Stars and Galaxies
... • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the heavy element of iron is formed ...
... • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the heavy element of iron is formed ...
Li-cai Deng
... of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scale structures of galaxies had just been discovered. But there was structure on all scales of the largest surveys of the day. There was a pressing ...
... of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scale structures of galaxies had just been discovered. But there was structure on all scales of the largest surveys of the day. There was a pressing ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • Neutron stars can form powerful jets of matter and energy • Previously only thought possible with black holes • Binary system with neutron star gaining matter from white dwarf companion’s atmosphere in an accretion disk • Neutron star is tiny compared to white dwarf but is very dense and about 14 ...
... • Neutron stars can form powerful jets of matter and energy • Previously only thought possible with black holes • Binary system with neutron star gaining matter from white dwarf companion’s atmosphere in an accretion disk • Neutron star is tiny compared to white dwarf but is very dense and about 14 ...
Stellar Nebulae
... usually do not radiate their own visible light and appear dark when viewed with an optical telescope. In these cold, dense environments, many atoms can combine into molecules. Giant molecular clouds can last for 10 to 100 million years before they dissipate, due to the heat and stellar winds from ne ...
... usually do not radiate their own visible light and appear dark when viewed with an optical telescope. In these cold, dense environments, many atoms can combine into molecules. Giant molecular clouds can last for 10 to 100 million years before they dissipate, due to the heat and stellar winds from ne ...
Astronomy Final C - Tarleton State University
... 4. Genetic replication involves A.nucleic acids B.ATP C.amino acids D.genetic replication involves all of these 5. Degenerate gases ? cool without losing their pressure. A.can B.cannot 6. ? develop where supernova explosions leave behind a “core” of approximately 1.4 to 2 or 3 stellar masses. A.Brow ...
... 4. Genetic replication involves A.nucleic acids B.ATP C.amino acids D.genetic replication involves all of these 5. Degenerate gases ? cool without losing their pressure. A.can B.cannot 6. ? develop where supernova explosions leave behind a “core” of approximately 1.4 to 2 or 3 stellar masses. A.Brow ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. Th ...
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. Th ...
Stellar Evolution
... eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, followed by collapse to white dwarf by blowing out their oute ...
... eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, followed by collapse to white dwarf by blowing out their oute ...
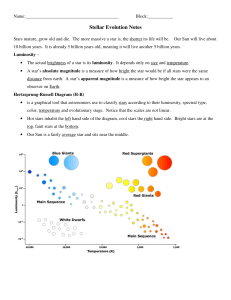
Stellar Evolution Notes
... and light is escaping into space, the star corpse cools down until it becomes black as space. Astronomers call these corpses black dwarfs. ...
... and light is escaping into space, the star corpse cools down until it becomes black as space. Astronomers call these corpses black dwarfs. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... and light is escaping into space, the star corpse cools down until it becomes black as space. Astronomers call these corpses black dwarfs. ...
... and light is escaping into space, the star corpse cools down until it becomes black as space. Astronomers call these corpses black dwarfs. ...
AST301.Ch21.StellarExpl - University of Texas Astronomy
... A SN produces a billion solar luminosities in just a few hours or less. Until discovery of gamma ray bursts (ch.22), these were, gram for gram, the most luminous objects in the universe. That is why they can be observed even in very distant galaxies (e.g. 100s of Mpc away), or even at the edge of th ...
... A SN produces a billion solar luminosities in just a few hours or less. Until discovery of gamma ray bursts (ch.22), these were, gram for gram, the most luminous objects in the universe. That is why they can be observed even in very distant galaxies (e.g. 100s of Mpc away), or even at the edge of th ...
After the ZAMS - Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School
... Astronomers treat photos of clusters as if they were family photos, and use them to look for changes in particular types of stars with time. However, human family members have their own peculiarities (like wearing lipstick or moustaches), and so do the stars in a cluster. They are of different masse ...
... Astronomers treat photos of clusters as if they were family photos, and use them to look for changes in particular types of stars with time. However, human family members have their own peculiarities (like wearing lipstick or moustaches), and so do the stars in a cluster. They are of different masse ...
Stars - PAMS-Doyle
... • Stars are assigned spectral types of O,B, A, F, G, K, and M which are based on their temperature • Each type is subdivided into the numbers 0-9 • Provide information about the stars composition and temperature ...
... • Stars are assigned spectral types of O,B, A, F, G, K, and M which are based on their temperature • Each type is subdivided into the numbers 0-9 • Provide information about the stars composition and temperature ...
here
... • For example, if our sun was the dot over this “i”, the nearest star would be ten miles away ...
... • For example, if our sun was the dot over this “i”, the nearest star would be ten miles away ...
Star Classification - University of Louisville
... surface temperatures are much higher, and shine white instead of red. When the Sun comes to the end of its life, it will become a White Dwarf. It will be much smaller than it is now, not quite as bright but twice as hot. Its matter (particles) will be more densely-packed together. ...
... surface temperatures are much higher, and shine white instead of red. When the Sun comes to the end of its life, it will become a White Dwarf. It will be much smaller than it is now, not quite as bright but twice as hot. Its matter (particles) will be more densely-packed together. ...
Groups of Stars
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
Stars: the Hertzsprung
... A ten solar mass star has about ten times the sun's supply of nuclear energy. Its luminosity is 3000 times that of the sun. How does the lifetime of the star compare with that of the ...
... A ten solar mass star has about ten times the sun's supply of nuclear energy. Its luminosity is 3000 times that of the sun. How does the lifetime of the star compare with that of the ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... bright light is a star beyond the supernova environs. Around the central supernova is a single ring but associated with the expansion of expelled gases are also a pair of rings further away that stand out when imaged at a wavelength that screens out much of this bright light.” ...
... bright light is a star beyond the supernova environs. Around the central supernova is a single ring but associated with the expansion of expelled gases are also a pair of rings further away that stand out when imaged at a wavelength that screens out much of this bright light.” ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.