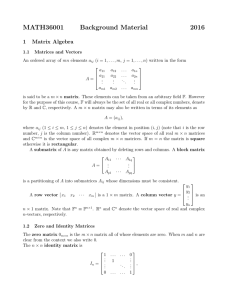
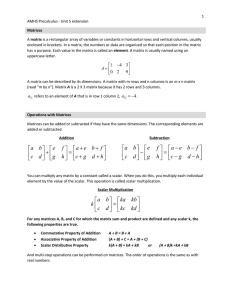
Slide 2.2
... ELEMENTARY MATRICES An interchange of rows 1 and 2 of A produces E2A, and multiplication of row 3 of A by 5 produces E3A. Left-multiplication by E1 in Example 1 has the same effect on any 3 n matrix. Since E1 I E1, we see that E1 itself is produced by this same row operation on the iden ...
... ELEMENTARY MATRICES An interchange of rows 1 and 2 of A produces E2A, and multiplication of row 3 of A by 5 produces E3A. Left-multiplication by E1 in Example 1 has the same effect on any 3 n matrix. Since E1 I E1, we see that E1 itself is produced by this same row operation on the iden ...
Solutions, PDF, 37 K - Brown math department
... is unique (and coincide with the inverse). But we have more than one right inverse, so the matrix cannot be left invertible. 2. Find all left inverses of the column (1, 2, 3)T Solution: (x, y, 1/3 − x/3 − 2x/3), x, y ∈ R. 3. Find two matrices A and B that AB is invertible, but A and B are not. Hint: ...
... is unique (and coincide with the inverse). But we have more than one right inverse, so the matrix cannot be left invertible. 2. Find all left inverses of the column (1, 2, 3)T Solution: (x, y, 1/3 − x/3 − 2x/3), x, y ∈ R. 3. Find two matrices A and B that AB is invertible, but A and B are not. Hint: ...