The Milky Way The Milky Way`s Neighbourhood
... A supernova is a tremendous explosion that occurs when the core of a star exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit, and its collapse is not halted by electron degeneracy. When that happens, it takes only a fraction of a second for the stellar core to collapse into a dense ball about ten miles across. The tem ...
... A supernova is a tremendous explosion that occurs when the core of a star exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit, and its collapse is not halted by electron degeneracy. When that happens, it takes only a fraction of a second for the stellar core to collapse into a dense ball about ten miles across. The tem ...
Distance measures - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... By measuring the parallax angle for a star, astronomers can then directly determine its distance. In reality it is not quite so simple for several reasons. The angle of parallax for even the closest stars is always < 1.0 arcsec so careful observation and precision is required. Corrections have to be ...
... By measuring the parallax angle for a star, astronomers can then directly determine its distance. In reality it is not quite so simple for several reasons. The angle of parallax for even the closest stars is always < 1.0 arcsec so careful observation and precision is required. Corrections have to be ...
Observational Lower mass limit on stars
... the galaxy. This gives us a good sample to study. Unlike the most massive stars, the low mass stars have a long lifespan which can be greater than 10 billion years. This tends to make observing stellar evolution of these low mass stars a bit more difficult. ...
... the galaxy. This gives us a good sample to study. Unlike the most massive stars, the low mass stars have a long lifespan which can be greater than 10 billion years. This tends to make observing stellar evolution of these low mass stars a bit more difficult. ...
58KB - NZQA
... hydrogen as fuel. The fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • Red Giant • Planetary Nebulae • White Dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Star birth e ...
... hydrogen as fuel. The fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • Red Giant • Planetary Nebulae • White Dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Star birth e ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... towards shorter wavelengths when the temperature increases. Wien’s ...
... towards shorter wavelengths when the temperature increases. Wien’s ...
Stellar Nebulae
... galaxies, reaching up to 300 light years in diameter. They contain enough dense gas and dust to form hundreds of thousands of Sun-like stars. These stars are formed in the densest parts of the clouds. Molecular clouds are very cold, having temperatures ranging from about -440 to -370 degrees Fahrenh ...
... galaxies, reaching up to 300 light years in diameter. They contain enough dense gas and dust to form hundreds of thousands of Sun-like stars. These stars are formed in the densest parts of the clouds. Molecular clouds are very cold, having temperatures ranging from about -440 to -370 degrees Fahrenh ...
Lec10
... Matter falling toward a neutron star forms an accretion disk, just as in a white-dwarf binary ...
... Matter falling toward a neutron star forms an accretion disk, just as in a white-dwarf binary ...
Solution key
... E. The Solar System ___C___9. A star moves horizontally and to the right on an HR diagram. Which is true? A. Surface temperature decreases and radius decreases B. Surface temperature increases and radius decreases C. Surface temperature decreases and radius increases D. Surface temperature increases ...
... E. The Solar System ___C___9. A star moves horizontally and to the right on an HR diagram. Which is true? A. Surface temperature decreases and radius decreases B. Surface temperature increases and radius decreases C. Surface temperature decreases and radius increases D. Surface temperature increases ...
The American Flag - US Citizenship Teachers
... was added for each new state. This is the flag the flew over Fort McHenry during the War of 1812. It inspired the national anthem, “The Star Spangled Banner.” ...
... was added for each new state. This is the flag the flew over Fort McHenry during the War of 1812. It inspired the national anthem, “The Star Spangled Banner.” ...
Which Stars Form Black Holes and Neutron Stars?
... would have implications for both the Galactic population of these unusual neutron stars, and for the evolution and deaths of massive stars. First, if magnetars only descend from massive progenitors, then they would be expected to be rare compared to radio pulsars [25]. For a standard initial mass fu ...
... would have implications for both the Galactic population of these unusual neutron stars, and for the evolution and deaths of massive stars. First, if magnetars only descend from massive progenitors, then they would be expected to be rare compared to radio pulsars [25]. For a standard initial mass fu ...
Dark matter in the Galactic Halo Rotation curve (i.e. the orbital
... clusters relative to the Sun. (details of these methods are given in Section 2.3 of Sparke & Gallagher…) ...
... clusters relative to the Sun. (details of these methods are given in Section 2.3 of Sparke & Gallagher…) ...
Energy production in stars
... Be and B, as well as with deuterons, are all very fast at the central temperature of the sun, but just this speed of the reaction rules them out: the partner of H is very quickly used up in the process. In fact, and just because of this reason, all the elements mentioned, from deuterium to boron, ar ...
... Be and B, as well as with deuterons, are all very fast at the central temperature of the sun, but just this speed of the reaction rules them out: the partner of H is very quickly used up in the process. In fact, and just because of this reason, all the elements mentioned, from deuterium to boron, ar ...
Stars part 1
... 2. Luminosity – the total amount of energy a star radiates each second. Luminosity of all visible stars range from 1/1,000,000 the luminosity of the sun to 1,000,000 time the luminosity of the sun. 90% of the stars are not as bright as the sun. ...
... 2. Luminosity – the total amount of energy a star radiates each second. Luminosity of all visible stars range from 1/1,000,000 the luminosity of the sun to 1,000,000 time the luminosity of the sun. 90% of the stars are not as bright as the sun. ...
Texts - mistergui
... more well-advanced stage in its evolution than the (4.5 billion year old) Sun is: HIP 13044 has exhausted its supply of hydrogen in its core, and is currently fusing helium into carbon. The Sun will be at this stage too, but not for another 6 billion years! What this means, though, is that the star ...
... more well-advanced stage in its evolution than the (4.5 billion year old) Sun is: HIP 13044 has exhausted its supply of hydrogen in its core, and is currently fusing helium into carbon. The Sun will be at this stage too, but not for another 6 billion years! What this means, though, is that the star ...
chap17_s05_probs
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third va ...
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third va ...
Problems_blackbody_spectra_hr
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
Stellar evolution
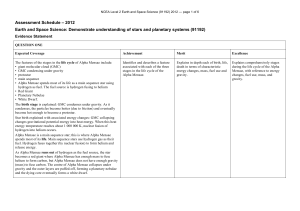
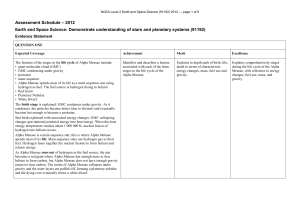
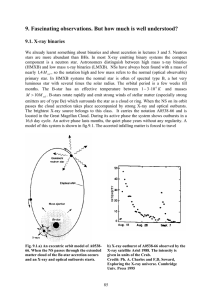
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.