PDF
... In the following, let X be a topological space. Theorem 1. Suppose Y ⊆ X is equipped with the subspace topology, and A ⊆ Y . Then A is closed in Y if and only if A = Y ∩ J for some closed set J ⊆ X. Proof. If A is closed in Y , then Y \ A is open in Y , and by the definition of the subspace topology ...
... In the following, let X be a topological space. Theorem 1. Suppose Y ⊆ X is equipped with the subspace topology, and A ⊆ Y . Then A is closed in Y if and only if A = Y ∩ J for some closed set J ⊆ X. Proof. If A is closed in Y , then Y \ A is open in Y , and by the definition of the subspace topology ...
(pdf)
... A reasonable question at this point would be “so what?” Now that we have identified a promising topology for modeling accessibility among secondary structure, what will we do with it? We have a topology on V, so we can define functions that map into V and determine if they are continuous. The functi ...
... A reasonable question at this point would be “so what?” Now that we have identified a promising topology for modeling accessibility among secondary structure, what will we do with it? We have a topology on V, so we can define functions that map into V and determine if they are continuous. The functi ...
PDF
... This definition has no particular relationship to the notion of an integral domain, used in algebra. In number theory, one sometimes talks about fundamental domains in the upper half-plane, these have a different definition and are not normally open. In set theory, one often talks about the domain o ...
... This definition has no particular relationship to the notion of an integral domain, used in algebra. In number theory, one sometimes talks about fundamental domains in the upper half-plane, these have a different definition and are not normally open. In set theory, one often talks about the domain o ...
Some comments on Heisenberg-picture QFT, Theo Johnson
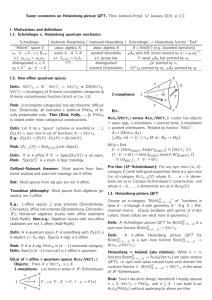
... Non-example (Brandenburg–Chirvasitu–JF): Let X be of SL(2)-local systems on M). a scheme. If X contains a closed projective subscheme, For general q, the TQFT is “quantum topological SL(2) then QCOH(X) is not 1-dualizable in PRESK . gauge theory” aka SL(2) Chern–Simons theory. (Non-)example (Branden ...
... Non-example (Brandenburg–Chirvasitu–JF): Let X be of SL(2)-local systems on M). a scheme. If X contains a closed projective subscheme, For general q, the TQFT is “quantum topological SL(2) then QCOH(X) is not 1-dualizable in PRESK . gauge theory” aka SL(2) Chern–Simons theory. (Non-)example (Branden ...
HOMEOMORPHISM IN IDEL TOPOLOGICAL SPACES Author: N.CHANDRAMATHI , K. BHUVANESWARI S.BHARATHI, INDIA
... (i) Semi open if A ⊆cl (int (A)) and semi closed if int(cl (A))⊆A. (ii) Pre-open if A ⊆ int (cl (A)) and pre-closed if cl (int (A))⊆ A. Definition 1.2: A subset A of a space (X,τ )is called ω-closed[9] if cl(A)⊆U whenever A⊆U and U is semi open in X. Definition 1.3:A map f:(X,τ )→(Y,σ) is said to be ...
... (i) Semi open if A ⊆cl (int (A)) and semi closed if int(cl (A))⊆A. (ii) Pre-open if A ⊆ int (cl (A)) and pre-closed if cl (int (A))⊆ A. Definition 1.2: A subset A of a space (X,τ )is called ω-closed[9] if cl(A)⊆U whenever A⊆U and U is semi open in X. Definition 1.3:A map f:(X,τ )→(Y,σ) is said to be ...
1 Basic notions, topologies
... b.) If d is the usual metric on X = R2 , then describe open balls centered at the origin with respect to the metric d0 . Using open balls, one can then consider ”open sets” which are defined as follows: Definition 7 A set U of X is called an ”open set” if for every point of it, you can find an open ...
... b.) If d is the usual metric on X = R2 , then describe open balls centered at the origin with respect to the metric d0 . Using open balls, one can then consider ”open sets” which are defined as follows: Definition 7 A set U of X is called an ”open set” if for every point of it, you can find an open ...
Answer Key
... [25 points] A subset A of a topological space X is said to be locally closed if A = E ∩ V , where E is closed in X and V is open in X. (a) Explain why the half-open interval [0, 1) is a locally closed subset of the real numbers (with the usual topology) but is neither open nor closed. (b) Let X be l ...
... [25 points] A subset A of a topological space X is said to be locally closed if A = E ∩ V , where E is closed in X and V is open in X. (a) Explain why the half-open interval [0, 1) is a locally closed subset of the real numbers (with the usual topology) but is neither open nor closed. (b) Let X be l ...