Slide 1 - swofford8
... accounts for the diversity of species developed through gradual processes over many generations. • Species acquire many of their unique characteristics through biological adaptation, which involves the selection of naturally occurring variations in populations ...
... accounts for the diversity of species developed through gradual processes over many generations. • Species acquire many of their unique characteristics through biological adaptation, which involves the selection of naturally occurring variations in populations ...
Principles of Ecology
... A. Habitat- part of the environment where an organism lives. Eagle in forest, Mouse in the classroom B. Niche- way of life, or role of a species in an ecosystem- the how, when and where an organism obtains its nutrients, its reproductive behavior, its habitat. C. Competition 1. In a balanced ecosy ...
... A. Habitat- part of the environment where an organism lives. Eagle in forest, Mouse in the classroom B. Niche- way of life, or role of a species in an ecosystem- the how, when and where an organism obtains its nutrients, its reproductive behavior, its habitat. C. Competition 1. In a balanced ecosy ...
The difference between population, communities, and
... The difference So the difference is that the population is how things of one species in a area. But a community is a group of plants and animals in a area. A ecosystem is a community of interacting organisms ...
... The difference So the difference is that the population is how things of one species in a area. But a community is a group of plants and animals in a area. A ecosystem is a community of interacting organisms ...
Changes Over Time Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST
... 9 What is it called when all of the organisms of a species completely die out? Extinction 10 Animals living in extremely hot environments usually have special characteristics like scales, ability to store water or other methods of staying cool. What do these characteristics represent? Adaptations 11 ...
... 9 What is it called when all of the organisms of a species completely die out? Extinction 10 Animals living in extremely hot environments usually have special characteristics like scales, ability to store water or other methods of staying cool. What do these characteristics represent? Adaptations 11 ...
evolution ppt
... • Organisms varying in inheritable characteristics (mechanics of genetics was unknown at this time!) • Large population size causes competition for resources & restricts survival rate ...
... • Organisms varying in inheritable characteristics (mechanics of genetics was unknown at this time!) • Large population size causes competition for resources & restricts survival rate ...
Practice Exam: Ecology
... 56. What is one difference between primary and secondary succession? a. Primary succession is slow, and secondary succession is rapid. b. Secondary succession begins on soil, and primary succession begins on newly exposed surfaces. c. Primary succession modifies the environment, and secondary succe ...
... 56. What is one difference between primary and secondary succession? a. Primary succession is slow, and secondary succession is rapid. b. Secondary succession begins on soil, and primary succession begins on newly exposed surfaces. c. Primary succession modifies the environment, and secondary succe ...
Natural Selection Darwin*s Ideas
... Objectives • Be able to explain Darwin’s journey to an idea. • Be able to explain how populations of organisms can adapt to their environment through natural selection. ...
... Objectives • Be able to explain Darwin’s journey to an idea. • Be able to explain how populations of organisms can adapt to their environment through natural selection. ...
Dates Topic Reading - Morgan
... Course Philosophy: This course is designed to give a general overview of the science of Ecology, as well as providing an understanding of the importance of evolution to the understanding of science. Ecology is a hands-on science, and the labs will provide you with a deeper understanding of the resea ...
... Course Philosophy: This course is designed to give a general overview of the science of Ecology, as well as providing an understanding of the importance of evolution to the understanding of science. Ecology is a hands-on science, and the labs will provide you with a deeper understanding of the resea ...
Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6 Test Review
... 1. The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called as Ecology. 2. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a community. 3. Matter can be recycled through the biosphere because biological systems ...
... 1. The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called as Ecology. 2. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a community. 3. Matter can be recycled through the biosphere because biological systems ...
File
... presence of field mice and an increase in the number of snakes. Which of these is the most likely explanation about why the population size of each animal changed? A. The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to live. B. The mice became prey to ...
... presence of field mice and an increase in the number of snakes. Which of these is the most likely explanation about why the population size of each animal changed? A. The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to live. B. The mice became prey to ...
Natural Selection - noraddin
... Before Darwin, scientists did not think this was important Darwin claimed that differences matter and can change the direction of a species ...
... Before Darwin, scientists did not think this was important Darwin claimed that differences matter and can change the direction of a species ...
ecology_intro_ppt
... • Environment – encompasses the interaction between the living and nonliving world in a particular geographic area. Ex. Rocks and Trees ...
... • Environment – encompasses the interaction between the living and nonliving world in a particular geographic area. Ex. Rocks and Trees ...
Ecosystems - funtastic physics
... If there are others of its kind, this is called a species. The number of this species is called the population. Populations interact to form habitats. Are there other organisms that live in this environment? If yes, what organisms? _______________________________________________. Add these organisms ...
... If there are others of its kind, this is called a species. The number of this species is called the population. Populations interact to form habitats. Are there other organisms that live in this environment? If yes, what organisms? _______________________________________________. Add these organisms ...
Document
... Abiotic Factors – all of the physical (non-living) aspects that belong to an organism’s environment. ...
... Abiotic Factors – all of the physical (non-living) aspects that belong to an organism’s environment. ...
Day 25 – Carbohydrates
... Individual organisms differ and some of these variations are heritable (passed on) Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and many that do survive do not reproduce Because more organisms are produce than can survive, they must compete for limited resources (food, shelter, etc) Eac ...
... Individual organisms differ and some of these variations are heritable (passed on) Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and many that do survive do not reproduce Because more organisms are produce than can survive, they must compete for limited resources (food, shelter, etc) Eac ...
Ecosystems meets Hydrology – synergies and opportunities
... and dynamics are important controls on the functioning of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems; hydrological system response depends on the structure and function of ecosystems – which in the short term control evaporation, runoff and fluvial processes, and in the long term influence landscape propert ...
... and dynamics are important controls on the functioning of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems; hydrological system response depends on the structure and function of ecosystems – which in the short term control evaporation, runoff and fluvial processes, and in the long term influence landscape propert ...
Prosperity without Growth?
... Prosperity consists in our ability to flourish as human beings – within the ecological limits of a finite planet. • material flourishing: food, clothing, shelter • social and psychological flourishing: identity, meaning, participation in the life of society • rethinking social goods and public space ...
... Prosperity consists in our ability to flourish as human beings – within the ecological limits of a finite planet. • material flourishing: food, clothing, shelter • social and psychological flourishing: identity, meaning, participation in the life of society • rethinking social goods and public space ...
Glossary
... for all endangered or threatened species in the state California Environmental Quality Act – passed in 1970, states that agencies and businesses must identify their environmental impacts and work to minimize them Climate – the general pattern of atmospheric or weather conditions in an area over a lo ...
... for all endangered or threatened species in the state California Environmental Quality Act – passed in 1970, states that agencies and businesses must identify their environmental impacts and work to minimize them Climate – the general pattern of atmospheric or weather conditions in an area over a lo ...
Introduction to Ecology
... many resources cycled throughout the water column and sediments, but very little, relative to the total, is transported in or out of the system the object of ecosystem studies - how energy and resources are cycled within the system ...
... many resources cycled throughout the water column and sediments, but very little, relative to the total, is transported in or out of the system the object of ecosystem studies - how energy and resources are cycled within the system ...
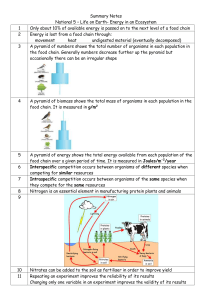
Energy in an Ecosystem Summary Notes
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
Evolution by natural selection
... – Struggle for existence: more individuals are born than can survive in the environment – Variation and adaptation: there is variation among individuals and some variations are more beneficial than others (adaptations) – Survival of the fittest: Differences in adaptations affect how well an organism ...
... – Struggle for existence: more individuals are born than can survive in the environment – Variation and adaptation: there is variation among individuals and some variations are more beneficial than others (adaptations) – Survival of the fittest: Differences in adaptations affect how well an organism ...
Evolution in biology
... populations 3) recombination – an exchange of genetic material during meiosis or between species ...
... populations 3) recombination – an exchange of genetic material during meiosis or between species ...
Humans in the Biosphere
... replenished by natural processes (eg. Fossil fuels, oil and natural gas 2. Sustainable use- using natural resources so that you don’t deplete them (based on principles of ecology and economics) ...
... replenished by natural processes (eg. Fossil fuels, oil and natural gas 2. Sustainable use- using natural resources so that you don’t deplete them (based on principles of ecology and economics) ...
Kanda: Research in Biology
... My work is in mammalian behavioral ecology and population dynamics. My main fieldwork is on spatial ecology, that is, how and why animals use their space and move from one space to another. While my experience is in mammals, I am also interested in movement ecology of other organisms, particularly d ...
... My work is in mammalian behavioral ecology and population dynamics. My main fieldwork is on spatial ecology, that is, how and why animals use their space and move from one space to another. While my experience is in mammals, I am also interested in movement ecology of other organisms, particularly d ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.