ACTIVITY 1: Forces and Motion
... Since friction causes objects to slow down, scientists have concluded that it is a force that acts in the opposite direction as an object’s motion. In the case of friction force (F ...
... Since friction causes objects to slow down, scientists have concluded that it is a force that acts in the opposite direction as an object’s motion. In the case of friction force (F ...
SPH3U: What is a Force?
... move in circles and steep curves make you feel like you’re being pushed outwards. People call this the centripetal force. Do you think that’s the same force that keeps you from falling out of a roller coaster when it goes upside down? Find out with this quick activity. Make sure every member of your ...
... move in circles and steep curves make you feel like you’re being pushed outwards. People call this the centripetal force. Do you think that’s the same force that keeps you from falling out of a roller coaster when it goes upside down? Find out with this quick activity. Make sure every member of your ...
FRICTION IN APPLICATIONS OF NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... 1a. Friction Needs Normal and Tangential Forces. In this module we introduce some effects of friction into some simple cases in mechanics.1 All such cases occur when there are two objects in contact and there are two force components that act on the objects: (1) a “normal force” which is perpendicul ...
... 1a. Friction Needs Normal and Tangential Forces. In this module we introduce some effects of friction into some simple cases in mechanics.1 All such cases occur when there are two objects in contact and there are two force components that act on the objects: (1) a “normal force” which is perpendicul ...
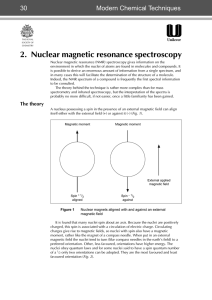
2. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
... difference between levels the population of the higher energy state increases as radiation is absorbed. The equilibrium population distribution is re-established by spin-lattice relaxation processes whereby the energy previously absorbed is shared with either the surroundings (spin-lattice relaxatio ...
... difference between levels the population of the higher energy state increases as radiation is absorbed. The equilibrium population distribution is re-established by spin-lattice relaxation processes whereby the energy previously absorbed is shared with either the surroundings (spin-lattice relaxatio ...
Exam 1
... 2. When you charge an object by induction, you... a. touch the ball with a charged object. b. move electrons from your finger to the ball. c. induct the ball with charge. d. bring a charged object near but do not touch the ball. 3. An electrical insulator is a material: a. must be a crystal b. that ...
... 2. When you charge an object by induction, you... a. touch the ball with a charged object. b. move electrons from your finger to the ball. c. induct the ball with charge. d. bring a charged object near but do not touch the ball. 3. An electrical insulator is a material: a. must be a crystal b. that ...
Is the electrostatic force between a point charge and a neutral
... that a positively charged point charge induces negative charges on the part of the sphere that is closest to it and positive charges on the part that is further away. It is natural to wonder if this phenomenon is more general and if the force is attractive for any geometry, not just a sphere. This q ...
... that a positively charged point charge induces negative charges on the part of the sphere that is closest to it and positive charges on the part that is further away. It is natural to wonder if this phenomenon is more general and if the force is attractive for any geometry, not just a sphere. This q ...
Friction - e
... table still does not start to move, it means that the frictional force exerted by the floor has automatically increased in order to balance the force that we applied. The frictional force is a force which automatically adjusts to balance the force we apply. However, if we keep on increasing the forc ...
... table still does not start to move, it means that the frictional force exerted by the floor has automatically increased in order to balance the force that we applied. The frictional force is a force which automatically adjusts to balance the force we apply. However, if we keep on increasing the forc ...
Nuclear Physics A. Stationary States of Nuclei
... particles of unit atomic weight some of which are positively charged while others are neutral. In fact, we know two nuclei of atomic weight unity, vis., the proton and the neutron (CS), the first bearing unit positive charge while the second is neutral. We are thus led to the hypothesis that every n ...
... particles of unit atomic weight some of which are positively charged while others are neutral. In fact, we know two nuclei of atomic weight unity, vis., the proton and the neutron (CS), the first bearing unit positive charge while the second is neutral. We are thus led to the hypothesis that every n ...
Energy, Work, and
... you exert a force, magnitude mg, upward. The two forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions. It appears that no work is done, but you know that you did work. Explain what work was done. You do positive work on the box because the force and motion are in the same direction. Gravity does neg ...
... you exert a force, magnitude mg, upward. The two forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions. It appears that no work is done, but you know that you did work. Explain what work was done. You do positive work on the box because the force and motion are in the same direction. Gravity does neg ...
Force and Motion In the last section we demonstrated and discussed
... now need to see if there is a way to connect this idea of mass with force and motion, such that the laws of motion take on a simple form. The case of Constant Velocity We demonstrated that if an object has no forces acting on it, it will stay at rest or move with a constant velocity. Is there any ot ...
... now need to see if there is a way to connect this idea of mass with force and motion, such that the laws of motion take on a simple form. The case of Constant Velocity We demonstrated that if an object has no forces acting on it, it will stay at rest or move with a constant velocity. Is there any ot ...
Notes on Forces with Friction
... If you push a cardboard box along a wooden floor, you have to push to overcome the force of friction. This force makes it harder for you to slide the box. The force of friction opposes any force that can cause one object to slide past another. There are two types of friction: static and kinetic. T ...
... If you push a cardboard box along a wooden floor, you have to push to overcome the force of friction. This force makes it harder for you to slide the box. The force of friction opposes any force that can cause one object to slide past another. There are two types of friction: static and kinetic. T ...
Nuclear force

The nuclear force (or nucleon–nucleon interaction or residual strong force) is the force between protons and neutrons, subatomic particles that are collectively called nucleons. The nuclear force is responsible for binding protons and neutrons into atomic nuclei. Neutrons and protons are affected by the nuclear force almost identically. Since protons have charge +1 e, they experience a Coulomb repulsion that tends to push them apart, but at short range the nuclear force is sufficiently attractive as to overcome the electromagnetic repulsive force. The mass of a nucleus is less than the sum total of the individual masses of the protons and neutrons which form it. The difference in mass between bound and unbound nucleons is known as the mass defect. Energy is released when nuclei break apart, and it is this energy that used in nuclear power and nuclear weapons.The nuclear force is powerfully attractive between nucleons at distances of about 1 femtometer (fm, or 1.0 × 10−15 metres) between their centers, but rapidly decreases to insignificance at distances beyond about 2.5 fm. At distances less than 0.7 fm, the nuclear force becomes repulsive. This repulsive component is responsible for the physical size of nuclei, since the nucleons can come no closer than the force allows. By comparison, the size of an atom, measured in angstroms (Å, or 1.0 × 10−10 m), is five orders of magnitude larger. The nuclear force is not simple, however, since it depends on the nucleon spins, has a tensor component, and may depend on the relative momentum of the nucleons.A quantitative description of the nuclear force relies on partially empirical equations that model the internucleon potential energies, or potentials. (Generally, forces within a system of particles can be more simply modeled by describing the system's potential energy; the negative gradient of a potential is equal to the vector force.) The constants for the equations are phenomenological, that is, determined by fitting the equations to experimental data. The internucleon potentials attempt to describe the properties of nucleon–nucleon interaction. Once determined, any given potential can be used in, e.g., the Schrödinger equation to determine the quantum mechanical properties of the nucleon system.The discovery of the neutron in 1932 revealed that atomic nuclei were made of protons and neutrons, held together by an attractive force. By 1935 the nuclear force was conceived to be transmitted by particles called mesons. This theoretical development included a description of the Yukawa potential, an early example of a nuclear potential. Mesons, predicted by theory, were discovered experimentally in 1947. By the 1970s, the quark model had been developed, which showed that the mesons and nucleons were composed of quarks and gluons. By this new model, the nuclear force, resulting from the exchange of mesons between neighboring nucleons, is a residual effect of the strong force.