbers of stars than galaxies do. _____ 3. The Pleiades, or Seven Sisters, is an example of a star cluster. _____ 4. Globular clusters have a lot of dust in addition to stars. _____ 5. The ...
... _____ 1. There are a total of about 5 million galaxies in the universe. _____ 2. Star clusters contain greater numbers of stars than galaxies do. _____ 3. The Pleiades, or Seven Sisters, is an example of a star cluster. _____ 4. Globular clusters have a lot of dust in addition to stars. _____ 5. The ...
absolute brightness: The apparent brightness a star would have if it
... and subsequently expanded and cooled. binary star system: A system in which two stars orbit about their common center of gravity. black-body radiation: The characteristic way in which the intensity of radiation emitted by a hot object in thermal equilibrium depends on frequency. The frequency at whi ...
... and subsequently expanded and cooled. binary star system: A system in which two stars orbit about their common center of gravity. black-body radiation: The characteristic way in which the intensity of radiation emitted by a hot object in thermal equilibrium depends on frequency. The frequency at whi ...
absolute brightness: The apparent brightness a star would have if it
... and subsequently expanded and cooled. binary star system: A system in which two stars orbit about their common center of gravity. black-body radiation: The characteristic way in which the intensity of radiation emitted by a hot object in thermal equilibrium depends on frequency. The frequency at whi ...
... and subsequently expanded and cooled. binary star system: A system in which two stars orbit about their common center of gravity. black-body radiation: The characteristic way in which the intensity of radiation emitted by a hot object in thermal equilibrium depends on frequency. The frequency at whi ...
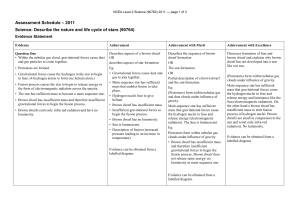
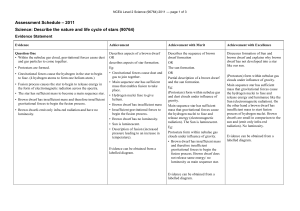
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... Discusses the formation and outcome of a supernova and explains the appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this ...
... Discusses the formation and outcome of a supernova and explains the appearance of a supernova. OR Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this ...
The evolution of stars - School of Physics
... Last week, we had just shown how a star was formed from the collapse of a cloud of interstellar gas. The cloud collapses from the inside out, with the central regions getting hotter and denser as they are squeezed by the pressure of the infalling material. As the temperature increases, the electron ...
... Last week, we had just shown how a star was formed from the collapse of a cloud of interstellar gas. The cloud collapses from the inside out, with the central regions getting hotter and denser as they are squeezed by the pressure of the infalling material. As the temperature increases, the electron ...
Ursa Major, the Great Bear
... M82 is another member of the M81 Group. It is less massive and fainter than M81. The irregular shape of M82 was believed to be caused by a relatively recent close encounter with M81 that distorted its shape. During this encounter, interstellar clouds were caused to collapse and trigger bursts of new ...
... M82 is another member of the M81 Group. It is less massive and fainter than M81. The irregular shape of M82 was believed to be caused by a relatively recent close encounter with M81 that distorted its shape. During this encounter, interstellar clouds were caused to collapse and trigger bursts of new ...
Cepheid
... Consider a Couple of Her Stars 1. The brightest Cepheid in the table varies over magnitudes ranging from 11.2 (at maximum luminosity) to 12.1 (at the faintest), with an ‘average’ of ~ 11.65. Its period is 127 days (more than four months). Note, by the way, that this star is ~5 magnitudes (a factor ...
... Consider a Couple of Her Stars 1. The brightest Cepheid in the table varies over magnitudes ranging from 11.2 (at maximum luminosity) to 12.1 (at the faintest), with an ‘average’ of ~ 11.65. Its period is 127 days (more than four months). Note, by the way, that this star is ~5 magnitudes (a factor ...
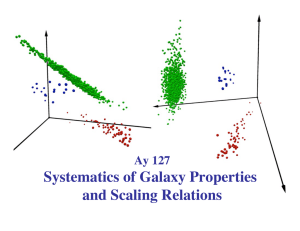
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured quantities such as R, σ , I, L, … ...
... Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured quantities such as R, σ , I, L, … ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... magnitude m, you then know its distance. This difference (m-M) is called the distance modulus ...
... magnitude m, you then know its distance. This difference (m-M) is called the distance modulus ...
PDF format
... a) rotation of Earth; motion of the Sun around the center of the Milky Way; motion of Earth around the Sun b) motion of the Sun around the center of the Milky Way; motion of Earth around the Sun; rotation of Earth c) motion of Earth around the Sun; rotation of Earth; motion of the Sun around the ...
... a) rotation of Earth; motion of the Sun around the center of the Milky Way; motion of Earth around the Sun b) motion of the Sun around the center of the Milky Way; motion of Earth around the Sun; rotation of Earth c) motion of Earth around the Sun; rotation of Earth; motion of the Sun around the ...
Rotation Periods and Relative Ages of Solar-Type Stars
... B - V spectral type. The formula for the calculation of rotation periods was derived from Noyes’ algorithm for determining Rossby number from mean stellar activity. A more detailed description is given by Noyes et al. (1984). These calculated rotation periods were compared against the observed rotat ...
... B - V spectral type. The formula for the calculation of rotation periods was derived from Noyes’ algorithm for determining Rossby number from mean stellar activity. A more detailed description is given by Noyes et al. (1984). These calculated rotation periods were compared against the observed rotat ...
The Cosmic Perspective Star Stuff
... b) They create new elements and blow them out into space so that new generations of stars can be made from them. c) They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... b) They create new elements and blow them out into space so that new generations of stars can be made from them. c) They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Carbon Stars - The OzSky Star Safari
... – Near the end of their life, they become a red giant star. – Then they leave the initial Red Giant phase via the Horizontal Branch as the helium ignites to form carbon. – On the Asymptotic Giant Branch, they become Carbon Stars and Red Giants again and eventually blow off their ...
... – Near the end of their life, they become a red giant star. – Then they leave the initial Red Giant phase via the Horizontal Branch as the helium ignites to form carbon. – On the Asymptotic Giant Branch, they become Carbon Stars and Red Giants again and eventually blow off their ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.