Star Formation in Disks: Spiral Arms, Turbulence, and Triggering
... There are many types and sources of energy in the ISM and many possible causes for triggering. Energy types include thermal, magnetic, turbulent, cosmic ray, and rotational. The first four are all comparable and equal to several tenths of an eV cm−3 . Rotational energy is much denser, several hundred ...
... There are many types and sources of energy in the ISM and many possible causes for triggering. Energy types include thermal, magnetic, turbulent, cosmic ray, and rotational. The first four are all comparable and equal to several tenths of an eV cm−3 . Rotational energy is much denser, several hundred ...
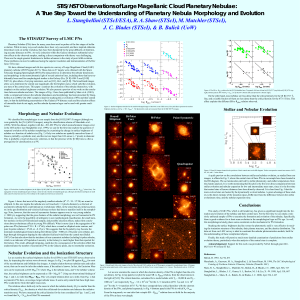
STIS/HST Observations of Large Magellanic Cloud Planetary
... This study of LMC PNs, which is still underway, has given us significant insight into the formation and evolution of the nebulae and their central stars. For the first time we can study a relatively unbiased sample of PNs to examine the formation and evolution of the nebulae. Specifically, there is ...
... This study of LMC PNs, which is still underway, has given us significant insight into the formation and evolution of the nebulae and their central stars. For the first time we can study a relatively unbiased sample of PNs to examine the formation and evolution of the nebulae. Specifically, there is ...
REVIEWS The formation of the first stars and galaxies Volker Bromm
... statistically described as a Gaussian random field. Such high-density peaks are expected to be strongly clustered15, and thus feedback effects from the first stars are important in determining the fate of the surrounding primordial gas clouds. It is very likely that only one star can be formed withi ...
... statistically described as a Gaussian random field. Such high-density peaks are expected to be strongly clustered15, and thus feedback effects from the first stars are important in determining the fate of the surrounding primordial gas clouds. It is very likely that only one star can be formed withi ...
The Mid-Infrared Spectrum of the Short Orbital Period Polar EF
... peak amplitudes, the cyclotron humps are too narrow compared to the observed nearIR spectrum. The fact that discrete cyclotron humps are observed requires kT . 20 keV. θ: In the absence of consistent information constraining this parameter, we chose to set θ = 75◦ for all models. In any case, θ cann ...
... peak amplitudes, the cyclotron humps are too narrow compared to the observed nearIR spectrum. The fact that discrete cyclotron humps are observed requires kT . 20 keV. θ: In the absence of consistent information constraining this parameter, we chose to set θ = 75◦ for all models. In any case, θ cann ...
Dust in protoplanetary disks
... laboratory experiments that the dust agglomeration is an efficient process in dense and relativ environments, like protostellar cores or protoplanetary discs (e.g., Blum et al., 2002; Kemp 1999; Kesselman, 1980; Nuth and Berg, 1994; Ossenkopf and Henning, 1994; Wurm an ...
... laboratory experiments that the dust agglomeration is an efficient process in dense and relativ environments, like protostellar cores or protoplanetary discs (e.g., Blum et al., 2002; Kemp 1999; Kesselman, 1980; Nuth and Berg, 1994; Ossenkopf and Henning, 1994; Wurm an ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS How many low
... Let us focus on the stars of the present sample that have passed the bump and do not behave as the majority. If we consider the objects with MV lower than -0.5, only 3 stars appear to be really “deviant” (see Table 2). V8 (NGC6656). As can be seen in Figs. 1 and 2, as soon as they are more luminous ...
... Let us focus on the stars of the present sample that have passed the bump and do not behave as the majority. If we consider the objects with MV lower than -0.5, only 3 stars appear to be really “deviant” (see Table 2). V8 (NGC6656). As can be seen in Figs. 1 and 2, as soon as they are more luminous ...
Clusters: age scales for stellar physics
... The second firmly established anchor is the age of the Solar System. The Sun is about 4.57 Gyr old. This value comes from two different methodologies based on estimates for the Sun as a star and for the the remnants of the formation of the Solar System: • Computer models of stellar evolution and ast ...
... The second firmly established anchor is the age of the Solar System. The Sun is about 4.57 Gyr old. This value comes from two different methodologies based on estimates for the Sun as a star and for the the remnants of the formation of the Solar System: • Computer models of stellar evolution and ast ...
Stellar Population Effects on the Inferred Photon Density at
... 2015). This ‘Lyman continuum’ flux is estimated through the use of stellar population synthesis models, fitted to the available data. For a stellar population of known age, metallicity and ultraviolet flux, the ionizing photon flux can be reliably estimated. However difficulties arise when any of these pr ...
... 2015). This ‘Lyman continuum’ flux is estimated through the use of stellar population synthesis models, fitted to the available data. For a stellar population of known age, metallicity and ultraviolet flux, the ionizing photon flux can be reliably estimated. However difficulties arise when any of these pr ...
Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics
... star/body of distant stars/bodies is important: often more important than influence of close stars/bodies Let us consider a IDEALIZED galaxy of N identical stars with mass m, size R and uniform density Let us focus on a single star that crosses the system How long does it take for this star to chang ...
... star/body of distant stars/bodies is important: often more important than influence of close stars/bodies Let us consider a IDEALIZED galaxy of N identical stars with mass m, size R and uniform density Let us focus on a single star that crosses the system How long does it take for this star to chang ...
The first gravitational-wave source from the isolated evolution of two
... ity and the intrinsic detectable mass distribution strongly favors sources with total redshifted masses between 25–73 M⊙ , consistent with our recent work (4), and matching the total redshifted mass of GW150914 (Mtot,z = 70.5 M⊙ ). In our simulations the maximum intrinsic mass of a merging BH-BH bi ...
... ity and the intrinsic detectable mass distribution strongly favors sources with total redshifted masses between 25–73 M⊙ , consistent with our recent work (4), and matching the total redshifted mass of GW150914 (Mtot,z = 70.5 M⊙ ). In our simulations the maximum intrinsic mass of a merging BH-BH bi ...
Potential for Life on the Terrestrial Planets
... atmospheres with CO2/N2 mixing ratios lower then 96% and exposed to intense XUV fluxes result in higher exospheric temperatures and more expanded thermosphereexosphere environments and, hence, suffer stronger atmospheric erosion, which may result in the total loss of several hundred bars even if an ...
... atmospheres with CO2/N2 mixing ratios lower then 96% and exposed to intense XUV fluxes result in higher exospheric temperatures and more expanded thermosphereexosphere environments and, hence, suffer stronger atmospheric erosion, which may result in the total loss of several hundred bars even if an ...
SOLAR HARD X-RAY AND GAMMA-RAY OBSERVATIONS FROM
... data was performed at a lower energy (30 keV) where the contribution of the hot thermal plasma is larger. The observations of the 1990 February 11 event with the Konus-B instrument on GRANAT support this explanation, since the time profiles recorded in three energy bands between 10 and 750 keV becom ...
... data was performed at a lower energy (30 keV) where the contribution of the hot thermal plasma is larger. The observations of the 1990 February 11 event with the Konus-B instrument on GRANAT support this explanation, since the time profiles recorded in three energy bands between 10 and 750 keV becom ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 1 Notes
... We can actually learn a tremendously larger amount by measuring the spectrum of stars. That’s because a real stellar spectrum isn’t just a simple continuous function like a blackbody. Instead, there are all sorts of spiky features. These were first studied by the German physicist Fraunhofer in 1814 ...
... We can actually learn a tremendously larger amount by measuring the spectrum of stars. That’s because a real stellar spectrum isn’t just a simple continuous function like a blackbody. Instead, there are all sorts of spiky features. These were first studied by the German physicist Fraunhofer in 1814 ...
Document
... Of the many possibilities for combining quarks with colour into colourless hadrons, only two configurations were found, till now… ...
... Of the many possibilities for combining quarks with colour into colourless hadrons, only two configurations were found, till now… ...