Progenitor systems of Type Ia Supernovae: mergers of white dwarfs
... For all the reasons described above, it is important to understand where type Ia supernovae come from and how they explode. Today, however, neither the progenitor systems are known nor the explosion mechanism of type Ia supernovae is understood. The goal of this thesis is to shed some light on both. ...
... For all the reasons described above, it is important to understand where type Ia supernovae come from and how they explode. Today, however, neither the progenitor systems are known nor the explosion mechanism of type Ia supernovae is understood. The goal of this thesis is to shed some light on both. ...
Supernova Echo - Subaru Telescope
... • Well known & studied SNR • Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe found very bright `new star’ in the constellation of Cassiopeia on the evening of 11th of November in 1572. He had observed its brightness, color, and proper motion until March in 1574. • In 20th century, the `new star’ = A supernova ...
... • Well known & studied SNR • Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe found very bright `new star’ in the constellation of Cassiopeia on the evening of 11th of November in 1572. He had observed its brightness, color, and proper motion until March in 1574. • In 20th century, the `new star’ = A supernova ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
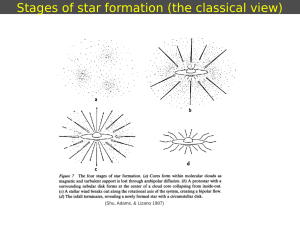
Stages of star formation (the classical view)
... The protostar becomes a pre-main sequence star (T Tauri star). However, for a high-mass star tKH<< tff (for a 50 Msol star, tKH= 3x104 yr) The star has not enough time to accrete more than ~10 Msol before starting to burn hydrogen, ionizing the material around the star, and disrupting the dense core ...
... The protostar becomes a pre-main sequence star (T Tauri star). However, for a high-mass star tKH<< tff (for a 50 Msol star, tKH= 3x104 yr) The star has not enough time to accrete more than ~10 Msol before starting to burn hydrogen, ionizing the material around the star, and disrupting the dense core ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... metals that are not very common in most stars. It was found that the 7 most abundant metals for Alioth are calcium, chromium, iron, magnesium, manganese, thallium, and strontium. Using a Doppler imaging code to analyze elements in complex spectral line blends, it is possible to map the structure of ...
... metals that are not very common in most stars. It was found that the 7 most abundant metals for Alioth are calcium, chromium, iron, magnesium, manganese, thallium, and strontium. Using a Doppler imaging code to analyze elements in complex spectral line blends, it is possible to map the structure of ...
low surface brightness galaxies
... However, the data also seem to indicate that only a small fraction of the mass is involved in such episodes. ...
... However, the data also seem to indicate that only a small fraction of the mass is involved in such episodes. ...
Stellar Evolution : The Life and Death of Our Luminous Neighbors
... e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's core remain under control so long as a. b. c. d. ...
... e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's core remain under control so long as a. b. c. d. ...
Chapter 4 [PDF only] - Princeton University Press
... undergo after the main sequence, and the properties of their compact remnants—white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. We then study the phenomena that can occur when such compact objects accrete material from a companion star in a binary pair. ...
... undergo after the main sequence, and the properties of their compact remnants—white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. We then study the phenomena that can occur when such compact objects accrete material from a companion star in a binary pair. ...
Downloadable Full Text
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
Staring Back to Cosmic Dawn - UC-HiPACC
... dwarfs? Scientists also need to see if there is a systematic trend in supernova luminosity that correlates with cosmic age. After all, early stars were poorer in elements heavier than helium. Moreover, the typical white dwarf in the early universe was more massive than a typical white dwarf today be ...
... dwarfs? Scientists also need to see if there is a systematic trend in supernova luminosity that correlates with cosmic age. After all, early stars were poorer in elements heavier than helium. Moreover, the typical white dwarf in the early universe was more massive than a typical white dwarf today be ...
New Scientist - Quark Nova Project
... stranger. They may mark the violent birth of a quark star, a cosmic oddity that has only existed so far in the imaginations and equations of a few physicists. If so they would be the strongest hints yet that these celestial creatures exist in the cosmic wild. The implications would be enormous. Thes ...
... stranger. They may mark the violent birth of a quark star, a cosmic oddity that has only existed so far in the imaginations and equations of a few physicists. If so they would be the strongest hints yet that these celestial creatures exist in the cosmic wild. The implications would be enormous. Thes ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 18. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
Toward $ ab\, initio $ extremely metal poor stars
... Toward ab initio extremely metal poor stars around the density maximum with an ‘active’ (gravitating) Pop III star particle. This replacement capped the gas density around the maximum, where the star particle was inserted, at a ceiling computed consistent with mass conservation. We ray-traced ioniz ...
... Toward ab initio extremely metal poor stars around the density maximum with an ‘active’ (gravitating) Pop III star particle. This replacement capped the gas density around the maximum, where the star particle was inserted, at a ceiling computed consistent with mass conservation. We ray-traced ioniz ...
with answers
... due to the sudden gravitational collapse of the massive star's core. These events are very short-lived and very bright. Only stars with very large initial mass develop into supergiants or hypergiants and thus are the only stars capable of “going supernova”. Less massive stars (up to 8 M☉) will evolv ...
... due to the sudden gravitational collapse of the massive star's core. These events are very short-lived and very bright. Only stars with very large initial mass develop into supergiants or hypergiants and thus are the only stars capable of “going supernova”. Less massive stars (up to 8 M☉) will evolv ...
Fluorine nucleosynthesis
... Neutrinos will carry away most of the energy released in the collapse (3 x1053 erg). Only 1051 erg come as photons or KE. There are two main mechanisms of neutrino production: a) neutronization (occurs during collapse in the homologous ...
... Neutrinos will carry away most of the energy released in the collapse (3 x1053 erg). Only 1051 erg come as photons or KE. There are two main mechanisms of neutrino production: a) neutronization (occurs during collapse in the homologous ...
Impact on stellar properties of changing physics SAC Summer
... was originally created by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. It shows the relationship between the star’s luminosity or absolute magnitude versus its effective temperature or spectral type. In general, stars of greater luminosity populate the top of the diagram, while stars with higher surf ...
... was originally created by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. It shows the relationship between the star’s luminosity or absolute magnitude versus its effective temperature or spectral type. In general, stars of greater luminosity populate the top of the diagram, while stars with higher surf ...
Z - STScI
... Zampieri et al., Nomoto et al - low luminosity SNe form black-holes No evidence so far of the branching at high luminosity Detailed comparison with models now possible ...
... Zampieri et al., Nomoto et al - low luminosity SNe form black-holes No evidence so far of the branching at high luminosity Detailed comparison with models now possible ...
Document
... • The transfer of mass from one star to its companion affects the life history (evolution) of both stars. • What is the Algol Paradox? • The star Algol is a binary star in which the lower mass star is in a more advanced stage of life than the higher mass star. This is a paradox, because both stars m ...
... • The transfer of mass from one star to its companion affects the life history (evolution) of both stars. • What is the Algol Paradox? • The star Algol is a binary star in which the lower mass star is in a more advanced stage of life than the higher mass star. This is a paradox, because both stars m ...
Resultados del Concurso 2008A para Observaciones en
... over the full range of observed metallicities using near-infrared photometry alone, because models cannot reliably reproduce the observed morphology in near-IR color-magnitude diagrams (CMDs). While a handful of isolated cases have provided age measurements over a narrow metallicity range, the abili ...
... over the full range of observed metallicities using near-infrared photometry alone, because models cannot reliably reproduce the observed morphology in near-IR color-magnitude diagrams (CMDs). While a handful of isolated cases have provided age measurements over a narrow metallicity range, the abili ...
Research proposal uploaded for ESO fellowship
... global star formation rate decline of the universe? Supernova feedback represents a long standing problem in galaxy formation model. Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. ...
... global star formation rate decline of the universe? Supernova feedback represents a long standing problem in galaxy formation model. Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. ...
Table of Contents March General Meeting March is Membership
... supernovae fell into different types based on their light curves, that is, their pattern of rising and falling brightness. Later, they found these types actually corresponded to different physical circumstances triggering the explosions. Even those types have fine distinctions based on their spectra ...
... supernovae fell into different types based on their light curves, that is, their pattern of rising and falling brightness. Later, they found these types actually corresponded to different physical circumstances triggering the explosions. Even those types have fine distinctions based on their spectra ...
Supernova

A supernova is a stellar explosion that briefly outshines an entire galaxy, radiating as much energy as the Sun or any ordinary star is expected to emit over its entire life span, before fading from view over several weeks or months. The extremely luminous burst of radiation expels much or all of a star's material at a velocity of up to 7007300000000000000♠30,000 km/s (10% of the speed of light), driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. This shock wave sweeps up an expanding shell of gas and dust called a supernova remnant. Supernovae are potentially strong galactic sources of gravitational waves. A great proportion of primary cosmic rays comes from supernovae.Supernovae are more energetic than novae. Nova means ""new"" in Latin, referring to what appears to be a very bright new star shining in the celestial sphere; the prefix ""super-"" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word supernova was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1931. It is pronounced /ˌsuːpərnoʊvə/ with the plural supernovae /ˌsuːpərnoʊviː/ or supernovas (abbreviated SN, plural SNe after ""supernovae"").Supernovae can be triggered in one of two ways: by the sudden re-ignition of nuclear fusion in a degenerate star; or by the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star. In the first case, a degenerate white dwarf may accumulate sufficient material from a companion, either through accretion or via a merger, to raise its core temperature, ignite carbon fusion, and trigger runaway nuclear fusion, completely disrupting the star. In the second case, the core of a massive star may undergo sudden gravitational collapse, releasing gravitational potential energy that can create a supernova explosion.The most recent directly observed supernova in the Milky Way was Kepler's Star of 1604 (SN 1604); remnants of two more recent supernovae have been found retrospectively. Observations in other galaxies indicate that supernovae should occur on average about three times every century in the Milky Way, and that any galactic supernova would almost certainly be observable in modern astronomical equipment. Supernovae play a significant role in enriching the interstellar medium with higher mass elements. Furthermore, the expanding shock waves from supernova explosions can trigger the formation of new stars.






![Chapter 4 [PDF only] - Princeton University Press](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016931743_1-7c8ec22374457bf50a0a03f55488ddc7-300x300.png)