The physics of star formation
... the result is that molecular clouds are very cold and have typical temperatures of only about 10–20 K. Higher temperatures of up to 100 K or more may exist locally in regions heated by luminous newly formed stars. In typical molecular clouds, cooling is due mostly to the emission of far-infrared rad ...
... the result is that molecular clouds are very cold and have typical temperatures of only about 10–20 K. Higher temperatures of up to 100 K or more may exist locally in regions heated by luminous newly formed stars. In typical molecular clouds, cooling is due mostly to the emission of far-infrared rad ...
Stellar Helium Burning in Other Universes: A
... Be. As long as the universe under consideration can produce 8 Be, and it retains an appreciable supply of 4 He, carbon can be produced in subsequent stellar generations through the reaction 4 He + 8 Be → 12 C. This reaction is a natural channel to produce carbon — alpha particles are energetically f ...
... Be. As long as the universe under consideration can produce 8 Be, and it retains an appreciable supply of 4 He, carbon can be produced in subsequent stellar generations through the reaction 4 He + 8 Be → 12 C. This reaction is a natural channel to produce carbon — alpha particles are energetically f ...
Bonnell_2015_MNRAS_Early - St Andrews Research Repository
... not in the other systems studied. Bastian et al. (2009) corrected for the non-constancy of star formation in the Antennae merger system and found evidence for cluster disruption taking place on time-scales <10 Myr, but not on longer time-scales. The observational picture of clusters at very young ag ...
... not in the other systems studied. Bastian et al. (2009) corrected for the non-constancy of star formation in the Antennae merger system and found evidence for cluster disruption taking place on time-scales <10 Myr, but not on longer time-scales. The observational picture of clusters at very young ag ...
NSDL_WS_1_Astonomy
... http://www.compadre.org/Astronomy Hubble Space Telescope http://hubblesite.org International Year of Astronomy 2009 http://astronomy2009.us http://astronomy2009.org ...
... http://www.compadre.org/Astronomy Hubble Space Telescope http://hubblesite.org International Year of Astronomy 2009 http://astronomy2009.us http://astronomy2009.org ...
(12) United States Patent
... The invention relates to mechanical computers that can be used for performing calculations relating to the positions of the sun, stars, and other objects in the sky. More particularly, the invention relates to an improved astrolabe having a rotating rete and plate. 2. Description of the Prior Art An ...
... The invention relates to mechanical computers that can be used for performing calculations relating to the positions of the sun, stars, and other objects in the sky. More particularly, the invention relates to an improved astrolabe having a rotating rete and plate. 2. Description of the Prior Art An ...
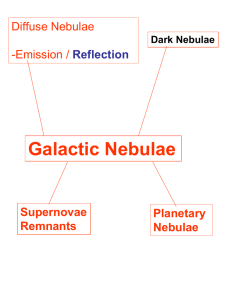
Orion the Hunter
... in a giant molecular cloud. Embedded in the nebulosity is the Orion Nebula Cluster, a gathering of more than 4,000 stars with an average age of only one million years. Because it’s the closest region of active star formation, M42 has been well studied. Astronomers have found more than a hundred prop ...
... in a giant molecular cloud. Embedded in the nebulosity is the Orion Nebula Cluster, a gathering of more than 4,000 stars with an average age of only one million years. Because it’s the closest region of active star formation, M42 has been well studied. Astronomers have found more than a hundred prop ...
Astro 102 Practice Test 3
... c. indicates that the sun's core is much hotter than expected. d. indicates the sun's core is convective. e. none of the above 6. The carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle a. operates at a slightly lower temperature than the proton-proton chain. b. is most efficient in a star less massive than the sun. c. oc ...
... c. indicates that the sun's core is much hotter than expected. d. indicates the sun's core is convective. e. none of the above 6. The carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle a. operates at a slightly lower temperature than the proton-proton chain. b. is most efficient in a star less massive than the sun. c. oc ...
Minimum Distance Estimation of Milky Way
... It may be questioned why the velocity data–observed or synthetic–alone are invoked to help learn the unknown model parameter vector X. Indeed, the data includes information on the spatial location of the stars as well as the velocity of the stars, but out of these, only the velocity data can be impl ...
... It may be questioned why the velocity data–observed or synthetic–alone are invoked to help learn the unknown model parameter vector X. Indeed, the data includes information on the spatial location of the stars as well as the velocity of the stars, but out of these, only the velocity data can be impl ...
solar twins and solar analogues in galactic surveys
... showing that all the colours of the rainbow exist within its light. Before then, astronomers could only look at stellar light as a whole, being able to distinguish more blue looking stars from more red looking stars, etc., but it gave them merely one overall colour. Through the invention and applica ...
... showing that all the colours of the rainbow exist within its light. Before then, astronomers could only look at stellar light as a whole, being able to distinguish more blue looking stars from more red looking stars, etc., but it gave them merely one overall colour. Through the invention and applica ...
ancient cultures 114 - Stellenbosch University
... viewers of the sky as much as they did people living thousands of years ago. For those captivated enough to view the sky over long periods and across successive days, it becomes obvious that the sky is not a stagnant beauty – everything in the sky tends to move. Once the interest of the viewer has b ...
... viewers of the sky as much as they did people living thousands of years ago. For those captivated enough to view the sky over long periods and across successive days, it becomes obvious that the sky is not a stagnant beauty – everything in the sky tends to move. Once the interest of the viewer has b ...
GALEX and Star Formation
... while optical colors are saturated in this regime (e.g. Bianchi 2007), and (ii) UV colors provide precise agedating of integrated stellar populations for ages less than 1Gyr. UV images give therefore an instant snapshot of young star-forming sites, uncomplicated by previous star-formation history, u ...
... while optical colors are saturated in this regime (e.g. Bianchi 2007), and (ii) UV colors provide precise agedating of integrated stellar populations for ages less than 1Gyr. UV images give therefore an instant snapshot of young star-forming sites, uncomplicated by previous star-formation history, u ...
The physics of star formation
... reference to structures of decreasing size. In this review, the term ‘clump’ will be used to denote any region of enhanced density in a larger cloud, while the term ‘core’ will be used to denote a particularly dense self-gravitating clump that might collapse to form a star or group of stars. The ter ...
... reference to structures of decreasing size. In this review, the term ‘clump’ will be used to denote any region of enhanced density in a larger cloud, while the term ‘core’ will be used to denote a particularly dense self-gravitating clump that might collapse to form a star or group of stars. The ter ...
Evolution of the Milky Way with radial motions of stars and gas
... Key words. Galaxy: general – Galaxy: disk – Galaxy: evolution – Galaxy: abundances – solar neighborhood – Galaxy: structure ...
... Key words. Galaxy: general – Galaxy: disk – Galaxy: evolution – Galaxy: abundances – solar neighborhood – Galaxy: structure ...
Section 1.2 Astrometric Data
... in accordance with the observations. In most cases a good empirical fit was obtained by including one or two additional terms in the Taylor expansion of the variation of the barycentric coordinate direction with time. In a few hundred cases even this was not sufficient, and Keplerian elements (somet ...
... in accordance with the observations. In most cases a good empirical fit was obtained by including one or two additional terms in the Taylor expansion of the variation of the barycentric coordinate direction with time. In a few hundred cases even this was not sufficient, and Keplerian elements (somet ...
The isotopic mixture of barium in the metal-poor
... occur in the helium and carbon shells of massive stars in their hydrostatic burning phases. The r-process is likely associated with the deep interior of Type II supernovae. Since massive stars dying as Type II supernovae evolve faster than the stars that populate and evolve from the AGB, one anticip ...
... occur in the helium and carbon shells of massive stars in their hydrostatic burning phases. The r-process is likely associated with the deep interior of Type II supernovae. Since massive stars dying as Type II supernovae evolve faster than the stars that populate and evolve from the AGB, one anticip ...
Note - HKU Physics
... 2. Right at the moment of formation of a star, its chemical composition is uniform. Why this is a good approximation? I shall further discuss the validity of this assumption when we study main sequence stars. 3. The star is irrotational and is spherically symmetric. The rotational energy of a star i ...
... 2. Right at the moment of formation of a star, its chemical composition is uniform. Why this is a good approximation? I shall further discuss the validity of this assumption when we study main sequence stars. 3. The star is irrotational and is spherically symmetric. The rotational energy of a star i ...
A Variability Study of the Typical Red Supergiant Antares A
... well described by models of convection. It was these studies of Betelgeuse that provided the main motivation for this thesis. We ask if the dramatic motions seen in the atmospheres of Betelgeuse (Gray 2008 amongst others) are typical of red supergiants and if their variations can be described by con ...
... well described by models of convection. It was these studies of Betelgeuse that provided the main motivation for this thesis. We ask if the dramatic motions seen in the atmospheres of Betelgeuse (Gray 2008 amongst others) are typical of red supergiants and if their variations can be described by con ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.