in the milky way - Chandra X
... The Milky Way is home to generations of stars past. Many stars become small, dense white dwarfs after a bloated ‘red giant’ phase. Other, more massive stars explode as supernovas, enriching the Galaxy with heavy elements manufactured in their cores, and leaving behind either neutron stars or black h ...
... The Milky Way is home to generations of stars past. Many stars become small, dense white dwarfs after a bloated ‘red giant’ phase. Other, more massive stars explode as supernovas, enriching the Galaxy with heavy elements manufactured in their cores, and leaving behind either neutron stars or black h ...
silicon and oxygen abundances in planet-host stars
... no such differences in their sample for alpha- and iron-peak elements. They observe no difference in the overall trends of [X/Fe] between planet hosts and their volume-limited sample of stars without any known planetary-mass companions. Based on their results, stars with planets appear to be indisti ...
... no such differences in their sample for alpha- and iron-peak elements. They observe no difference in the overall trends of [X/Fe] between planet hosts and their volume-limited sample of stars without any known planetary-mass companions. Based on their results, stars with planets appear to be indisti ...
Red Supergiants as Cosmic Abundance Probes
... method requires measurements of auroral lines, such as [O III] 436.3 nm, which allows the observer to uniquely determine the gas temperature and, crucially, the abundance of the element. Unfortunately, these auroral lines are often very weak, especially at high metallicity. This means that one must ...
... method requires measurements of auroral lines, such as [O III] 436.3 nm, which allows the observer to uniquely determine the gas temperature and, crucially, the abundance of the element. Unfortunately, these auroral lines are often very weak, especially at high metallicity. This means that one must ...
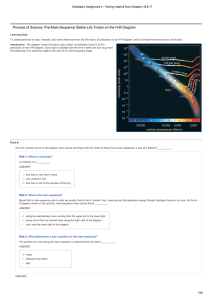
Process of Science: PreMainSequence Stellar Life Tracks on the HR
... 2. All the stars in the cluster formed from the same interstellar cloud and therefore began to form at about the same time. Astronomers can therefore use star clusters as laboratories for comparing the properties of stars at about the same distance or of about the same age. ANSWER: By observing and ...
... 2. All the stars in the cluster formed from the same interstellar cloud and therefore began to form at about the same time. Astronomers can therefore use star clusters as laboratories for comparing the properties of stars at about the same distance or of about the same age. ANSWER: By observing and ...
FIRST LIGHT IN THE UNIVERSE
... Myr with large dust opacity (sub-mm galaxy overlap) • Superwinds drive out both gas and dust, resulting in more quiescent star formation (10’s M yr-1) and smaller UV extinction • Quiescent star formation phase lasts for at least a few hundred Myr; by end at least a few 1010 M of stars have formed ...
... Myr with large dust opacity (sub-mm galaxy overlap) • Superwinds drive out both gas and dust, resulting in more quiescent star formation (10’s M yr-1) and smaller UV extinction • Quiescent star formation phase lasts for at least a few hundred Myr; by end at least a few 1010 M of stars have formed ...
Document
... Aristotle disbelieved the ancient Greek theory of atoms being of different sizes, regular geometric shapes and being in constant motion. He didn't think atoms could be in constant motion in an empty space. Aristotle’s theory was used for almost 2000 years, until after the scientific revolution, when ...
... Aristotle disbelieved the ancient Greek theory of atoms being of different sizes, regular geometric shapes and being in constant motion. He didn't think atoms could be in constant motion in an empty space. Aristotle’s theory was used for almost 2000 years, until after the scientific revolution, when ...
Stellar Temperatures
... Stellar Spectral Energy Distributions Stellar temperatures range from ~3000 K to ~100,000 K (although there are exceptions). To zeroth order, they can be considered blackbodies, with stellar absorption lines on top. There is a great variety of stellar absorption lines; the strength of any individua ...
... Stellar Spectral Energy Distributions Stellar temperatures range from ~3000 K to ~100,000 K (although there are exceptions). To zeroth order, they can be considered blackbodies, with stellar absorption lines on top. There is a great variety of stellar absorption lines; the strength of any individua ...
The Big Bang and Stellar Evolution
... They only allow about 2½ billion years for it to clump together into stars! Their dating problem has been caused by the discovery of supposedly faraway quasars (which we will discuss later), some of which are dated at 15 billion light-years, since they have a redshift of 400 percent. That would make ...
... They only allow about 2½ billion years for it to clump together into stars! Their dating problem has been caused by the discovery of supposedly faraway quasars (which we will discuss later), some of which are dated at 15 billion light-years, since they have a redshift of 400 percent. That would make ...
Introduc on to the Fundamental Astrophysics Course
... Introduc)on to the Fundamental Astrophysics Course -‐ 2013 ...
... Introduc)on to the Fundamental Astrophysics Course -‐ 2013 ...
Visions of the Universe
... Monday at 7:00 PM (see the schedule of homeworks on page 3). Late homeworks are not accepted. It is expected that you will have read the relevant sections of the text (see the schedule on the next page) before it is covered in class, and the homework is designed to focus your reading. You will need ...
... Monday at 7:00 PM (see the schedule of homeworks on page 3). Late homeworks are not accepted. It is expected that you will have read the relevant sections of the text (see the schedule on the next page) before it is covered in class, and the homework is designed to focus your reading. You will need ...
Answer Key 2
... What do the following words refer to? 1. Line 4, their the stars’. 2. Line 6, it the cloud of gas. 3. Line 18, this the enrichment of the space with heavy elements. 4. Line 23, these objects planetary nebulae 5. Line 38, that the side ...
... What do the following words refer to? 1. Line 4, their the stars’. 2. Line 6, it the cloud of gas. 3. Line 18, this the enrichment of the space with heavy elements. 4. Line 23, these objects planetary nebulae 5. Line 38, that the side ...
Pre-supernova evolution of massive stars
... We have seen that low- and intermediate-mass stars (with masses up to ≈ 8 M⊙ ) develop carbonoxygen cores that become degenerate after central He burning. As a consequence the maximum core temperature reached is smaller than required for carbon fusion. During the latest stages of evolution on the AG ...
... We have seen that low- and intermediate-mass stars (with masses up to ≈ 8 M⊙ ) develop carbonoxygen cores that become degenerate after central He burning. As a consequence the maximum core temperature reached is smaller than required for carbon fusion. During the latest stages of evolution on the AG ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... phase transition might occur in the dense interiors of neutron stars [1,2]. At temperatures T ~ 0 - 40 MeV, there are two possibilities for phase transitions (see the QGP diagram showing quantum chromodynamics (QCD) phases in Figure 1). As density increases, hadronic matter first converts into QGP, ...
... phase transition might occur in the dense interiors of neutron stars [1,2]. At temperatures T ~ 0 - 40 MeV, there are two possibilities for phase transitions (see the QGP diagram showing quantum chromodynamics (QCD) phases in Figure 1). As density increases, hadronic matter first converts into QGP, ...
Cosmology – The Origin and Evolution of the Universe
... “Standard Big Bang” Model… • Problem #1 - Age of the universe as measured by Hubble Law disagrees with the age of oldest globular clusters. If H=70 km/sec/Mpc in a critical density universe, implies the universe is only 9.3 Billion years old. But stellar structure astronomers calculate that globular ...
... “Standard Big Bang” Model… • Problem #1 - Age of the universe as measured by Hubble Law disagrees with the age of oldest globular clusters. If H=70 km/sec/Mpc in a critical density universe, implies the universe is only 9.3 Billion years old. But stellar structure astronomers calculate that globular ...
First Light: Physical Characterization of Early Star Formation in the
... the merging of clumps of gas and stars, accompanied by slower accretion of gas. In this picture, dwarf galaxies may represent protogalactic fragments that have not yet been accreted into larger galaxies. However, a recent VLT spectroscopic study of red giants in four dwarf spheroidal companions to t ...
... the merging of clumps of gas and stars, accompanied by slower accretion of gas. In this picture, dwarf galaxies may represent protogalactic fragments that have not yet been accreted into larger galaxies. However, a recent VLT spectroscopic study of red giants in four dwarf spheroidal companions to t ...
Gamma Ray Bursts
... collisions of two very dense objects, such as neutron stars in a binary. Also, some think, they could be from the same process as the long GRB but were not directly along the axis of the emission, i.e. not seeing it face on. ...
... collisions of two very dense objects, such as neutron stars in a binary. Also, some think, they could be from the same process as the long GRB but were not directly along the axis of the emission, i.e. not seeing it face on. ...
Tracing the evolution of NGC 6397 through the chemical
... many clusters (D’Antona & Caloi 2008). We are, however, far from building a fully consistent picture of the chemical evolution of globular clusters that can explain all the various observations simultaneously. A key unknown is the nature of the polluting objects. One possibility is that so-called ho ...
... many clusters (D’Antona & Caloi 2008). We are, however, far from building a fully consistent picture of the chemical evolution of globular clusters that can explain all the various observations simultaneously. A key unknown is the nature of the polluting objects. One possibility is that so-called ho ...
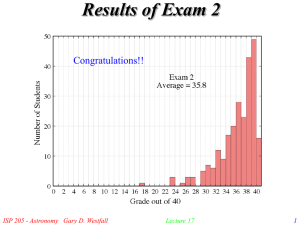
Lecture17
... Energy is generated through fusion in the core of the star which extends 1/4 of the way to the surface The core contains 1/3 of the mass of the star Temperatures reach 15 million K and the density is 150 times the density of water The energy is transported toward the surface by radiation until it re ...
... Energy is generated through fusion in the core of the star which extends 1/4 of the way to the surface The core contains 1/3 of the mass of the star Temperatures reach 15 million K and the density is 150 times the density of water The energy is transported toward the surface by radiation until it re ...
The chemical composition of IK Pegasi
... The chemical composition of IK Pegasi 689 show that the mean metal abundance does not differ significantly from that of the Sun. Any anomalies are therefore subtle and are likely to be detected only at high-resolution. There have been relatively few abundance studies of IK Peg A. Cowley & Aikman (19 ...
... The chemical composition of IK Pegasi 689 show that the mean metal abundance does not differ significantly from that of the Sun. Any anomalies are therefore subtle and are likely to be detected only at high-resolution. There have been relatively few abundance studies of IK Peg A. Cowley & Aikman (19 ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... transition from normal nuclear matter to a new state, the quarks condensate, the quark-gluon plasma, in which the quarks mingle with one another, rather than being segregated in triplets as they are in neutrons and protons. If in the nuclear physics the meaning of isotope is establishing one [7, 9, ...
... transition from normal nuclear matter to a new state, the quarks condensate, the quark-gluon plasma, in which the quarks mingle with one another, rather than being segregated in triplets as they are in neutrons and protons. If in the nuclear physics the meaning of isotope is establishing one [7, 9, ...
Test 2 - Physics@Brock
... (a) a high concentration of swimming pools, sports cars, and affected accents. (b) more than one million galaxies. (c) more than one thousand galaxies. (d) more than one hundred galaxies. 18. A common result of a galaxy collision is (a) the creation of several “child” galaxies. (b) the formation of ...
... (a) a high concentration of swimming pools, sports cars, and affected accents. (b) more than one million galaxies. (c) more than one thousand galaxies. (d) more than one hundred galaxies. 18. A common result of a galaxy collision is (a) the creation of several “child” galaxies. (b) the formation of ...
Numerical Evolu4on of Soliton Stars
... • They have ground states and excited states. The excited states although inherently unstable can cascade to a stable ground state configura.on losing mass via emission of scalar radia.on. • Excited states can be intermediate states during the forma.on of these stars. • They have gravita.o ...
... • They have ground states and excited states. The excited states although inherently unstable can cascade to a stable ground state configura.on losing mass via emission of scalar radia.on. • Excited states can be intermediate states during the forma.on of these stars. • They have gravita.o ...
All About Elements
... in the universe. Only Hydrogen is more abundant! These two elements were copiously formed during the creation of the universe. In the early stages of the universe, helium and hydrogen nuclei were actually formed. No atoms were formed until about 300,000 years after the Big Bang took place, when the ...
... in the universe. Only Hydrogen is more abundant! These two elements were copiously formed during the creation of the universe. In the early stages of the universe, helium and hydrogen nuclei were actually formed. No atoms were formed until about 300,000 years after the Big Bang took place, when the ...
Star Clusters and Stellar Dynamics
... Evaporation: two-body relaxation allows stars to exchange energy amongst themselves. If at some moment a star becomes unbound (kinetic + potential energy > 0) then it will escape the cluster entirely. Evaporation time tevap ~ 100 trelax , and although long, it limits the cluster lifetime. Evaporatio ...
... Evaporation: two-body relaxation allows stars to exchange energy amongst themselves. If at some moment a star becomes unbound (kinetic + potential energy > 0) then it will escape the cluster entirely. Evaporation time tevap ~ 100 trelax , and although long, it limits the cluster lifetime. Evaporatio ...
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons, primarily protons and neutrons. The first nuclei were formed about three minutes after the Big Bang, through the process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. It was then that hydrogen and helium formed to become the content of the first stars, and this primeval process is responsible for the present hydrogen/helium ratio of the cosmos.With the formation of stars, heavier nuclei were created from hydrogen and helium by stellar nucleosynthesis, a process that continues today. Some of these elements, particularly those lighter than iron, continue to be delivered to the interstellar medium when low mass stars eject their outer envelope before they collapse to form white dwarfs. The remains of their ejected mass form the planetary nebulae observable throughout our galaxy.Supernova nucleosynthesis within exploding stars by fusing carbon and oxygen is responsible for the abundances of elements between magnesium (atomic number 12) and nickel (atomic number 28). Supernova nucleosynthesis is also thought to be responsible for the creation of rarer elements heavier than iron and nickel, in the last few seconds of a type II supernova event. The synthesis of these heavier elements absorbs energy (endothermic) as they are created, from the energy produced during the supernova explosion. Some of those elements are created from the absorption of multiple neutrons (the R process) in the period of a few seconds during the explosion. The elements formed in supernovas include the heaviest elements known, such as the long-lived elements uranium and thorium.Cosmic ray spallation, caused when cosmic rays impact the interstellar medium and fragment larger atomic species, is a significant source of the lighter nuclei, particularly 3He, 9Be and 10,11B, that are not created by stellar nucleosynthesis.In addition to the fusion processes responsible for the growing abundances of elements in the universe, a few minor natural processes continue to produce very small numbers of new nuclides on Earth. These nuclides contribute little to their abundances, but may account for the presence of specific new nuclei. These nuclides are produced via radiogenesis (decay) of long-lived, heavy, primordial radionuclides such as uranium and thorium. Cosmic ray bombardment of elements on Earth also contribute to the presence of rare, short-lived atomic species called cosmogenic nuclides.