Space Science Chapter 4 Reading Guide BIG IDEA: Our Sun is
... Why is the photosphere often called the Sun’s surface? Why is the corona NOT normally visible? ...
... Why is the photosphere often called the Sun’s surface? Why is the corona NOT normally visible? ...
Supernovae - Michigan State University
... • core shrinks until degeneracy pressure sets in and halts collapse star is HOT (gravitational energy !) star is small WD M-R relation Hamada-Salpeter Ap.J. 134 (1961) 683 ...
... • core shrinks until degeneracy pressure sets in and halts collapse star is HOT (gravitational energy !) star is small WD M-R relation Hamada-Salpeter Ap.J. 134 (1961) 683 ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
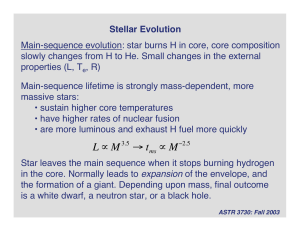
... Main sequence is a mass sequence Lifetime of stars Do you understand? HR Diagram of star cluster ...
... Main sequence is a mass sequence Lifetime of stars Do you understand? HR Diagram of star cluster ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... What are the possible end-products of a supernova? ...
... What are the possible end-products of a supernova? ...
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... by fusing hydrogen atoms into _____ atoms. Can shine for _____________of years even after they die. ...
... by fusing hydrogen atoms into _____ atoms. Can shine for _____________of years even after they die. ...
spectral-type
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
Eclipsing Binaries
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
Activity Sheet: Galaxies and Stars
... Matching: Write the letter of the most appropriate term in the blank before each description. _____ 1. ...
... Matching: Write the letter of the most appropriate term in the blank before each description. _____ 1. ...
death_low_mass
... burning until at last the temperature is high enough in the core to begin helium fusion. This is around 100 million degrees. • When this happens the star is fusing Helium into Carbon in its core, and still is fusing Hydrogen into Helium is a shell around the core. ...
... burning until at last the temperature is high enough in the core to begin helium fusion. This is around 100 million degrees. • When this happens the star is fusing Helium into Carbon in its core, and still is fusing Hydrogen into Helium is a shell around the core. ...
Scientists classify stars by
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
Essay - CLC Charter School
... pressure. When the core shrinks too much, the star swells and grows, iron atoms are crushed together, temperatures reach billions of degrees Celsius, and then a series of nuclear reactions is unleashed. The supernova produces a giant shock wave that throws matter into space at 9,000 to 25,000 miles ...
... pressure. When the core shrinks too much, the star swells and grows, iron atoms are crushed together, temperatures reach billions of degrees Celsius, and then a series of nuclear reactions is unleashed. The supernova produces a giant shock wave that throws matter into space at 9,000 to 25,000 miles ...
Stars, The Sun, and Star Constellation
... The suns pressure is 340 billion times of earths air pressure at sea level A nuclear reaction can occur with protons and hydrogen nuclei to fuse together Its mass is expelled as energy because of convection Every second 700 million tons of hydrogen is converted to helium ash The corona is the outer ...
... The suns pressure is 340 billion times of earths air pressure at sea level A nuclear reaction can occur with protons and hydrogen nuclei to fuse together Its mass is expelled as energy because of convection Every second 700 million tons of hydrogen is converted to helium ash The corona is the outer ...
kaekae14 dae dae15 lifecycleofastar
... cloud picks up stellar dust and other space junk the increasing gravity causes the cloud to collapse. As it collapses the cloud becomes smaller and hotter. After a few million years the low mass star begins to fuse helium into hydrogen. When this happens the collapse is ended because the fusion rais ...
... cloud picks up stellar dust and other space junk the increasing gravity causes the cloud to collapse. As it collapses the cloud becomes smaller and hotter. After a few million years the low mass star begins to fuse helium into hydrogen. When this happens the collapse is ended because the fusion rais ...
Stars - Moodle
... Color and Stars Think of a candle • Hottest part is blue • Red is the cool part at the top ...
... Color and Stars Think of a candle • Hottest part is blue • Red is the cool part at the top ...
PHYSICS 015
... Neutron stars of a few solar masses are already very close to the Schwarzschild radius, so it wouldn’t take much to tip the balance. For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, abo ...
... Neutron stars of a few solar masses are already very close to the Schwarzschild radius, so it wouldn’t take much to tip the balance. For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, abo ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM • In the 1920’s, 2 astronomers looked for patterns in star data • Independently, they observed that star types have ...
... HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM • In the 1920’s, 2 astronomers looked for patterns in star data • Independently, they observed that star types have ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.