Lambda Calculus
... Alpha renaming is used to prevent capturing free occurrences of variables when reducing a lambda calculus expression, e.g., (λx.λy.(x y) (y w)) ⇒λy.((y w) y) This reduction erroneously captures the free occurrence of y. A correct reduction first renames y to z, (or any other fresh variable) e.g., (λ ...
... Alpha renaming is used to prevent capturing free occurrences of variables when reducing a lambda calculus expression, e.g., (λx.λy.(x y) (y w)) ⇒λy.((y w) y) This reduction erroneously captures the free occurrence of y. A correct reduction first renames y to z, (or any other fresh variable) e.g., (λ ...
LambdaCalculus
... f(x) = x2 , g(x) = x+1 f g is the composition of f and g: f g (x) = f(g(x)) f g (x) = f(g(x)) = f(x+1) = (x+1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1 g f (x) = g(f(x)) = g(x2) = x2 + 1 Function composition is therefore not commutative. Function composition can be regarded as a (higher-order) function with the ...
... f(x) = x2 , g(x) = x+1 f g is the composition of f and g: f g (x) = f(g(x)) f g (x) = f(g(x)) = f(x+1) = (x+1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1 g f (x) = g(f(x)) = g(x2) = x2 + 1 Function composition is therefore not commutative. Function composition can be regarded as a (higher-order) function with the ...
PowerPoint
... • ML is a static-scoped and strongly typed functional language which includes type inference, exception handling, and a variety of data structures and abstract data types • Haskell is a lazy functional language supporting infinite lists and set comprehension. • Purely functional languages have advan ...
... • ML is a static-scoped and strongly typed functional language which includes type inference, exception handling, and a variety of data structures and abstract data types • Haskell is a lazy functional language supporting infinite lists and set comprehension. • Purely functional languages have advan ...
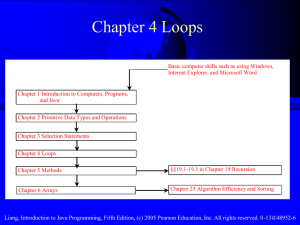
Elements of Programming Languages Overview Advanced
... Modern languages extend this model in several ways We can define a structure (class/object/trait) inside another: As a member of the enclosing class (tied to a specific instance) or as a static member (shared across all instances) As a local definition inside a method As an anonymous local definitio ...
... Modern languages extend this model in several ways We can define a structure (class/object/trait) inside another: As a member of the enclosing class (tied to a specific instance) or as a static member (shared across all instances) As a local definition inside a method As an anonymous local definitio ...
A Functional Approach to the Observer Pattern
... The values must be updated automatically any time some other depending value is changed. ...
... The values must be updated automatically any time some other depending value is changed. ...
1 Salient Features of Functional Programming
... type: It means an arbitrary unknown type. – Haskell has parametric polymorphism. ∗ A kind of polymorphism which goes well with type inference. ∗ The same idea is called generics in e.g. Ada, C++ and Java 5, but they do not infer generic types automagically. – 6= the Object Oriented polymorphism whic ...
... type: It means an arbitrary unknown type. – Haskell has parametric polymorphism. ∗ A kind of polymorphism which goes well with type inference. ∗ The same idea is called generics in e.g. Ada, C++ and Java 5, but they do not infer generic types automagically. – 6= the Object Oriented polymorphism whic ...
Functional programming languages - Part I - Gallium
... β-reductions in the λ-calculus can occur anywhere and in any order. This can affect termination and algorithmic efficiency of programs. A fixed reduction strategy enables the programmer to reason about termination and algorithmic complexity. ...
... β-reductions in the λ-calculus can occur anywhere and in any order. This can affect termination and algorithmic efficiency of programs. A fixed reduction strategy enables the programmer to reason about termination and algorithmic complexity. ...