
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... a function of wavelength. In the diagram above the three types of spectra are shown. In the bottom frame they are shown together, as they might appear in an object’s spectrum. ...
... a function of wavelength. In the diagram above the three types of spectra are shown. In the bottom frame they are shown together, as they might appear in an object’s spectrum. ...
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University
... EGB 5 peculiar. All known detached double-degenerate systems with very low-mass WDs have much shorter periods (Steinfadt et al. 2010, and references therein), which may again be caused by selection effects. Furthermore, EGB 5 may be the first very young postCE system, where the ejected envelope is st ...
... EGB 5 peculiar. All known detached double-degenerate systems with very low-mass WDs have much shorter periods (Steinfadt et al. 2010, and references therein), which may again be caused by selection effects. Furthermore, EGB 5 may be the first very young postCE system, where the ejected envelope is st ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... special training. The problem with cloudy skies we cover here is that of identifying unknown stars in isolated patches of clear sky. Such stars may be in view for a few minutes only, just long enough to get a sextant sight of them. New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the onl ...
... special training. The problem with cloudy skies we cover here is that of identifying unknown stars in isolated patches of clear sky. Such stars may be in view for a few minutes only, just long enough to get a sextant sight of them. New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the onl ...
幻灯片 1
... Do what mini-SONG is really good at ! • There are tons of small telescopes out there with similar or better instruments • What makes mini-SONG unique is the SONG network and the way it schedules observations: – High duty cycle, long time baseline – Identical instruments – Can follow ToOs at any tim ...
... Do what mini-SONG is really good at ! • There are tons of small telescopes out there with similar or better instruments • What makes mini-SONG unique is the SONG network and the way it schedules observations: – High duty cycle, long time baseline – Identical instruments – Can follow ToOs at any tim ...
arXiv:1102.4757v1 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Feb 2011
... EGB 5 peculiar. All known detached double-degenerate systems with very low-mass WDs have much shorter periods (Steinfadt et al. 2010 and references therein), which may again be caused by selection effects. Furthermore, EGB 5 may be the first very young post-CE system, where the ejected envelope is s ...
... EGB 5 peculiar. All known detached double-degenerate systems with very low-mass WDs have much shorter periods (Steinfadt et al. 2010 and references therein), which may again be caused by selection effects. Furthermore, EGB 5 may be the first very young post-CE system, where the ejected envelope is s ...
The star-forming environment of an ultraluminous X-ray
... directly with the tracks and isochrones in the WFPC2 photometric system; such models are available for f555w and f814w. However, they are not available for the blue filter f450w: the other, more commonly used blue filter f439w is generally chosen for synthetic models, because it is a closer approxim ...
... directly with the tracks and isochrones in the WFPC2 photometric system; such models are available for f555w and f814w. However, they are not available for the blue filter f450w: the other, more commonly used blue filter f439w is generally chosen for synthetic models, because it is a closer approxim ...
hwd_ewd_v3 - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... the surface) causes rapid downward diffusion of elements heavier than the principal H or He component. Hence, Schatzman predicted that white dwarf atmospheres should be extremely pure. Consequently, the spectra should be devoid of most elements, showing signatures of only hydrogen and, possibly, hel ...
... the surface) causes rapid downward diffusion of elements heavier than the principal H or He component. Hence, Schatzman predicted that white dwarf atmospheres should be extremely pure. Consequently, the spectra should be devoid of most elements, showing signatures of only hydrogen and, possibly, hel ...
Detection of Planetary Transits Across a Sun
... stable for the majority of its orbit (and thus support the hypothesis that the observed radial velocity variations were due to an orbiting companion and not due to some form of stellar variability), and to search for planetary transits. We obtained photometric observations using the STARE Project Sc ...
... stable for the majority of its orbit (and thus support the hypothesis that the observed radial velocity variations were due to an orbiting companion and not due to some form of stellar variability), and to search for planetary transits. We obtained photometric observations using the STARE Project Sc ...
Lecture 7
... Only real possibility is a Black Hole! Must have a mass of 2.7x106M. Not a black hole from a single stellar collapse, but must be built up over time. We shall meet these again when we come to look at quasars, but we have to ask “Just how active was the young Milky Way”? Continuing Education 2009 ...
... Only real possibility is a Black Hole! Must have a mass of 2.7x106M. Not a black hole from a single stellar collapse, but must be built up over time. We shall meet these again when we come to look at quasars, but we have to ask “Just how active was the young Milky Way”? Continuing Education 2009 ...
A seismic and gravitationally-bound double star observed by Kepler
... of mode frequencies required for seismic analysis (See Appourchaux et al. 2012, and references therein). Additional invaluable information about the evolution of stars is provided by the study of the internal structure of red giants (Bedding et al. 2011; Beck et al. 2011, 2012; Mosser et al. 2012a,b ...
... of mode frequencies required for seismic analysis (See Appourchaux et al. 2012, and references therein). Additional invaluable information about the evolution of stars is provided by the study of the internal structure of red giants (Bedding et al. 2011; Beck et al. 2011, 2012; Mosser et al. 2012a,b ...
$doc.title
... • Studies of the FP in both clusters and field out to z > 1 indicate that ellipticals were brighter in the past, but the data are consistent with a model where they are formed at high redshifts (z > 3, say) and evolve nearly passively since then ...
... • Studies of the FP in both clusters and field out to z > 1 indicate that ellipticals were brighter in the past, but the data are consistent with a model where they are formed at high redshifts (z > 3, say) and evolve nearly passively since then ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... Another method of determining distances to late-type stars is by means of the Wilson-Bappu effect, namely that the width of the central emission component of the Ca II K line in G and K-type stars is directly related to the absolute magnitude of the star — the broader the emission line width, denot ...
... Another method of determining distances to late-type stars is by means of the Wilson-Bappu effect, namely that the width of the central emission component of the Ca II K line in G and K-type stars is directly related to the absolute magnitude of the star — the broader the emission line width, denot ...
Line-profile tomography of exoplanet transits – II. A gas
... transits have previously been reported in the lightcurve obtained by the SuperWASP survey of the A5 star HD15082 (WASP-33; V = 8.3, v sin i = 86 km s−1 ). Here we report further photometry and time-series spectroscopy through three separate transits, which we use to confirm the existence of a gas gi ...
... transits have previously been reported in the lightcurve obtained by the SuperWASP survey of the A5 star HD15082 (WASP-33; V = 8.3, v sin i = 86 km s−1 ). Here we report further photometry and time-series spectroscopy through three separate transits, which we use to confirm the existence of a gas gi ...
arXiv:1505.07406v1 [hep-ph] 27 May 2015
... Undeniably, Einstein’s theory of general relativity (GR) has been an extremely successful theory for around a century [1]. However, the theory is expected to break down at some points at very high energies where quantum effects are expected to become crucial, such as in the past expansion of the Uni ...
... Undeniably, Einstein’s theory of general relativity (GR) has been an extremely successful theory for around a century [1]. However, the theory is expected to break down at some points at very high energies where quantum effects are expected to become crucial, such as in the past expansion of the Uni ...
astro-ph/9410035 PDF
... the rate is strongly suppressed, because of large phase space reduction due to degeneracy. The suppression is smaller if the momentum can be absorbed by bosons such as pions (Bahcall & Wolf 1965) or kaons (Brown et al. 1988). These and other variants of Urca reactions are reviewed by Pethick (1992). ...
... the rate is strongly suppressed, because of large phase space reduction due to degeneracy. The suppression is smaller if the momentum can be absorbed by bosons such as pions (Bahcall & Wolf 1965) or kaons (Brown et al. 1988). These and other variants of Urca reactions are reviewed by Pethick (1992). ...
Molecular gas in z~6 quasar host galaxies
... • FIR-CO luminosity relationship. • Star formation rate: 530 to 2380 Msun yr-1. • Gas depletion time scale: 107 yr, similar to that of the extreme starburst systems, such as the SMGs, ULIRGs, and much smaller that of the star forming galaxies found at z~1 and 2 (Daddi et al. 2010; Tacconi ...
... • FIR-CO luminosity relationship. • Star formation rate: 530 to 2380 Msun yr-1. • Gas depletion time scale: 107 yr, similar to that of the extreme starburst systems, such as the SMGs, ULIRGs, and much smaller that of the star forming galaxies found at z~1 and 2 (Daddi et al. 2010; Tacconi ...
General Module information
... Explain what is meant by a Hayashi track and sketch such a track on an HR diagram. Explain qualitatively how planetary systems might form. Explain what is meant by the zero age main sequence (ZAMS). Explain in words the evolution of a star on the main sequence and know approximately how the main seq ...
... Explain what is meant by a Hayashi track and sketch such a track on an HR diagram. Explain qualitatively how planetary systems might form. Explain what is meant by the zero age main sequence (ZAMS). Explain in words the evolution of a star on the main sequence and know approximately how the main seq ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.






![arXiv:1102.4757v1 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Feb 2011](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017735077_1-cb16692362fed9e2a0fe2690d128f0ce-300x300.png)





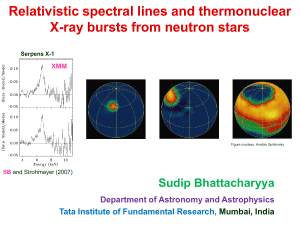

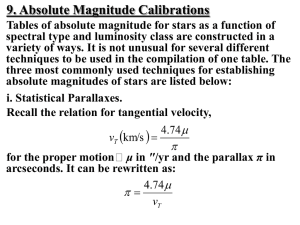
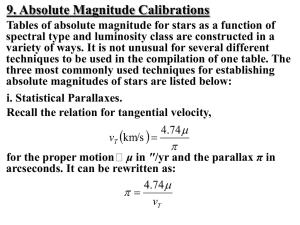


![arXiv:1505.07406v1 [hep-ph] 27 May 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007750137_1-1343a5635a0dda57ac4b2d01226e2ce5-300x300.png)




