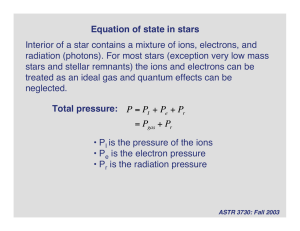
(massive) binary stars
... for single B-type stars. In our analysis, we will benefit from the precisely determined values of the surface gravity (from dynamical mass and radius) and the effective temperature (net result of the Fig. 2 Nitrogen abundance (12 + log[N/H]) vs. the vsini for core hydrogen burning stars. The removed ...
... for single B-type stars. In our analysis, we will benefit from the precisely determined values of the surface gravity (from dynamical mass and radius) and the effective temperature (net result of the Fig. 2 Nitrogen abundance (12 + log[N/H]) vs. the vsini for core hydrogen burning stars. The removed ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference in colour? Rigel is a blue/white star roughly twice as hot as the Sun, whereas Betelgeuse is orange-red, showing it to be much cooler. Both stars ...
... the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference in colour? Rigel is a blue/white star roughly twice as hot as the Sun, whereas Betelgeuse is orange-red, showing it to be much cooler. Both stars ...
Exploding carbon star blowing molecules (red gas) into space Focus
... Oka,Avery,Bronson,McLeod(NRC);Alexander,Kirby,Walton(Sussex) ...
... Oka,Avery,Bronson,McLeod(NRC);Alexander,Kirby,Walton(Sussex) ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... 1. Which of the following properties of stars does NOT require knowledge of the earth-star distance to find it out? A. Mass. B. Luminosity. C. Density. D. Surface temperature. 2. The color of a star is MOST DIRECTLY related to its: A. mass. B. surface temperature. C. central (core) temperature. D. l ...
... 1. Which of the following properties of stars does NOT require knowledge of the earth-star distance to find it out? A. Mass. B. Luminosity. C. Density. D. Surface temperature. 2. The color of a star is MOST DIRECTLY related to its: A. mass. B. surface temperature. C. central (core) temperature. D. l ...
Powerpoint - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... We have found the synthetic data from the simulations that use the MagneticallyChanneled Wind-Shock Model (MCWS) to be in good agreement with what is actually observed with respect to θ1 Ori C. It is important to remember that this simulation is still incomplete since it is only a two-dimensional si ...
... We have found the synthetic data from the simulations that use the MagneticallyChanneled Wind-Shock Model (MCWS) to be in good agreement with what is actually observed with respect to θ1 Ori C. It is important to remember that this simulation is still incomplete since it is only a two-dimensional si ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Hydrogen burning ceases, the star contracts until the temperature again is high enough for hydrogen burning. The whole process repeats, the produced helium falls on to lower layers which finally start burning helium in another helium shell flash. The star is very unstable and the repeated helium fl ...
... Hydrogen burning ceases, the star contracts until the temperature again is high enough for hydrogen burning. The whole process repeats, the produced helium falls on to lower layers which finally start burning helium in another helium shell flash. The star is very unstable and the repeated helium fl ...
Lecture 28 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... that a highly concentrated spherical mass would shrink to a point and have an event horizon around it beyond which nothing could escape (Vescape> c). The Schwarzschild radius, R(event horizon) = 3 km x mass (in solar masses). Oppenheimer (~1940) demonstrated that a stellar remnant above 3 solar mass ...
... that a highly concentrated spherical mass would shrink to a point and have an event horizon around it beyond which nothing could escape (Vescape> c). The Schwarzschild radius, R(event horizon) = 3 km x mass (in solar masses). Oppenheimer (~1940) demonstrated that a stellar remnant above 3 solar mass ...
Northern Circumpolar Constellations
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
The star is born
... The proto-star-phase. Protostars are still in the process of attaining star-like structure. Protostars are accompanied by strong outflows and jets, and are surrounded by accretion disks. The disk is pouring more mass onto the protostar. The protostar is hidden within the cocoon of the birth cloud an ...
... The proto-star-phase. Protostars are still in the process of attaining star-like structure. Protostars are accompanied by strong outflows and jets, and are surrounded by accretion disks. The disk is pouring more mass onto the protostar. The protostar is hidden within the cocoon of the birth cloud an ...
ppt - Serbian Virtual Observatory - astronomical observatory belgrade
... A double star is more general than a binary. To form a binary a star pair must be gravitationally bound. Consequently, to establish the nature means to examine if a given pair is gravitationally bound or, at least, how probable this is. Why probable, because of data lack, very often the data body i ...
... A double star is more general than a binary. To form a binary a star pair must be gravitationally bound. Consequently, to establish the nature means to examine if a given pair is gravitationally bound or, at least, how probable this is. Why probable, because of data lack, very often the data body i ...
To the Stars - LBlackwell
... other. Many star systems have two stars, called a binary system. Often the stars are so close together, they appear as a single point of light. Even though the stars of the Centauri system are closest to Earth, they do not appear to be the brightest in the sky. The brightest star in the night sky is ...
... other. Many star systems have two stars, called a binary system. Often the stars are so close together, they appear as a single point of light. Even though the stars of the Centauri system are closest to Earth, they do not appear to be the brightest in the sky. The brightest star in the night sky is ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... the SMC stars, typically 175 ± 100 km s–1 (Mokiem et al. 2006). Rotational velocities have not been significantly affected by stellar winds, and are significantly lower than 300 km s–1 presently adopted in evolutionary models of Meynet and Maeder (2000). Although the majority of high-mass stars unde ...
... the SMC stars, typically 175 ± 100 km s–1 (Mokiem et al. 2006). Rotational velocities have not been significantly affected by stellar winds, and are significantly lower than 300 km s–1 presently adopted in evolutionary models of Meynet and Maeder (2000). Although the majority of high-mass stars unde ...
The H-R Diagram
... • 19th century astronomer N.R. Pogson proposed a formula which captures the essence of the Greek idea. • A mag=2 star is 2.5 times brighter than a mag=3 star, and a mag 3 star is 2.5 times brighter than a mag=4 star, etc. • If you imagine moving a star to a standard distance of 10 parsecs, the appar ...
... • 19th century astronomer N.R. Pogson proposed a formula which captures the essence of the Greek idea. • A mag=2 star is 2.5 times brighter than a mag=3 star, and a mag 3 star is 2.5 times brighter than a mag=4 star, etc. • If you imagine moving a star to a standard distance of 10 parsecs, the appar ...
Stellar Remnants - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... Earth’s), and a teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh 2 tons. ...
... Earth’s), and a teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh 2 tons. ...
Deep Infrared Images of Star-Forming - University of Missouri
... ionization fronts, supernovae explosions, and strong stellar winds from nearby B-type stars (de Geus 1992). Stellar winds can then compress the medium surrounding the young stars and produce shock-excited Herbig-Haro (HH) objects. Many of the stellar outflows may carry enough momentum and kinetic en ...
... ionization fronts, supernovae explosions, and strong stellar winds from nearby B-type stars (de Geus 1992). Stellar winds can then compress the medium surrounding the young stars and produce shock-excited Herbig-Haro (HH) objects. Many of the stellar outflows may carry enough momentum and kinetic en ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.
![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)