Programming Languages (PL)
... For both a primitive and a compound type, informally describe the values that have that type. [Familiarity] For a language with a static type system, describe the operations that are forbidden statically, such as passing the wrong type of value to a function or method. [Familiarity] Describe example ...
... For both a primitive and a compound type, informally describe the values that have that type. [Familiarity] For a language with a static type system, describe the operations that are forbidden statically, such as passing the wrong type of value to a function or method. [Familiarity] Describe example ...
Introduction - Portal UniMAP
... More than 80% of the software budget went to maintenance (only the remaining 20% for new software development). ...
... More than 80% of the software budget went to maintenance (only the remaining 20% for new software development). ...
Lecture slides
... – The compiler should tell you about typing errors in advance (not at runtime!) – The language structure should make it difficult to write programs that might crash (no unsafe casts!) – 80% of your time should be spent getting the program to compile, and only 20% on debugging – should be tractable t ...
... – The compiler should tell you about typing errors in advance (not at runtime!) – The language structure should make it difficult to write programs that might crash (no unsafe casts!) – 80% of your time should be spent getting the program to compile, and only 20% on debugging – should be tractable t ...
The Fun of Programming - Department of Computer Science, Oxford
... Functional programming has come of age: it is now a standard course in any computer science curriculum. Ideas that were first developed in the laboratory environment of functional programming have proved their values in wider settings, such as generic Java and XML. The time is ripe, therefore, to te ...
... Functional programming has come of age: it is now a standard course in any computer science curriculum. Ideas that were first developed in the laboratory environment of functional programming have proved their values in wider settings, such as generic Java and XML. The time is ripe, therefore, to te ...
Programming Languages
... Lexical analysis Also known as scanning Divides the string of input characters into single elements, tokens, based on strict computer punctuation ...
... Lexical analysis Also known as scanning Divides the string of input characters into single elements, tokens, based on strict computer punctuation ...
Thursday
... • May mean add the contents of two registers and put the result in a third register in the MIPS processor, while it may no be a part of the instruction set for the Intel processor ...
... • May mean add the contents of two registers and put the result in a third register in the MIPS processor, while it may no be a part of the instruction set for the Intel processor ...
Lecture Slides
... – The compiler should tell you about typing errors in advance (not at runtime!) – The language structure should make it difficult to write programs that might crash (no unsafe casts!) – 80% of your time should be spent getting the program to compile, and only 20% on debugging – should be tractable t ...
... – The compiler should tell you about typing errors in advance (not at runtime!) – The language structure should make it difficult to write programs that might crash (no unsafe casts!) – 80% of your time should be spent getting the program to compile, and only 20% on debugging – should be tractable t ...
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot
... Construct a world object using a constructor method Create an object using a constructor Define the purpose and syntax of a variable Recognize the syntax to define and test variables Write programming statements to end a game ...
... Construct a world object using a constructor method Create an object using a constructor Define the purpose and syntax of a variable Recognize the syntax to define and test variables Write programming statements to end a game ...
國立聯合大學電子工程學系蕭裕弘
... one computer language (called the source language) into a program written in another computer language (called the output or the target language). ...
... one computer language (called the source language) into a program written in another computer language (called the output or the target language). ...
Functional and Imperative Programming
... said how this should be done: the statement is with a single output can’t work. So pure functional languages do not allow side-effects. purely declarative. You’d be forgiven for feeling a little confused i.e. they only use proper functions. with regards ML—there you wrote out a series of things to d ...
... said how this should be done: the statement is with a single output can’t work. So pure functional languages do not allow side-effects. purely declarative. You’d be forgiven for feeling a little confused i.e. they only use proper functions. with regards ML—there you wrote out a series of things to d ...
paradigm
... – In Functional Programming Languages: Scheme (define (fact n) (if (< n 1) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))) ...
... – In Functional Programming Languages: Scheme (define (fact n) (if (< n 1) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))) ...
Overview of programming languages
... – In Functional Programming Languages: Scheme (define (fact n) (if (< n 1) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))) ...
... – In Functional Programming Languages: Scheme (define (fact n) (if (< n 1) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))) ...
COMP 1001 : Introduction to Programming
... •To try things on your computer and learn from mistakes ...
... •To try things on your computer and learn from mistakes ...
12.5 Examples of Programming Languages
... The developement of sh, aka Bourne Shell, is no different from other shell scripting languages. Created in 1971 by Steve Bourne, the shell has been included on all Unix and Linux systems, and more-or-less complete versions are available for many other systems. Eventually, this would become part the ...
... The developement of sh, aka Bourne Shell, is no different from other shell scripting languages. Created in 1971 by Steve Bourne, the shell has been included on all Unix and Linux systems, and more-or-less complete versions are available for many other systems. Eventually, this would become part the ...
Introduction to Programming Systems Goals CS 217
... • Systems programming language – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
... • Systems programming language – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
additional notes - School of Computing Science
... Pairs The natural concept is a pair of values, both of which will be used exactly once. The type of linear pairs is traditionally written T U (pronounced “tensor”). If we have e : T U then both components must be used. This makes it tricky to work with fst and snd because they discard the other ...
... Pairs The natural concept is a pair of values, both of which will be used exactly once. The type of linear pairs is traditionally written T U (pronounced “tensor”). If we have e : T U then both components must be used. This makes it tricky to work with fst and snd because they discard the other ...
ppt
... Computers can only do very simple things (like adding two numbers), but they can do millions or billions of simple things a second. ...
... Computers can only do very simple things (like adding two numbers), but they can do millions or billions of simple things a second. ...
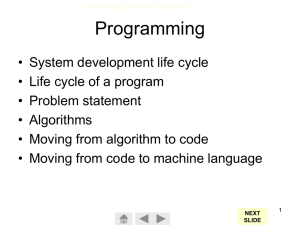
Programming
... – Developed for system programmers – Combines high and low level programming features – Modern operating systems were written in C ...
... – Developed for system programmers – Combines high and low level programming features – Modern operating systems were written in C ...
CS 331, Principles of Programming Languages
... – more ability to perform diagnostics (or changes) at run-time – examples: Basic, UNIX shells, Lisp Slides borrowed from Instructor: Wajih Alouini ...
... – more ability to perform diagnostics (or changes) at run-time – examples: Basic, UNIX shells, Lisp Slides borrowed from Instructor: Wajih Alouini ...
Programming language

A programming language is a formal constructed language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs to control the behavior of a machine or to express algorithms.The earliest programming languages preceded the invention of the digital computer and were used to direct the behavior of machines such as Jacquard looms and player pianos. Thousands of different programming languages have been created, mainly in the computer field, and many more still are being created every year. Many programming languages require computation to be specified in an imperative form (i.e., as a sequence of operations to perform), while other languages use other forms of program specification such as the declarative form (i.e. the desired result is specified, not how to achieve it).The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning). Some languages are defined by a specification document (for example, the C programming language is specified by an ISO Standard), while other languages (such as Perl) have a dominant implementation that is treated as a reference.