REVIEWS 18 years of science with the Hubble Space Telescope Julianne J. Dalcanton
... stellar clusters. The HST is yielding surprises even for more ordinary stars. For most of the past century, astronomers believed that the simplest collections of stars could be found in globular clusters, which are dense, gravitationally bound groups of ,104–106 stars. The stars in globular clusters ...
... stellar clusters. The HST is yielding surprises even for more ordinary stars. For most of the past century, astronomers believed that the simplest collections of stars could be found in globular clusters, which are dense, gravitationally bound groups of ,104–106 stars. The stars in globular clusters ...
The incidence of stellar mergers and mass gainers among massive
... have gained mass through accretion or coalescence, resulting in an increase in brightness. Stars that were initially not massive and luminous enough to be included in our brightness limited sample can become bright enough after mass accretion. In other words, the binary products in our sample come f ...
... have gained mass through accretion or coalescence, resulting in an increase in brightness. Stars that were initially not massive and luminous enough to be included in our brightness limited sample can become bright enough after mass accretion. In other words, the binary products in our sample come f ...
Inflation Basics
... If E<<1015 GeV (e.g., if inflation from PQSB), then polarization far too small to ever be detected. But, if E~1015-16 GeV (i.e., if inflation has something to do with GUTs), then polarization signal is conceivably detectable by Planck ...
... If E<<1015 GeV (e.g., if inflation from PQSB), then polarization far too small to ever be detected. But, if E~1015-16 GeV (i.e., if inflation has something to do with GUTs), then polarization signal is conceivably detectable by Planck ...
The impact of rotation on the line profiles of Wolf
... Context. Massive Wolf-Rayet stars are recognized today to be in a very common, but short, evolutionary phase of massive stars. While our understanding of Wolf-Rayet stars has increased dramatically over the past decades, it remains unclear whether rapid rotators are among them. There are various ind ...
... Context. Massive Wolf-Rayet stars are recognized today to be in a very common, but short, evolutionary phase of massive stars. While our understanding of Wolf-Rayet stars has increased dramatically over the past decades, it remains unclear whether rapid rotators are among them. There are various ind ...
Period Changes of Delta Scuti Stars and Stellar Evolution
... are found, stellar evolution leads to increasing periods in the vast majority of stars, with predicted increases of (1/P)dP/dt from 10−10 year−1 on the MS to 10−7 year−1 for the longer-period evolved variables. (More exact values will be computed in a later section of this paper.) Such period change ...
... are found, stellar evolution leads to increasing periods in the vast majority of stars, with predicted increases of (1/P)dP/dt from 10−10 year−1 on the MS to 10−7 year−1 for the longer-period evolved variables. (More exact values will be computed in a later section of this paper.) Such period change ...
Lithium abundances in nearby FGK dwarf and subgiant stars
... high resolution spectroscopic study of nearby stars from about 500 to 800 objects (Ramı́rez, Allende Prieto, & Lambert, in preparation, hereafter RAL). Their data are being used to study oxygen abundances in local stellar populations, but their spectra cover the 6708 Å region, which contains the li ...
... high resolution spectroscopic study of nearby stars from about 500 to 800 objects (Ramı́rez, Allende Prieto, & Lambert, in preparation, hereafter RAL). Their data are being used to study oxygen abundances in local stellar populations, but their spectra cover the 6708 Å region, which contains the li ...
What happened to discrete chaos, the Quenouille process, and the
... for p = λ/N , and notes that if the events occur in a given time interval or set, the probability corresponding to a three-fold increase in the time interval or set will be of the same form, but with a λ which is three times larger. Given that on average over several years there are 6.9 comet sighti ...
... for p = λ/N , and notes that if the events occur in a given time interval or set, the probability corresponding to a three-fold increase in the time interval or set will be of the same form, but with a λ which is three times larger. Given that on average over several years there are 6.9 comet sighti ...
Supervisors
... Introduction Stellar spectra provide most of the information that is known about the stars, such as their chemical composition, rotation, magnetic fields etc. The light that makes up the spectrum of a star is radiated by its outer layers that are called a stellar atmosphere. Understanding stellar a ...
... Introduction Stellar spectra provide most of the information that is known about the stars, such as their chemical composition, rotation, magnetic fields etc. The light that makes up the spectrum of a star is radiated by its outer layers that are called a stellar atmosphere. Understanding stellar a ...
pptx - Serbian Virtual Observatory
... •It is a part of the atomic and molecular databases of the Paris Observatory •Link (and mirror site in progress) to SerVO - Serbian Virtual Observatory http://servo.aob.rs/~darko/ •It is a part of VAMDC- Virtual Atomic and Molecular Data Centre •it follows the standards of VAMDC and Virtual Observat ...
... •It is a part of the atomic and molecular databases of the Paris Observatory •Link (and mirror site in progress) to SerVO - Serbian Virtual Observatory http://servo.aob.rs/~darko/ •It is a part of VAMDC- Virtual Atomic and Molecular Data Centre •it follows the standards of VAMDC and Virtual Observat ...
Slides - Indico
... Presently, LUNA is the world’s only underground accelerator at LNGS, Italy, with a maximal energy of Ebeam=400 keV Many accelerators have been proposed in the world, operating up to several MeV, i.e. well suited to study BBN reactions. ...
... Presently, LUNA is the world’s only underground accelerator at LNGS, Italy, with a maximal energy of Ebeam=400 keV Many accelerators have been proposed in the world, operating up to several MeV, i.e. well suited to study BBN reactions. ...
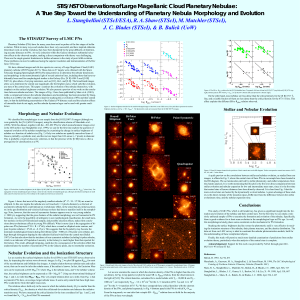
STIS/HST Observations of Large Magellanic Cloud Planetary
... (< 2000 yr), suggesting that the gross features of the nebular morphology are well connected to PN formation. As well, the possibility of ambiguity in our morphological classification, the small number statistics in this ([O III]-selected) sample, and possible selection effects, makes firm conclusio ...
... (< 2000 yr), suggesting that the gross features of the nebular morphology are well connected to PN formation. As well, the possibility of ambiguity in our morphological classification, the small number statistics in this ([O III]-selected) sample, and possible selection effects, makes firm conclusio ...
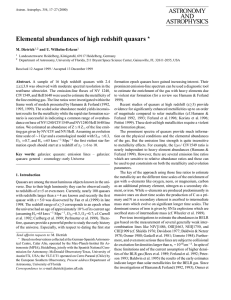
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Elemental abundances of
... to metallicity effects. For example, the Lyα/ CIV1549 ratio is nearly independent to heavy element abundances (Hamann & Ferland 1999). However, there are several emission line ratios which are sensitive to relative abundance ratios and these can be used to put constraints on both the metallicity and ...
... to metallicity effects. For example, the Lyα/ CIV1549 ratio is nearly independent to heavy element abundances (Hamann & Ferland 1999). However, there are several emission line ratios which are sensitive to relative abundance ratios and these can be used to put constraints on both the metallicity and ...
Pulsars as Astrophysical Laboratories for Nuclear and Particle Physics
... potential energy of the matter accreted from a low-mass companion is the energy source, and (3) magnetars (e.g, SGR 1806-20), where the decay of a ultra-strong magnetic field powers the radiation. The fastest, very recently discovered neutron star, PSR J1748-2446ad, rotates at a period of 1.39 ms (w ...
... potential energy of the matter accreted from a low-mass companion is the energy source, and (3) magnetars (e.g, SGR 1806-20), where the decay of a ultra-strong magnetic field powers the radiation. The fastest, very recently discovered neutron star, PSR J1748-2446ad, rotates at a period of 1.39 ms (w ...
The eccentricities of the barium stars
... The actual distribution of eccentricities is quite sensitive to the strength of the tides, so that we are able to confirm that this strength is close to, but less than, what is expected theoretically and found with alternative observational tests. Two systems ± one very shortperiod but eccentric, an ...
... The actual distribution of eccentricities is quite sensitive to the strength of the tides, so that we are able to confirm that this strength is close to, but less than, what is expected theoretically and found with alternative observational tests. Two systems ± one very shortperiod but eccentric, an ...
ECOS Report
... was recently synthesized at RIKEN. Secondly, reactions between lighter ions and radioactive actinide targets have been employed. These combinations, especially with 48Ca beams, have been used to produce more neutron rich isotopes of elements from Z=112 to 116 and 118 at FLNR. The figure below summar ...
... was recently synthesized at RIKEN. Secondly, reactions between lighter ions and radioactive actinide targets have been employed. These combinations, especially with 48Ca beams, have been used to produce more neutron rich isotopes of elements from Z=112 to 116 and 118 at FLNR. The figure below summar ...
Rapid Rotation of Low-Mass Red Giants Using APOKASC: A
... placing a lower limit on the rate of stellar interactions during giant branch evolution offers an avenue to investigate this problem. One way of identifying stars that have interacted or merged with a companion is measuring their rotation rates. A stellar interaction or merger can produce a star wit ...
... placing a lower limit on the rate of stellar interactions during giant branch evolution offers an avenue to investigate this problem. One way of identifying stars that have interacted or merged with a companion is measuring their rotation rates. A stellar interaction or merger can produce a star wit ...
Theory of cooling neutron stars versus observations
... Let us summarize the main neutrino emission mechanisms in the neutron star core. They are strongly affected by baryon superfluidity. More details can be found, e.g., in Refs. [18, 19, 20]. Neutrino emission in nonsuperfluid cores. The major neutrino mechanisms in nucleon matter of the outer core (ρ ...
... Let us summarize the main neutrino emission mechanisms in the neutron star core. They are strongly affected by baryon superfluidity. More details can be found, e.g., in Refs. [18, 19, 20]. Neutrino emission in nonsuperfluid cores. The major neutrino mechanisms in nucleon matter of the outer core (ρ ...
IR-excesses around nearby Lambda Boo stars are caused by debris
... abundance pattern on the surface (Paunzen 2004). This has yet to be a well developed theory, but it is a unique characteristic of these stars which is rooted in observations and therefore should not be ignored (e.g. see Moya et al. 2010) As for external mechanisms, spectroscopic binaries, debris dis ...
... abundance pattern on the surface (Paunzen 2004). This has yet to be a well developed theory, but it is a unique characteristic of these stars which is rooted in observations and therefore should not be ignored (e.g. see Moya et al. 2010) As for external mechanisms, spectroscopic binaries, debris dis ...
Imaging and spectroscopy of ejected common envelopes
... to derive essentially model-independent masses and radii (with errors generally <10 per cent) for their components. Assuming that the primary components can be considered to be true post-asymptotic giant branch stars and not a product of close binary evolution, these results allow meaningful compari ...
... to derive essentially model-independent masses and radii (with errors generally <10 per cent) for their components. Assuming that the primary components can be considered to be true post-asymptotic giant branch stars and not a product of close binary evolution, these results allow meaningful compari ...
Planets and Debris Disks: Results from a Spitzer/MIPS Search for IR
... Rather than infer the presence of large planets, we consider here systems whose planets are well established by radial-velocity measurements of the central star (e.g. Butler et al. 2006). For such systems, it is not clear what relationship to expect between planets and debris, since the dust respons ...
... Rather than infer the presence of large planets, we consider here systems whose planets are well established by radial-velocity measurements of the central star (e.g. Butler et al. 2006). For such systems, it is not clear what relationship to expect between planets and debris, since the dust respons ...
LATE STAGES OF CLOSE BINARY SYSTEMS 1. Introduction The X
... are expected to finish their life with a supernova explosion, leaving behind a neutron star or a black hole. A helium star of 3 Af is the core of a hydrogen-rich star of about MM®. Consequently, the lower mass limit for finishing with a supernova explosion, for primaries of mass-exchange binaries, i ...
... are expected to finish their life with a supernova explosion, leaving behind a neutron star or a black hole. A helium star of 3 Af is the core of a hydrogen-rich star of about MM®. Consequently, the lower mass limit for finishing with a supernova explosion, for primaries of mass-exchange binaries, i ...
View - ESA
... requiring further major development. The first part of this report addresses the preliminary phase in which information about the Solar Neighborhood has been collected. This part has been particularly time consuming since the data sources are many and generally incomplete in several respects, making ...
... requiring further major development. The first part of this report addresses the preliminary phase in which information about the Solar Neighborhood has been collected. This part has been particularly time consuming since the data sources are many and generally incomplete in several respects, making ...
The effect of helium sedimentation on galaxy cluster masses and
... Context. Recent theoretical studies predict that the inner regions of galaxy clusters may have an enhanced helium abundance due to sedimentation over the cluster lifetime. If sedimentation is not suppressed (e.g., by tangled magnetic fields), this may significantly affect the cluster mass estimates. ...
... Context. Recent theoretical studies predict that the inner regions of galaxy clusters may have an enhanced helium abundance due to sedimentation over the cluster lifetime. If sedimentation is not suppressed (e.g., by tangled magnetic fields), this may significantly affect the cluster mass estimates. ...
The binary fraction of the young cluster NGC 1818 in the Large
... too crowded and their distances too great, so that their member stars are too faint to be examined individually for binarity. Fortunately, there is an alternative approach, i.e., by means of an artificial-star-test technique, which allows us to estimate the binary fractions in crowded environments. ...
... too crowded and their distances too great, so that their member stars are too faint to be examined individually for binarity. Fortunately, there is an alternative approach, i.e., by means of an artificial-star-test technique, which allows us to estimate the binary fractions in crowded environments. ...
ppt - Serbian Virtual Observatory
... - a very quick increase of the brightness and a decline from maximum to minimum for some minutes up to some hours; - a common characteristic in the early evolution of all red dwarf stars. Belonging: - to the population of young stellar clusters and associations. Flare-like activity: some Wolf-Rayet ...
... - a very quick increase of the brightness and a decline from maximum to minimum for some minutes up to some hours; - a common characteristic in the early evolution of all red dwarf stars. Belonging: - to the population of young stellar clusters and associations. Flare-like activity: some Wolf-Rayet ...
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons, primarily protons and neutrons. The first nuclei were formed about three minutes after the Big Bang, through the process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. It was then that hydrogen and helium formed to become the content of the first stars, and this primeval process is responsible for the present hydrogen/helium ratio of the cosmos.With the formation of stars, heavier nuclei were created from hydrogen and helium by stellar nucleosynthesis, a process that continues today. Some of these elements, particularly those lighter than iron, continue to be delivered to the interstellar medium when low mass stars eject their outer envelope before they collapse to form white dwarfs. The remains of their ejected mass form the planetary nebulae observable throughout our galaxy.Supernova nucleosynthesis within exploding stars by fusing carbon and oxygen is responsible for the abundances of elements between magnesium (atomic number 12) and nickel (atomic number 28). Supernova nucleosynthesis is also thought to be responsible for the creation of rarer elements heavier than iron and nickel, in the last few seconds of a type II supernova event. The synthesis of these heavier elements absorbs energy (endothermic) as they are created, from the energy produced during the supernova explosion. Some of those elements are created from the absorption of multiple neutrons (the R process) in the period of a few seconds during the explosion. The elements formed in supernovas include the heaviest elements known, such as the long-lived elements uranium and thorium.Cosmic ray spallation, caused when cosmic rays impact the interstellar medium and fragment larger atomic species, is a significant source of the lighter nuclei, particularly 3He, 9Be and 10,11B, that are not created by stellar nucleosynthesis.In addition to the fusion processes responsible for the growing abundances of elements in the universe, a few minor natural processes continue to produce very small numbers of new nuclides on Earth. These nuclides contribute little to their abundances, but may account for the presence of specific new nuclei. These nuclides are produced via radiogenesis (decay) of long-lived, heavy, primordial radionuclides such as uranium and thorium. Cosmic ray bombardment of elements on Earth also contribute to the presence of rare, short-lived atomic species called cosmogenic nuclides.