SHELL H II REGIONS IN NGC 6334
... • The large, lineal motions are due to the relative motion between the Sun and the object and they coincide with what is expected. • However, there is also relative motion between the two components, suggesting orbital motions. ...
... • The large, lineal motions are due to the relative motion between the Sun and the object and they coincide with what is expected. • However, there is also relative motion between the two components, suggesting orbital motions. ...
The Sizes of Stars
... much material in the interstellar medium as there is in stars. Much of this matter is far, far from any star. It is therefore very cold. In these cold regions, atoms can stick together to form molecules, such as H2. A Giant Molecular Cloud may contain over 100,000,000 M of material! ...
... much material in the interstellar medium as there is in stars. Much of this matter is far, far from any star. It is therefore very cold. In these cold regions, atoms can stick together to form molecules, such as H2. A Giant Molecular Cloud may contain over 100,000,000 M of material! ...
Earth Science Exam Review 1
... relationship between Earth and the Milky Way Galaxy? A. Earth is billions of light-years away from the Milky Way Galaxy. B. Earth is part of a galaxy that is nearest to the Milky Way Galaxy. C. Earth is located in the Milky Way galaxy but far from the galaxy center. D. Earth is positioned in the cen ...
... relationship between Earth and the Milky Way Galaxy? A. Earth is billions of light-years away from the Milky Way Galaxy. B. Earth is part of a galaxy that is nearest to the Milky Way Galaxy. C. Earth is located in the Milky Way galaxy but far from the galaxy center. D. Earth is positioned in the cen ...
Role of column density in the formation of stars
... gas becomes optically thick to its cooling radiation. These results are plausible because molecule formation is evidently necessary for star formation, and because the onset of a high optical depth in a galactic nucleus may suppress continuing star formation and favour the growth of a central black ...
... gas becomes optically thick to its cooling radiation. These results are plausible because molecule formation is evidently necessary for star formation, and because the onset of a high optical depth in a galactic nucleus may suppress continuing star formation and favour the growth of a central black ...
On the Moon, this crater rules. Copernicus, King of Craters
... are held close to Andromeda’s spiral see. arms, he thought they one another by What about the might also trace the gravity. Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way’s spiral The stars of Andromeda People wondered arms. So in 1951, even reveal how far away the whether it was a spiral, too. But Morgan mapped the l ...
... are held close to Andromeda’s spiral see. arms, he thought they one another by What about the might also trace the gravity. Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way’s spiral The stars of Andromeda People wondered arms. So in 1951, even reveal how far away the whether it was a spiral, too. But Morgan mapped the l ...
milkyway - University of Pittsburgh
... formation of new stars is becoming rare • To an observer outside our galaxy, the overall color of ...
... formation of new stars is becoming rare • To an observer outside our galaxy, the overall color of ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... Kip went to work on the problem and actually worked out the details using relativity theory. He suggested that wormholes might work. Intringued, Thorne picked up the wormhole problem over the next several years and began pursuing it as an active research project. Inspired by his bold lead on s ...
... Kip went to work on the problem and actually worked out the details using relativity theory. He suggested that wormholes might work. Intringued, Thorne picked up the wormhole problem over the next several years and began pursuing it as an active research project. Inspired by his bold lead on s ...
Draft paper (Published in ApJL)
... 50 as they traverse the pancake, as well as the rest of the galaxies labeled in Fig. 2 as non-star forming. One may wonder how the pancake, which is only a few times overdense relative to the mean baryonic density of the Universe (see middle panels of Fig. 4), is able to remove the much denser gas t ...
... 50 as they traverse the pancake, as well as the rest of the galaxies labeled in Fig. 2 as non-star forming. One may wonder how the pancake, which is only a few times overdense relative to the mean baryonic density of the Universe (see middle panels of Fig. 4), is able to remove the much denser gas t ...
What is chemistry????
... past one another. A gas has neither a fixed shape nor fixed volume. It ...
... past one another. A gas has neither a fixed shape nor fixed volume. It ...
- ORIGINS Space Telescope
... comprises less than one-hundredth of one percent of the baryonic mass of the Universe, yet approximately one-half of all energy radiated by stars and accreting black holes over its history has been reprocessed by dust to long wavelengths. Dust shrouds the most intense regions of black hole accretion ...
... comprises less than one-hundredth of one percent of the baryonic mass of the Universe, yet approximately one-half of all energy radiated by stars and accreting black holes over its history has been reprocessed by dust to long wavelengths. Dust shrouds the most intense regions of black hole accretion ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... Massive stars, with denser and hotter cores, burn faster their fuel than smaller stars, living shorter (only a few million years). Smaller stars, like our Sun, live much longer, 10 billions years. Very small star can live up to hundreds of billions of years. ...
... Massive stars, with denser and hotter cores, burn faster their fuel than smaller stars, living shorter (only a few million years). Smaller stars, like our Sun, live much longer, 10 billions years. Very small star can live up to hundreds of billions of years. ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... The speed of light is a universal constant, it does not change over time or from place to place. Thought Experiment: imagine two teams of scientist measuring the speed of a beam of light. One team measures the speed from a ground. The second team measures the speed from a fast moving airplane foll ...
... The speed of light is a universal constant, it does not change over time or from place to place. Thought Experiment: imagine two teams of scientist measuring the speed of a beam of light. One team measures the speed from a ground. The second team measures the speed from a fast moving airplane foll ...
driving galaxy evolution since z=1
... • We observe starlight – which results from the condensation of baryonic matter ...
... • We observe starlight – which results from the condensation of baryonic matter ...
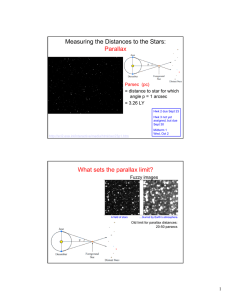
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... • Must use other methods. • Must know actual distance + velocity. Mostly radio data with tangent point method ...
... • Must use other methods. • Must know actual distance + velocity. Mostly radio data with tangent point method ...
Galaxy interaction and transformation
... simulations are used to understand the properties of merger remnants. Some of the most important results obtained are 1. Major mergers of galaxies generally lead to elliptical-like remnants, with some irregular structures in the outer regions. Depending on the orbital geometry of the merger, the rem ...
... simulations are used to understand the properties of merger remnants. Some of the most important results obtained are 1. Major mergers of galaxies generally lead to elliptical-like remnants, with some irregular structures in the outer regions. Depending on the orbital geometry of the merger, the rem ...
Dark Matter Burners
... The white dwarf WIMP burner hypothesis White dwarfs are everywhere! Some just happen to fall into Hertzsprung-Russell diagram the high density dark matter region near the black hole where they appear as WIMP burners Compact structure: more stable against extreme gravitational conditions near the ...
... The white dwarf WIMP burner hypothesis White dwarfs are everywhere! Some just happen to fall into Hertzsprung-Russell diagram the high density dark matter region near the black hole where they appear as WIMP burners Compact structure: more stable against extreme gravitational conditions near the ...
AGN Workshop
... • Is the IGM sensitive to these processes? In what element (O, C, Mg, H, N)? • But if it’s all light, why isn’t Joe seeing the QPE? • How powerful are AGN/QSO outflows? • How to reconcile Smita’s & Xinyu’s results (Seyfert winds are just wimpy?)? • Lot’s of heat? No mass? • Timescale issue! Looking ...
... • Is the IGM sensitive to these processes? In what element (O, C, Mg, H, N)? • But if it’s all light, why isn’t Joe seeing the QPE? • How powerful are AGN/QSO outflows? • How to reconcile Smita’s & Xinyu’s results (Seyfert winds are just wimpy?)? • Lot’s of heat? No mass? • Timescale issue! Looking ...
Galaxy Collisions, Gas Stripping and Star Formation in the Evolution
... 5 Evolution of galaxies in clusters An overabundance of spiral galaxies and an under abundance of S0 galaxies in highredshift clusters, when it is compared to low z clusters, is a consequences of galaxy merger events and of other environmental effects. In ΛDCM cosmological models with Ω0 = 0.4 and Ω ...
... 5 Evolution of galaxies in clusters An overabundance of spiral galaxies and an under abundance of S0 galaxies in highredshift clusters, when it is compared to low z clusters, is a consequences of galaxy merger events and of other environmental effects. In ΛDCM cosmological models with Ω0 = 0.4 and Ω ...
Figure 1. Map showing the region of the Fourth Quadrant selected
... In these turbulent models (see MacLow & Klessen 2004) supersonic turbulence is driven on large scales (tens of parsecs or more) and generates turbulence on smaller scales via an energy cascade. The supersonic gas motions quickly compress regions of gas, which may then undergo collapse in these dense ...
... In these turbulent models (see MacLow & Klessen 2004) supersonic turbulence is driven on large scales (tens of parsecs or more) and generates turbulence on smaller scales via an energy cascade. The supersonic gas motions quickly compress regions of gas, which may then undergo collapse in these dense ...
PowerPoint file - Adin Community Bible Church
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...
Letter to the Editor ASTRONOMY ASTROPHYSICS
... the stars that ionize the Hll nebulae at the tip of the stream is ~ 10 7 years, these stars were borned well after the ejection of the material from which they have been formed. Although the computer models of the Antennae succesfully simulate the major features of this system, they do not reproduce ...
... the stars that ionize the Hll nebulae at the tip of the stream is ~ 10 7 years, these stars were borned well after the ejection of the material from which they have been formed. Although the computer models of the Antennae succesfully simulate the major features of this system, they do not reproduce ...