Stars Answers - Science Skool!
... 6. How did the elements come to be formed? Nuclear fusion of hydrogen forms helium; heavy elements are formed by the fusion of lighter elements during a supernova 7. Describe how a star forms. Dust and gas is pulled together by gravity 8. What happens to massive stars after the red super giant stage ...
... 6. How did the elements come to be formed? Nuclear fusion of hydrogen forms helium; heavy elements are formed by the fusion of lighter elements during a supernova 7. Describe how a star forms. Dust and gas is pulled together by gravity 8. What happens to massive stars after the red super giant stage ...
Saraswati River - Ancient Greece
... the 48 ancient constellations which were formalised by Ptolemy (c.AD100 – 178) 3. Occasional phenomena – e.g. eclipses, comets and shooting stars. All ancients (the Greeks included) had a geocentric view of the universe i.e., the assumption that the earth was at the centre of the universe with plane ...
... the 48 ancient constellations which were formalised by Ptolemy (c.AD100 – 178) 3. Occasional phenomena – e.g. eclipses, comets and shooting stars. All ancients (the Greeks included) had a geocentric view of the universe i.e., the assumption that the earth was at the centre of the universe with plane ...
Adobe Acrobat - Ancient Greece
... ancient constellations which were formalised by Ptolemy (c.AD100 – 178) 3. Occasional phenomena – e.g. eclipses, comets and shooting stars. All ancients (the Greeks included) had a geocentric view of the universe i.e., the assumption that the earth was at the centre of the universe with planets orbi ...
... ancient constellations which were formalised by Ptolemy (c.AD100 – 178) 3. Occasional phenomena – e.g. eclipses, comets and shooting stars. All ancients (the Greeks included) had a geocentric view of the universe i.e., the assumption that the earth was at the centre of the universe with planets orbi ...
PH109 Exploring the Universe, Test 3, Fall 2001 Please indicate the
... 29. The most common elemen found in the interstellar medium is a) Hydrogen, b) Helium, c) Carbon, d) ammonia 30. The bubbling of the Sun's surface is seen as a) solar wind, b) solar flares, c) granulation, d) corona 31. All stars with masses equal to or greater than the sun expand to become a) red g ...
... 29. The most common elemen found in the interstellar medium is a) Hydrogen, b) Helium, c) Carbon, d) ammonia 30. The bubbling of the Sun's surface is seen as a) solar wind, b) solar flares, c) granulation, d) corona 31. All stars with masses equal to or greater than the sun expand to become a) red g ...
Stars and constellations
... What is a star? The first thing to remember is that the Sun is a star and quite an ordinary one at that. The only reason that it looks so bright is that is so close to us – the next nearest star is more than 250 000 times further away. We now know that the Sun is just an average sort of star. It onl ...
... What is a star? The first thing to remember is that the Sun is a star and quite an ordinary one at that. The only reason that it looks so bright is that is so close to us – the next nearest star is more than 250 000 times further away. We now know that the Sun is just an average sort of star. It onl ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
The Stars
... Absolute Magnitude • A star can be bright as we see it for two reasons: it actually is bright, or it is close to us. • Absolute magnitude compares star brightness as if they were 10 parsecs away. ...
... Absolute Magnitude • A star can be bright as we see it for two reasons: it actually is bright, or it is close to us. • Absolute magnitude compares star brightness as if they were 10 parsecs away. ...
Earth in the Universe
... many times the size of today’s solar system. Gravitation caused the cloud to condense, most of the mass was pulled to the center and formed our sun. • After Earth and other planets were formed, their gravity pulled on other smaller objects causing them to collide with the planets. This is called an ...
... many times the size of today’s solar system. Gravitation caused the cloud to condense, most of the mass was pulled to the center and formed our sun. • After Earth and other planets were formed, their gravity pulled on other smaller objects causing them to collide with the planets. This is called an ...
What are yellow stars?
... a Yellow Star in the sky. But not all stars are yellow, most of them are red dwarf stars. • The Biggest stars usually live the youngest, and the smallest Stars live the shortest. • Pure Yellow Stars are difficult to see. ...
... a Yellow Star in the sky. But not all stars are yellow, most of them are red dwarf stars. • The Biggest stars usually live the youngest, and the smallest Stars live the shortest. • Pure Yellow Stars are difficult to see. ...
What is a Red Shift?
... sky for 10 days? What was one difference with the telescope the second time they pointed it at a black area in space? Technology is defined as the use of knowledge gained through science to make new products or tools people can use. What role does technology have in science? ...
... sky for 10 days? What was one difference with the telescope the second time they pointed it at a black area in space? Technology is defined as the use of knowledge gained through science to make new products or tools people can use. What role does technology have in science? ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Sun’s Energy Output = 90 billion megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 90 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 4 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
... • Sun’s Energy Output = 90 billion megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 90 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 4 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
Constellation Part II readingConstellation Part II reading(es)
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... 3. Conservation of angular momentum ensures the remaining gas ___________ into a disk. 4. Billions of years later, the star-gas-star cycle supports ongoing _________ ______________ within the disk. The lack of gas in the halo _______________ star formation outside the disk. Facts about Galaxies and ...
... 3. Conservation of angular momentum ensures the remaining gas ___________ into a disk. 4. Billions of years later, the star-gas-star cycle supports ongoing _________ ______________ within the disk. The lack of gas in the halo _______________ star formation outside the disk. Facts about Galaxies and ...
Star Jeopardy Review #2
... At 8 solar masses a star will go through a violent ending, forming a Type II supernova and ending in a nuetron star or balck hole ...
... At 8 solar masses a star will go through a violent ending, forming a Type II supernova and ending in a nuetron star or balck hole ...
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star
... needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
... needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
Milky Way galaxy - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
Relative sizes of astronomical objects
... In this comparison our Sun is down to 1 pixel, a mote of dust with an arrow pointing to it. Jupiter is invisible. Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) is a red supergiant. If Betelgeuse replaced our Sun, its surface would lie between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Antares (Alpha Scorpii) is a red supergiant 7 ...
... In this comparison our Sun is down to 1 pixel, a mote of dust with an arrow pointing to it. Jupiter is invisible. Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) is a red supergiant. If Betelgeuse replaced our Sun, its surface would lie between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Antares (Alpha Scorpii) is a red supergiant 7 ...
powerpoint version
... Black Holes If the mass of the core is more than about 3 solar masses the neutron degeneracy is overwhelmed and the core goes on collapsing. When the core diameter reaches the Schwarzschild radius (9 km for a 3 solar mass remnant) nothing, not even light, can escape. ...
... Black Holes If the mass of the core is more than about 3 solar masses the neutron degeneracy is overwhelmed and the core goes on collapsing. When the core diameter reaches the Schwarzschild radius (9 km for a 3 solar mass remnant) nothing, not even light, can escape. ...
stars - allenscience
... These celestial objects are extremely dense (a lot of matter in a very small volume). ...
... These celestial objects are extremely dense (a lot of matter in a very small volume). ...
Astronomy Quiz 12 “Stars
... A. white dwarfs / red giant C. red giants / blue dwarfs B. yellow dwarfs / red supergiant D. red dwarfs / blue supergiant _____3. The actual 3D motion of stars relative to each other in a rotating and swirling galaxy is called __ motion. A. radial B. proper C. real D. transverse _____4. How far away ...
... A. white dwarfs / red giant C. red giants / blue dwarfs B. yellow dwarfs / red supergiant D. red dwarfs / blue supergiant _____3. The actual 3D motion of stars relative to each other in a rotating and swirling galaxy is called __ motion. A. radial B. proper C. real D. transverse _____4. How far away ...
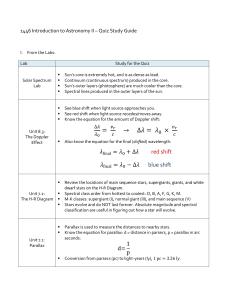
red shift blue shift
... Know the relationship between apparent magnitude (m), absolute magnitude (M) and distance (D): ...
... Know the relationship between apparent magnitude (m), absolute magnitude (M) and distance (D): ...
te acher`s guide te acher`s guide
... Stars asks the following five questions about our Sun and all of its shining counterparts. Space travelers Adi and Woops help viewers clearly answer each question using computer graphics and space footage. What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars ...
... Stars asks the following five questions about our Sun and all of its shining counterparts. Space travelers Adi and Woops help viewers clearly answer each question using computer graphics and space footage. What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.