Lives of Stars - McDonald Observatory
... look big, but I’ve only got about 0.8 solar masses of gas in there. PAGE: Well, finally all the available gravitational potential energy was spent. The fusion stops, leaving the carbon core. What happens next? SOL: Just before the core went out, the outer envelope transformed into a beautiful sight. ...
... look big, but I’ve only got about 0.8 solar masses of gas in there. PAGE: Well, finally all the available gravitational potential energy was spent. The fusion stops, leaving the carbon core. What happens next? SOL: Just before the core went out, the outer envelope transformed into a beautiful sight. ...
The SMC as a probe of dust in the early Universe
... the formation of molecular hydrogen (Hollenbach & Salpeter 1970), another key coolant. The formation of dust in the outflows from evolved stars governs the rate of enrichment of the interstellar medium (ISM) (e.g. Ferrarotti & Gail 2006). Sub-mm surveys have revealed extensive populations of dusty g ...
... the formation of molecular hydrogen (Hollenbach & Salpeter 1970), another key coolant. The formation of dust in the outflows from evolved stars governs the rate of enrichment of the interstellar medium (ISM) (e.g. Ferrarotti & Gail 2006). Sub-mm surveys have revealed extensive populations of dusty g ...
Quantitative constraints on starburst cycles in galaxies with stellar
... libraries contain models with burst fractions very close to zero, which are essentially identical to the models in the continuous library, so the new minimum χ2 is guaranteed to be equal to or smaller than the old one. If the new χ2min /Nd lies in the range 2.37-6.25, the probability that the model ...
... libraries contain models with burst fractions very close to zero, which are essentially identical to the models in the continuous library, so the new minimum χ2 is guaranteed to be equal to or smaller than the old one. If the new χ2min /Nd lies in the range 2.37-6.25, the probability that the model ...
Gas Evolution in Disk Galaxies
... the Universe, gas cools and gradually falls into a potential well due to the overdensity of dark matter. Eventually, stars form collectively through gravitational collapse of gas and galaxies are born. Recently, large scale survey such as Two-degree-Field Galaxy Redshift Survey (2dFGRS) and Sloan Di ...
... the Universe, gas cools and gradually falls into a potential well due to the overdensity of dark matter. Eventually, stars form collectively through gravitational collapse of gas and galaxies are born. Recently, large scale survey such as Two-degree-Field Galaxy Redshift Survey (2dFGRS) and Sloan Di ...
The Green Valley is a Red Herring: Galaxy Zoo reveals two
... Ever since the discovery of the bimodality in galaxy colour in the galaxy colour-magnitude and colour-mass diagrams from largescale surveys (Strateva et al. 2001; Baldry et al. 2004, 2006), the colour space between the two main populations — the green valley — has been viewed as the crossroads of ga ...
... Ever since the discovery of the bimodality in galaxy colour in the galaxy colour-magnitude and colour-mass diagrams from largescale surveys (Strateva et al. 2001; Baldry et al. 2004, 2006), the colour space between the two main populations — the green valley — has been viewed as the crossroads of ga ...
SherwoodWA_1973redux - Edinburgh Research Archive
... recently have 21-cm observations mapped the distribution of neutral ...
... recently have 21-cm observations mapped the distribution of neutral ...
Magnificent Cosmos - Academic Program Pages at Evergreen
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
MUFASA: The assembly of the red sequence
... accretion and hence star formation restarts after 1–2 Gyr. Instead, a model where diffuse hot gas in massive halos is prevented from cooling was able to broadly reproduce observed galaxy colours and the red and blue galaxy mass functions (Gabor et al. 2011), albeit with too few passive galaxies at h ...
... accretion and hence star formation restarts after 1–2 Gyr. Instead, a model where diffuse hot gas in massive halos is prevented from cooling was able to broadly reproduce observed galaxy colours and the red and blue galaxy mass functions (Gabor et al. 2011), albeit with too few passive galaxies at h ...
[C ii] 157 μm Emission in a Five-component Interstellar
... provides one of the main cooling channels of the ISM via the [C II] 157 μm emission. While the strength of the [C II] line correlates with the star formation rate, the contributions of the various gas phases to the [C II] emission on galactic scales are not well established. In this study we establi ...
... provides one of the main cooling channels of the ISM via the [C II] 157 μm emission. While the strength of the [C II] line correlates with the star formation rate, the contributions of the various gas phases to the [C II] emission on galactic scales are not well established. In this study we establi ...
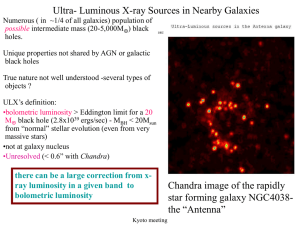
ULXs: General Properties and Variability - X
... around them- require high luminosity to photoionize them •Quite a few have “soft” components well fit by low kT black body- consistent with high mass (Miller this meeting). ...
... around them- require high luminosity to photoionize them •Quite a few have “soft” components well fit by low kT black body- consistent with high mass (Miller this meeting). ...
Neutral material around the B[e] supergiant star LHA 115
... Context. B[e] supergiants are surrounded by large amounts of hydrogen neutral material, traced by the emission in the optical [Oi] lines. This neutral material is most plausibly located within their dense, cool circumstellar disks, which are formed from the (probably non-spherically symmetric) wind ...
... Context. B[e] supergiants are surrounded by large amounts of hydrogen neutral material, traced by the emission in the optical [Oi] lines. This neutral material is most plausibly located within their dense, cool circumstellar disks, which are formed from the (probably non-spherically symmetric) wind ...
Molecular Clouds and the Onset of Star Formation
... higher than those in the surrounding interstellar medium, and almost all molecular clouds in our galaxy exhibit star formation. The deduced mean lifetime of molecular clouds is 10 Myr (subject to considerable argument). The suggested mechanism for breakup and destruction of the clouds is ionization ...
... higher than those in the surrounding interstellar medium, and almost all molecular clouds in our galaxy exhibit star formation. The deduced mean lifetime of molecular clouds is 10 Myr (subject to considerable argument). The suggested mechanism for breakup and destruction of the clouds is ionization ...
the density profiles of massive, relaxed galaxy clusters. i. the total
... to be β < 1, shallower than a standard NFW profile. Sand et al. (2008) improved the analysis in two clusters by moving beyond axisymmetric lens models, which had been suggested as a source of systematic bias (Meneghetti et al. 2007), and found similar results on the DM slope. Newman et al. (2009, N0 ...
... to be β < 1, shallower than a standard NFW profile. Sand et al. (2008) improved the analysis in two clusters by moving beyond axisymmetric lens models, which had been suggested as a source of systematic bias (Meneghetti et al. 2007), and found similar results on the DM slope. Newman et al. (2009, N0 ...
Candidate star clusters toward the inner Milky Way discovered on
... have projected on-sky separation of ∼2 arcmin, but these objects have different extinctions and distances (Table 1), so it is unlikely that they are physically connected. A physical connection between VVV CC 168 and VVV CC 169, separated by ∼9 arcmin and located at similar distances is more likely, ...
... have projected on-sky separation of ∼2 arcmin, but these objects have different extinctions and distances (Table 1), so it is unlikely that they are physically connected. A physical connection between VVV CC 168 and VVV CC 169, separated by ∼9 arcmin and located at similar distances is more likely, ...
The Density Profiles of Massive, Relaxed Galaxy Clusters - HAL-Insu
... and clusters through the imprint of baryons on their halos. For instance, dark and baryonic density profiles can inform us about the relative importance of dissipational and dissipationless assembly processes (e.g., Lackner & Ostriker 2010). The observation from that massive ellipticals have nearly ...
... and clusters through the imprint of baryons on their halos. For instance, dark and baryonic density profiles can inform us about the relative importance of dissipational and dissipationless assembly processes (e.g., Lackner & Ostriker 2010). The observation from that massive ellipticals have nearly ...
Astrophysics Pristine CNO abundances from Magellanic Cloud B stars
... stars of Rolleston et al. (1996) one (PS 34–144) is classified as a He-weak star which we will therefore disregard in what follows. The CNO abundances of the remaining three MS stars are confronted with the most recent measurements from H ii regions in Table 1: While the consistency among determinat ...
... stars of Rolleston et al. (1996) one (PS 34–144) is classified as a He-weak star which we will therefore disregard in what follows. The CNO abundances of the remaining three MS stars are confronted with the most recent measurements from H ii regions in Table 1: While the consistency among determinat ...
CHAPTER 1 The Formation and Structure of Stars
... move more rapidly than do those in a cool gas. – Although the interstellar clouds are very cold, even at a temperature of only 10 K, the average hydrogen atom moves about 0.5 km/s (1,100 mph). – This thermal motion would make the cloud drift apart if gravity were too weak to hold it together. ...
... move more rapidly than do those in a cool gas. – Although the interstellar clouds are very cold, even at a temperature of only 10 K, the average hydrogen atom moves about 0.5 km/s (1,100 mph). – This thermal motion would make the cloud drift apart if gravity were too weak to hold it together. ...
A Second Shell in the Fornax dSph Galaxy
... 1998) and proper motion measurements indicate it is on a polar orbit with a small eccentricity (e = 0.27) and is currently at perigalacticon (Dinescu et al. 2004). Moreover, Fornax contains a mass larger than all the other Galactic dSphs combined (excluding Sagittarius), which further precludes the ...
... 1998) and proper motion measurements indicate it is on a polar orbit with a small eccentricity (e = 0.27) and is currently at perigalacticon (Dinescu et al. 2004). Moreover, Fornax contains a mass larger than all the other Galactic dSphs combined (excluding Sagittarius), which further precludes the ...
don_lamb - New Views of the Universe
... of greatest remaining mystery of GRBs: The Nature of short GRBs Follow-up observations at X-ray, optical, and radio wavelengths have led to compelling evidence that short GRBs come from merging compact binaries (as David Eichler, Mario Livio, Tsvi Piran, and David Schramm conjectured in 1989) It ...
... of greatest remaining mystery of GRBs: The Nature of short GRBs Follow-up observations at X-ray, optical, and radio wavelengths have led to compelling evidence that short GRBs come from merging compact binaries (as David Eichler, Mario Livio, Tsvi Piran, and David Schramm conjectured in 1989) It ...
Program and Abstract Book - European Southern Observatory
... Stars form from the gravitational collapse of dense molecular cloud cores. In the protostellar phase, mass both accretes from the core onto a protostar, likely through an accretion disk, and is ejected in the form of jets and outflows. It is during this protostellar phase that the initial masses of ...
... Stars form from the gravitational collapse of dense molecular cloud cores. In the protostellar phase, mass both accretes from the core onto a protostar, likely through an accretion disk, and is ejected in the form of jets and outflows. It is during this protostellar phase that the initial masses of ...
Elliptical Galaxies
... Similarly if galaxies possess disks of excited or ionized gas we can trace the mass distribution in the same way as for spiral galaxies. A review of the topics covered in this section can be found in de Zeeuw and Franx (1992). Dark haloes: mass at large radius Spiral galaxy rotation curves have been ...
... Similarly if galaxies possess disks of excited or ionized gas we can trace the mass distribution in the same way as for spiral galaxies. A review of the topics covered in this section can be found in de Zeeuw and Franx (1992). Dark haloes: mass at large radius Spiral galaxy rotation curves have been ...
Numerical simulations of wind–equatorial gas
... The WBE has been ejected by the system more than a century ago. However, some dense equatorial outflow might have been continued for tens of years. It is impossible to know the exact mass-loss history and mass-loss rate that led to the formation of the WBE. Considering that our goals are (a) to show ...
... The WBE has been ejected by the system more than a century ago. However, some dense equatorial outflow might have been continued for tens of years. It is impossible to know the exact mass-loss history and mass-loss rate that led to the formation of the WBE. Considering that our goals are (a) to show ...
Rotation Curves of Spiral Galaxies
... nebula the ratio f of mass density to light density is found to be very high; and this conclusion holds for whatever dynamical model we consider. The spectrum of the nebula shows the characteristics of G-type dwarfs. Since f cannot be much larger than 1 for such stars, they can account for roughly o ...
... nebula the ratio f of mass density to light density is found to be very high; and this conclusion holds for whatever dynamical model we consider. The spectrum of the nebula shows the characteristics of G-type dwarfs. Since f cannot be much larger than 1 for such stars, they can account for roughly o ...
Astronomy Astrophysics − Astrophysical parameters of the peculiar X-ray transient
... We used the interstellar lines in the spectrum of HD 306414 to study the radial velocity distribution of interstellar material along its line of sight. We calculated the velocity scale with respect to the local standard of rest (LSR) by assuming that the Sun’s motion with respect to the LSR correspo ...
... We used the interstellar lines in the spectrum of HD 306414 to study the radial velocity distribution of interstellar material along its line of sight. We calculated the velocity scale with respect to the local standard of rest (LSR) by assuming that the Sun’s motion with respect to the LSR correspo ...
A new view of galaxy evolution
... internal motion similar to nearby disc/ellipticals – further evidence for their violent origin. There are other clues we must consider. One is that these galaxies are undergoing intense star formation with on the order of a few hundred solar masses of new stars formed per year, compared with just a ...
... internal motion similar to nearby disc/ellipticals – further evidence for their violent origin. There are other clues we must consider. One is that these galaxies are undergoing intense star formation with on the order of a few hundred solar masses of new stars formed per year, compared with just a ...







![[C ii] 157 μm Emission in a Five-component Interstellar](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/019898103_1-04a729a979ed8700f387bc0fbfcce724-300x300.png)
![Neutral material around the B[e] supergiant star LHA 115](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015508749_1-459b4c864ff7fdb1bc1eff2b9c6df4c4-300x300.png)