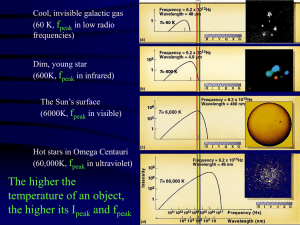
Light and Telescopes - Otterbein University
... gas) emits light of all wavelengths: the black body spectrum 2. Light of a low density hot gas consists of a series of discrete bright emission lines: the positive “fingerprints” of its chemical elements! 3. A cool, thin gas absorbs certain wavelengths from a continuous spectrum dark absorption ( ...
... gas) emits light of all wavelengths: the black body spectrum 2. Light of a low density hot gas consists of a series of discrete bright emission lines: the positive “fingerprints” of its chemical elements! 3. A cool, thin gas absorbs certain wavelengths from a continuous spectrum dark absorption ( ...
Recent Advances in Astrometry with the VLBA
... • Reduces kinematic distances: Dk by 15%, hence… Molecular cloud sizes (R D) by 15% Young star luminosities: L R2 by 30% (increasing YSO ages) Cloud masses (from column density & size): M R2 by 30% • Milky Way’s dark matter halo mass: M (Vmax) 2 RVir Vmax Q0 & RVir Q0 M Q03 or up by 5 ...
... • Reduces kinematic distances: Dk by 15%, hence… Molecular cloud sizes (R D) by 15% Young star luminosities: L R2 by 30% (increasing YSO ages) Cloud masses (from column density & size): M R2 by 30% • Milky Way’s dark matter halo mass: M (Vmax) 2 RVir Vmax Q0 & RVir Q0 M Q03 or up by 5 ...
Astronomy Review revised Key
... 23. If the star is located 4.3 light years away, how long will it be before we see the light of the star? 4.4 years. 18. What is the Big Bang Theory? The theory that all matter was once condensed into a single point called the singularity, and that singularity exploded sending matter out in all dir ...
... 23. If the star is located 4.3 light years away, how long will it be before we see the light of the star? 4.4 years. 18. What is the Big Bang Theory? The theory that all matter was once condensed into a single point called the singularity, and that singularity exploded sending matter out in all dir ...
Abundance Patterns and Star Formation
... Stellar halo comes from the outer part of the progenitor discs when the bulge is formed by a major merger of two spirals. Correlation between halo metallicity and bulge mass ...
... Stellar halo comes from the outer part of the progenitor discs when the bulge is formed by a major merger of two spirals. Correlation between halo metallicity and bulge mass ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... contains about 100 stars. is the largest known object in the universe. is about 75,000 light-years in diameter. is located about 2.2 million light years from the sun. Only a. and c. are correct. ...
... contains about 100 stars. is the largest known object in the universe. is about 75,000 light-years in diameter. is located about 2.2 million light years from the sun. Only a. and c. are correct. ...
universe.pps - Prophet Muhammad For All
... A spiral galaxy of at least two hundred billion stars. Our Sun is buried deep within the Orion Arm about 26 000 light years from the centre. Towards the centre of the Galaxy the stars are packed together much closer than they are where we live. Notice also the presence of small globular clusters of ...
... A spiral galaxy of at least two hundred billion stars. Our Sun is buried deep within the Orion Arm about 26 000 light years from the centre. Towards the centre of the Galaxy the stars are packed together much closer than they are where we live. Notice also the presence of small globular clusters of ...
NOVA - Black Holes
... The star that Andrea Ghez found was moving on order of__________________ miles per hour. 10 million Not only were the stars accelerating to phenomenal speeds, their orbits were perfectly _____________. smooth Most black holes are thought to be about ____________ more massive than our Sun, but the ob ...
... The star that Andrea Ghez found was moving on order of__________________ miles per hour. 10 million Not only were the stars accelerating to phenomenal speeds, their orbits were perfectly _____________. smooth Most black holes are thought to be about ____________ more massive than our Sun, but the ob ...
the size and structure of the universe
... black hole is a region of space that has so much mass concentrated in it that there is no way for a nearby object to escape its gravitational pull. Black holes are the evolutionary endpoints of stars at least 10 to 15 times as massive as the Sun. ...
... black hole is a region of space that has so much mass concentrated in it that there is no way for a nearby object to escape its gravitational pull. Black holes are the evolutionary endpoints of stars at least 10 to 15 times as massive as the Sun. ...
Interstellar Cloud
... A protostar is the center of the disc formed in the center of the interstellar gas cloud. Hotter than the gas it condensed, but cooler than a star. Further collapse occurs when the protostar reaches seven million Kelvin and nuclear reactions begin in the core. ...
... A protostar is the center of the disc formed in the center of the interstellar gas cloud. Hotter than the gas it condensed, but cooler than a star. Further collapse occurs when the protostar reaches seven million Kelvin and nuclear reactions begin in the core. ...
The Curtis-Shapley debate – two different views of
... with a diameter of 17 kiloparsecs with the Sun apparently close to its centre. Shapley’s view of the Universe He believed that out galaxy was the whole universe, that it had a diameter 300 000 light years (100 kiloparsecs) and that the Sun was about 20 kiloparsecs from its centre. He argued that the ...
... with a diameter of 17 kiloparsecs with the Sun apparently close to its centre. Shapley’s view of the Universe He believed that out galaxy was the whole universe, that it had a diameter 300 000 light years (100 kiloparsecs) and that the Sun was about 20 kiloparsecs from its centre. He argued that the ...
Chapter 4: Spectroscopy
... Pattern of dark spectral lines where light within a number of narrow frequency ranges has been removed. ...
... Pattern of dark spectral lines where light within a number of narrow frequency ranges has been removed. ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 18 Galaxy Interactions Here we briefly
... it will spend half as much time near a given object and the impulse will be half as large. Then the density enhancement will develop only half as fast, and M will be twice as far away by the time the enhancement arises. This means that slow encounters are much more effective at decreasing the speed ...
... it will spend half as much time near a given object and the impulse will be half as large. Then the density enhancement will develop only half as fast, and M will be twice as far away by the time the enhancement arises. This means that slow encounters are much more effective at decreasing the speed ...
proposed research projects for pparc gemini studentships
... formation of S0 galaxies, and their dependency on galaxy mass. To this end, we propose a spectral study of a large sample of lenticular systems to establish the links between the properties of their stellar populations (ages and chemical abundances) and their kinematic properties (masses and dynamic ...
... formation of S0 galaxies, and their dependency on galaxy mass. To this end, we propose a spectral study of a large sample of lenticular systems to establish the links between the properties of their stellar populations (ages and chemical abundances) and their kinematic properties (masses and dynamic ...
No Slide Title
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
An additional term of the Galactic tide due to dark matter
... Galactic centre. Consequently, the correspodingly derived behaviour of mass, M(r), inside the galactocentric sphere of radius r, increases almost linearly with r. (A good example can be seen in Bosma 1978, Chap. 6.4, Fig. 3.) We are aware of a suggestion that this linear approximation is sufficient fo ...
... Galactic centre. Consequently, the correspodingly derived behaviour of mass, M(r), inside the galactocentric sphere of radius r, increases almost linearly with r. (A good example can be seen in Bosma 1978, Chap. 6.4, Fig. 3.) We are aware of a suggestion that this linear approximation is sufficient fo ...
spiral galaxies
... will take about 2 billion years to finish, once it’s begun. That means the whole process won’t be completed until about 6 billion years from now — probably long after the sun runs out of fuel and swells to become a bright, cool star known as a red giant. Collisions aren’t that unusual. Small, neighb ...
... will take about 2 billion years to finish, once it’s begun. That means the whole process won’t be completed until about 6 billion years from now — probably long after the sun runs out of fuel and swells to become a bright, cool star known as a red giant. Collisions aren’t that unusual. Small, neighb ...
Rosolowsky
... 2. Another factor [f(R)] determines what fraction of these clouds are converted to molecular gas 3. Different environments create different mass distributions of bound molecular clouds. ...
... 2. Another factor [f(R)] determines what fraction of these clouds are converted to molecular gas 3. Different environments create different mass distributions of bound molecular clouds. ...
Astronomy Unit 4 Galaxies
... 38. Galaxies that are brighter than normal are called __________________________ and emit most of their radiation at ________________ wavelengths. 39. The source of energy in active galaxies changes over short periods of time implying they come from regions which are _______________ in size. 40. Exp ...
... 38. Galaxies that are brighter than normal are called __________________________ and emit most of their radiation at ________________ wavelengths. 39. The source of energy in active galaxies changes over short periods of time implying they come from regions which are _______________ in size. 40. Exp ...
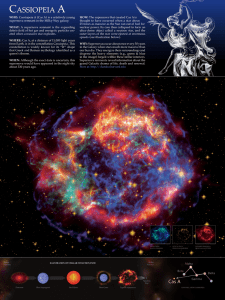
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... HOW: The supernova that created Cas A is thought to have occurred when a star about 25 times as massive as the Sun ran out of fuel for nuclear power. Its core then collapsed to form an ultra-dense object called a neutron star, and the outer layers of the star were ejected at enormous speeds (see ill ...
... HOW: The supernova that created Cas A is thought to have occurred when a star about 25 times as massive as the Sun ran out of fuel for nuclear power. Its core then collapsed to form an ultra-dense object called a neutron star, and the outer layers of the star were ejected at enormous speeds (see ill ...
15 Billion
... b. Computer models of planetary collisions create an Earth-Moon system like ours. The composition of the Moon matches the mantle. c. The age of large impact craters on the Earth match the age extinctions in the fossil record. d. In 1987, a supernova is observed creating heavy elements. e. 4.3 billio ...
... b. Computer models of planetary collisions create an Earth-Moon system like ours. The composition of the Moon matches the mantle. c. The age of large impact craters on the Earth match the age extinctions in the fossil record. d. In 1987, a supernova is observed creating heavy elements. e. 4.3 billio ...
The Andromeda Galaxy
... Way are expected to collide in about 4.5 billion years. A likely result of the collision is that the galaxies will combine to form a giant elliptical (egg shaped) ...
... Way are expected to collide in about 4.5 billion years. A likely result of the collision is that the galaxies will combine to form a giant elliptical (egg shaped) ...
Star Formation
... So if we can detect them (using specialized radio telescopes), we deduce the presence of a big cool cloud of material, ready for gravity to cause its collapse. ...
... So if we can detect them (using specialized radio telescopes), we deduce the presence of a big cool cloud of material, ready for gravity to cause its collapse. ...
Sample final exam
... 18. Two binary stars, each with a mass of 0.5 solar masses, orbit each other. Each has a semi-major axis of its orbit of 1.0 AU. What is the period (in years) of these stars? Essay section part one — Choose two of the following questions, and answer them in paragraph style or with drawings, as the ...
... 18. Two binary stars, each with a mass of 0.5 solar masses, orbit each other. Each has a semi-major axis of its orbit of 1.0 AU. What is the period (in years) of these stars? Essay section part one — Choose two of the following questions, and answer them in paragraph style or with drawings, as the ...
Astronomy 110G Review Sheet for Exam #3 The
... • Luminous properties of various types of stars are conveniently displayed in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The main sequence is a mass sequence with high mass stars near the top left (high temperature, large luminosity) region. Giants, etc., represent different and later stages in the lives of s ...
... • Luminous properties of various types of stars are conveniently displayed in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The main sequence is a mass sequence with high mass stars near the top left (high temperature, large luminosity) region. Giants, etc., represent different and later stages in the lives of s ...