Cell Review Power Point
... skin and heart stomach and pancreas bladder and kidneys lungs and heart ...
... skin and heart stomach and pancreas bladder and kidneys lungs and heart ...
Cell Transport
... • Active transport is the transport of a molecule across a membrane AGAINST its concentration gradient and requires energy. • We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be stored inside body as it is water-soluble, so it must be converted into gl ...
... • Active transport is the transport of a molecule across a membrane AGAINST its concentration gradient and requires energy. • We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be stored inside body as it is water-soluble, so it must be converted into gl ...
Cell Division
... then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; humans have 23 ...
... then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; humans have 23 ...
using the compound microscope to study animal and plant cells
... have a cell wall. The outer surface of the cell is the plasma membrane. Notice as you focus up and down that these cells are more squashed than were the parenchyma cells of the banana, even though you did not apply pressure on the cover slip. This is because they lack a rigid cell wall. Animal cells ...
... have a cell wall. The outer surface of the cell is the plasma membrane. Notice as you focus up and down that these cells are more squashed than were the parenchyma cells of the banana, even though you did not apply pressure on the cover slip. This is because they lack a rigid cell wall. Animal cells ...
Teacher Notes PDF - TI Education
... Q15. Both smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum are responsible for transport. Where do their contents get transported to? Answer: A. other organelles, B. cell wall, C. outside the cell Q16. Which organelle contains grana? Answer: C. chloroplast Q17. Plants inherit characteristics from their parent ...
... Q15. Both smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum are responsible for transport. Where do their contents get transported to? Answer: A. other organelles, B. cell wall, C. outside the cell Q16. Which organelle contains grana? Answer: C. chloroplast Q17. Plants inherit characteristics from their parent ...
Lesson 1.1.1 Cells
... Lesson 1.1.1 Continued We now know a lot about the structures and functions of parts of cells, and we know they are small. So how small are they? 1. Measure the diameter of the field of view 2. Count how many cells are along the diameter of that field of view 3. Divide the diameter of the field of v ...
... Lesson 1.1.1 Continued We now know a lot about the structures and functions of parts of cells, and we know they are small. So how small are they? 1. Measure the diameter of the field of view 2. Count how many cells are along the diameter of that field of view 3. Divide the diameter of the field of v ...
Cell Division - s3.amazonaws.com
... then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; humans have 23 ...
... then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; humans have 23 ...
Animal vs Plant Cells- Information for Diagrams
... The structures possessed by plant cells for performing these two functions create the primary differences between plant and animals cells. These structures are: ...
... The structures possessed by plant cells for performing these two functions create the primary differences between plant and animals cells. These structures are: ...
A1987G155900001
... Evidence was obtained showing that the FC-sensitive H + pump is regulated by intracellular pH, transmembrane potential, and by some natural hormones other than auxin.3 Some new, potentially important metabolic responses, such as abscisic acid-induced proline accumulation and the phosphorylation of a ...
... Evidence was obtained showing that the FC-sensitive H + pump is regulated by intracellular pH, transmembrane potential, and by some natural hormones other than auxin.3 Some new, potentially important metabolic responses, such as abscisic acid-induced proline accumulation and the phosphorylation of a ...
CHAPTER 7
... channels passing through cell walls of adjacent plant cells. – Are lined by plasma membrane. – Contain a central structure, the desmotubule. – Serve as sites of cell-cell communication. ...
... channels passing through cell walls of adjacent plant cells. – Are lined by plasma membrane. – Contain a central structure, the desmotubule. – Serve as sites of cell-cell communication. ...
IntoScience topic: Cells
... Cells don't live forever! Fortunately before they die, they can reproduce. Learn the different types of cell division: budding, binary fission, mitosis and meiosis. Elaboration: recognising that cells reproduce ...
... Cells don't live forever! Fortunately before they die, they can reproduce. Learn the different types of cell division: budding, binary fission, mitosis and meiosis. Elaboration: recognising that cells reproduce ...
Document
... prophase of meiosis I, when chromosomes have condensed. 2. Synapsis, during prophase I. Homologous chromosome are held together by proteins in the synaptonemal complex. ...
... prophase of meiosis I, when chromosomes have condensed. 2. Synapsis, during prophase I. Homologous chromosome are held together by proteins in the synaptonemal complex. ...
Chapter 5 Chemical Messengers
... o Amino acids neurotransmitters are synthesized within a neuron stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis o Amines are derived from amino acids with exception of thyroid hormones. o Peptide and proteins are formed as other proteins. o Steroids are derived from the cholesterol molecule o Eicosano ...
... o Amino acids neurotransmitters are synthesized within a neuron stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis o Amines are derived from amino acids with exception of thyroid hormones. o Peptide and proteins are formed as other proteins. o Steroids are derived from the cholesterol molecule o Eicosano ...
PROJECT PROPOSAL for applicants for ITC fellowships
... OF PP2A-LIKE PROTEIN PHOSPHATASES IN FRUITFLIES ...
... OF PP2A-LIKE PROTEIN PHOSPHATASES IN FRUITFLIES ...
Cell Membranes
... *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transport Co-transport – process cells use to bring large mo ...
... *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transport Co-transport – process cells use to bring large mo ...
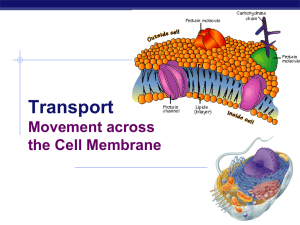
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Diffusion (passive transport) movement from high low concentration ...
... Diffusion (passive transport) movement from high low concentration ...
Diffusion, Osmosis, And Some Others…
... • fatty acid tails are nonpolar – as a result they are attracted to each other and repel water • (hates water – hydrophobic) * So if a bunch of phospholipids were dropped in a container of water they would always form a cell membrane like structure. ...
... • fatty acid tails are nonpolar – as a result they are attracted to each other and repel water • (hates water – hydrophobic) * So if a bunch of phospholipids were dropped in a container of water they would always form a cell membrane like structure. ...
MEDICAL BIOLOGY AND GENETICS 1 Comenius
... hypotonic solution an animal cell will lyse and destroy while a plant cell will turgid as the cell wall will not let it burst. On the other hand, in a hypertonic solution animal cells will lose water to their surroundings, ...
... hypotonic solution an animal cell will lyse and destroy while a plant cell will turgid as the cell wall will not let it burst. On the other hand, in a hypertonic solution animal cells will lose water to their surroundings, ...
10269.05 GCE AS 1 Biology (MV18) Summer 2016.indd
... including cholesterol and glycoproteins. (a) (i) Identify the group of proteins to which glycoproteins belong. Explain your answer. [2 marks] ...
... including cholesterol and glycoproteins. (a) (i) Identify the group of proteins to which glycoproteins belong. Explain your answer. [2 marks] ...
Cell Nutrients
... Nutrients required by cell living can be categorized into macronutrient that are required higher than 10-4M, micronutrients that less than 10-4M. Macronutrients include N, C, O, H, S, P, K and Mg. They are major components in cell dry weight. Micronutrients are classified into most widely needed ele ...
... Nutrients required by cell living can be categorized into macronutrient that are required higher than 10-4M, micronutrients that less than 10-4M. Macronutrients include N, C, O, H, S, P, K and Mg. They are major components in cell dry weight. Micronutrients are classified into most widely needed ele ...
Document
... (neutrophil) on a blood film, crawling among red blood cells, notable for their dark color and principally spherical shape. The neutrophil is "chasing" Staphylococcus aureus microorganisms, added to the film. The chemoattractant derived from the microbe is unclear, but may be complement fragment C5a ...
... (neutrophil) on a blood film, crawling among red blood cells, notable for their dark color and principally spherical shape. The neutrophil is "chasing" Staphylococcus aureus microorganisms, added to the film. The chemoattractant derived from the microbe is unclear, but may be complement fragment C5a ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.