Tungsten - Government of New Brunswick
... main tungsten-bearing mineral accompanied by variable proportions of molybdenite, scheelite, cassiterite, bismuthinite, base-metal sulphides, beryl, topaz, and fluorite. The quartz veins are steeply dipping, mostly southeast-trending, and range in width from a few centimetres to several metres. Mine ...
... main tungsten-bearing mineral accompanied by variable proportions of molybdenite, scheelite, cassiterite, bismuthinite, base-metal sulphides, beryl, topaz, and fluorite. The quartz veins are steeply dipping, mostly southeast-trending, and range in width from a few centimetres to several metres. Mine ...
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1. Purpose of the investigation
... Kaapvaal and the older parts of the Namaqua Province at approximately 1600 Ma (Theart, 1985) (Fig. 2.1). The oceanic basin was affected by calc-alkaline and tholeiite volcanism until 1285 ± 14 Ma (Cornell et al., 1990a) in the area now preserved in the east-central Namaqua-Natal Province. These extr ...
... Kaapvaal and the older parts of the Namaqua Province at approximately 1600 Ma (Theart, 1985) (Fig. 2.1). The oceanic basin was affected by calc-alkaline and tholeiite volcanism until 1285 ± 14 Ma (Cornell et al., 1990a) in the area now preserved in the east-central Namaqua-Natal Province. These extr ...
Contact metamorphism and hydrothermal alterations around
... Presence of sanidine and wollastonite (±diopside) can suggest that sanidinite facies conditions were developed temporarily within sedimentary rocks in the immediate vicinity of the intrusion. Moreover sanidine can be found also in marginal zones of the andesite intrusion. The presence of sanidine ca ...
... Presence of sanidine and wollastonite (±diopside) can suggest that sanidinite facies conditions were developed temporarily within sedimentary rocks in the immediate vicinity of the intrusion. Moreover sanidine can be found also in marginal zones of the andesite intrusion. The presence of sanidine ca ...
volcanic and metallogenic evolution of the momchilgrad depression
... The volcanic activity in the Momchilgrad depression took place in shallow marine basin as the volcanic cones are islands. Coral reefs often grew up around them as well as along the periphery of the basin. The tuffs of the Beli Plast rhyodacite and Perperek trachyrhyolite complexes deposited chiefly ...
... The volcanic activity in the Momchilgrad depression took place in shallow marine basin as the volcanic cones are islands. Coral reefs often grew up around them as well as along the periphery of the basin. The tuffs of the Beli Plast rhyodacite and Perperek trachyrhyolite complexes deposited chiefly ...
Earth Sciences 089G: Short Written Assignment
... Realize low concentration of metals in the Earth’s crust compared to silicon and oxygen (Aluminum most common metal—relatively light). Many metals of significant use to society occur in only trace quantities in the Earth’s crust. Metals are not uniformly distributed throughout crust, but are concent ...
... Realize low concentration of metals in the Earth’s crust compared to silicon and oxygen (Aluminum most common metal—relatively light). Many metals of significant use to society occur in only trace quantities in the Earth’s crust. Metals are not uniformly distributed throughout crust, but are concent ...
Sillitoe Hedenquist Linkages between volcanotectonic settings Soc
... Most low-sulfidation deposits, including nearly 60 percent of the world’s bonanza veins, are associated with bimodal (basalt-rhyolite) volcanic suites in a broad spectrum of extensional tectonic settings, including intra-, near-, and back-arc, as well as postcollisional rifts. Some low-sulfidation d ...
... Most low-sulfidation deposits, including nearly 60 percent of the world’s bonanza veins, are associated with bimodal (basalt-rhyolite) volcanic suites in a broad spectrum of extensional tectonic settings, including intra-, near-, and back-arc, as well as postcollisional rifts. Some low-sulfidation d ...
Minerals and Rocks Notes
... Mineral identification refers to the way to tell one mineral from another. The _______________ is the most obvious but one of the least reliable methods for identifying a mineral. ___________________ is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. The _____________ hardness scale lists hardne ...
... Mineral identification refers to the way to tell one mineral from another. The _______________ is the most obvious but one of the least reliable methods for identifying a mineral. ___________________ is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. The _____________ hardness scale lists hardne ...
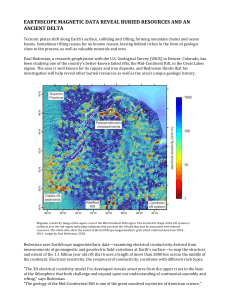
earthscope magnetic data reveal buried resources and an ancient
... Tectonic plates shift along Earth’s surface, colliding and rifting, forming mountain chains and ocean basins. Sometimes rifting ceases for no known reason, leaving behind riches in the form of geologic clues ...
... Tectonic plates shift along Earth’s surface, colliding and rifting, forming mountain chains and ocean basins. Sometimes rifting ceases for no known reason, leaving behind riches in the form of geologic clues ...
Rock Identification Lab
... Background: Metamorphic Rocks are rocks that have been changed by the action of heat, pressure and fluids. These forces can either cause minerals in the original rock (called the host rock) to rearrange and form new minerals, or will cause a distortion of existing minerals. All types of rocks---igne ...
... Background: Metamorphic Rocks are rocks that have been changed by the action of heat, pressure and fluids. These forces can either cause minerals in the original rock (called the host rock) to rearrange and form new minerals, or will cause a distortion of existing minerals. All types of rocks---igne ...
Rocks, Part II: the rock "cycle"
... Geology is that of the rock cycle. In its simplest presentation, the rock cycle is the erosion of matter in igneous rocks to yield sedimentary rocks, the metamorphism of sedimentary rocks to give metamorphic rocks, and the melting of metamorphic rocks to give the magmas that form igneous rocks. That ...
... Geology is that of the rock cycle. In its simplest presentation, the rock cycle is the erosion of matter in igneous rocks to yield sedimentary rocks, the metamorphism of sedimentary rocks to give metamorphic rocks, and the melting of metamorphic rocks to give the magmas that form igneous rocks. That ...
Sydney
... *I am the mineral form of iron. *My colors range from gray-metallic, black, and reddish-brown. ...
... *I am the mineral form of iron. *My colors range from gray-metallic, black, and reddish-brown. ...
Document
... The Rock CycleMinerals form rocks All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are divided into 3 categories Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are heated and squeezed Sedimentary- non-crystalline- smaller pieces or chemicals from other ro ...
... The Rock CycleMinerals form rocks All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are divided into 3 categories Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are heated and squeezed Sedimentary- non-crystalline- smaller pieces or chemicals from other ro ...
THE CQPPER DEPOSITS N,EAH SALMON, `IDAHO:
... many the quartz is in a mosaic of interlocking grains with the original texture obscured. In the thin sections examined the quartz grains range from 0.08 to 0. 78 millimeters in maximum dimension. The other constituents are nearly all micaceous minerals--sericite, muscovite, chlorite, and dark-green ...
... many the quartz is in a mosaic of interlocking grains with the original texture obscured. In the thin sections examined the quartz grains range from 0.08 to 0. 78 millimeters in maximum dimension. The other constituents are nearly all micaceous minerals--sericite, muscovite, chlorite, and dark-green ...
Rocks in - Earth Science
... Sedimentary Rocks form when sediments are transported to large bodies of water and are … Deposited in horizontal layers called beds or strata Buried Compacted – particles forced extremely close together because of the pressure of the overlying layers and water Cemented – glued together ...
... Sedimentary Rocks form when sediments are transported to large bodies of water and are … Deposited in horizontal layers called beds or strata Buried Compacted – particles forced extremely close together because of the pressure of the overlying layers and water Cemented – glued together ...
Lab 2
... sand, silt, and clay. Properties of parent materials within the same landform vary if changes in texture occur. For example, a single floodplain may contain pockets of sands and clays at different locations These differences produce changes in soil water holding capacity and fertility. Two different ...
... sand, silt, and clay. Properties of parent materials within the same landform vary if changes in texture occur. For example, a single floodplain may contain pockets of sands and clays at different locations These differences produce changes in soil water holding capacity and fertility. Two different ...
Mineral potential of Malawi
... gradient through permeable arkosic sandstones. The uranium, along with other dissolved metals such as molybdenum, vanadium, selenium and arsenic, precipitates out when the groundwaters encounter the oxidation/reduction interface often forming a crescent-shaped ore body. Uranium, being more mobile un ...
... gradient through permeable arkosic sandstones. The uranium, along with other dissolved metals such as molybdenum, vanadium, selenium and arsenic, precipitates out when the groundwaters encounter the oxidation/reduction interface often forming a crescent-shaped ore body. Uranium, being more mobile un ...
Some Common Sedimentary Rocks
... Fascinating Fact: Digging at a rate of one foot per minute, it would take you 87 years to tunnel all the way through Earth. ...
... Fascinating Fact: Digging at a rate of one foot per minute, it would take you 87 years to tunnel all the way through Earth. ...
Percolating Through Volcanic Subsurface Rocks, Seawater is
... the upper layer of the oceanic crust, which is concalcium concentration of the fluid. At temperatures structed of highly porous and permeable volcanic greater than 250°C, the remaining sulfate in the rocks that are broken apart in many places by coolfluid reacts with iron in the crust to form metal ...
... the upper layer of the oceanic crust, which is concalcium concentration of the fluid. At temperatures structed of highly porous and permeable volcanic greater than 250°C, the remaining sulfate in the rocks that are broken apart in many places by coolfluid reacts with iron in the crust to form metal ...
Geology, Mineral Deposits, and Geochemical and Radiometric
... mercury, arsenic, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, nickel, lead, antimony, tin, tungsten, and zinc occur in panned stream concentrates and in altered bedrock that is associated with steep faults, thrust faults, and quartz veins. Two mineralized and altered fault zones were sampled in detail; one contains ...
... mercury, arsenic, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, nickel, lead, antimony, tin, tungsten, and zinc occur in panned stream concentrates and in altered bedrock that is associated with steep faults, thrust faults, and quartz veins. Two mineralized and altered fault zones were sampled in detail; one contains ...
Basic Geology
... mineral alteration occurs when the minerals in igneous rocks are transformed chemically into new minerals that are more stable at or near the Earth’s surface processes of mineral alteration include oxidation, hydrolysis, and solution in the process of mineral alteration, solid rock is weakened, soft ...
... mineral alteration occurs when the minerals in igneous rocks are transformed chemically into new minerals that are more stable at or near the Earth’s surface processes of mineral alteration include oxidation, hydrolysis, and solution in the process of mineral alteration, solid rock is weakened, soft ...
the White-Inyo field-trip guidebook
... rocks yielded a concordant U/Pb crystallization age of about 154 Ma, and an analyzed hypabyssal porphyritic stock exposed at the summit of White Mountain Peak gave an even younger, but highly discordant age of 137 Ma (Hanson et al., 1987). The times of formation of the metavolcanic and volcanogenic ...
... rocks yielded a concordant U/Pb crystallization age of about 154 Ma, and an analyzed hypabyssal porphyritic stock exposed at the summit of White Mountain Peak gave an even younger, but highly discordant age of 137 Ma (Hanson et al., 1987). The times of formation of the metavolcanic and volcanogenic ...
Geology of Caves and Rockshelters
... opened, the cave may fill rapidly with sediment that resembles colluvium, containing large and small clasts mixed with finer material. As for rockshelters, sediments near the openings or mouths of caves are susceptible to the climatic conditions that prevail, so soils can form in the cave deposits n ...
... opened, the cave may fill rapidly with sediment that resembles colluvium, containing large and small clasts mixed with finer material. As for rockshelters, sediments near the openings or mouths of caves are susceptible to the climatic conditions that prevail, so soils can form in the cave deposits n ...
Ore genesis

The various theories of ore genesis explain how the various types of mineral deposits form within the Earth's crust. Ore genesis theories are dependent on the mineral or commodity.Ore genesis theories generally involve three components: source, transport or conduit, and trap. This also applies to the petroleum industry, which was first to use this methodology. Source is required because metal must come from somewhere, and be liberated by some process Transport is required first to move the metal-bearing fluids or solid minerals into the right position, and refers to the act of physically moving the metal, as well as chemical or physical phenomenon which encourage movement Trapping is required to concentrate the metal via some physical, chemical or geological mechanism into a concentration which forms mineable oreThe biggest deposits are formed when the source is large, the transport mechanism is efficient, and the trap is active and ready at the right time.