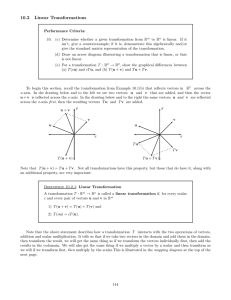
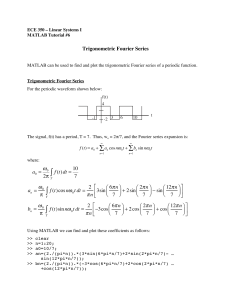
lecture
... examines all possible paths. Give a simple recursive function that calculates the fastest path through the assembly line What is the base case? How can we make the problem smaller? HINT: You can use two mutually recursive functions if you want to Second step Use a table to avoid recalculating values ...
... examines all possible paths. Give a simple recursive function that calculates the fastest path through the assembly line What is the base case? How can we make the problem smaller? HINT: You can use two mutually recursive functions if you want to Second step Use a table to avoid recalculating values ...
Introduction. This primer will serve as a introduction to Maple 10 and
... Procedures are small programs that are used when your function cannot be expressed with a straightforward formula. (Please refer to the Help program or user manual for further details.) In our example we shall use a conditional "if statement". It must be terminated with end if. The procedure itself ...
... Procedures are small programs that are used when your function cannot be expressed with a straightforward formula. (Please refer to the Help program or user manual for further details.) In our example we shall use a conditional "if statement". It must be terminated with end if. The procedure itself ...
thesis
... while the total count for the one-stage calculations given by Equation (1.7) is N 2 = p2 q2 . This algorithm therefore represents a significant improvement in complexity, and ultimately leads to the O( N log N ) running time of the Cooley-Tukey FFT. Abelian groups other than the cyclic groups afford ...
... while the total count for the one-stage calculations given by Equation (1.7) is N 2 = p2 q2 . This algorithm therefore represents a significant improvement in complexity, and ultimately leads to the O( N log N ) running time of the Cooley-Tukey FFT. Abelian groups other than the cyclic groups afford ...
- Free Documents
... invertible matrix M such that is an upper triangular system. Indeed. it would be equivalent to solving n systems of linear equations. we use sometimes the notation M x but the inverse is never computed in practise. . triangular.Principle of direct methods I For solving Conditioning Direct methods It ...
... invertible matrix M such that is an upper triangular system. Indeed. it would be equivalent to solving n systems of linear equations. we use sometimes the notation M x but the inverse is never computed in practise. . triangular.Principle of direct methods I For solving Conditioning Direct methods It ...
Robust convex relaxation for the planted clique and densest k
... to a community of users in a social network or cluster of similar items in a given data set. Unfortunately, the problem of finding a densest subgraph of given size is known to be both NP-hard [23] and hard to approximate [20, 34, 2]. Our results can be thought of as a generalization to the densest ...
... to a community of users in a social network or cluster of similar items in a given data set. Unfortunately, the problem of finding a densest subgraph of given size is known to be both NP-hard [23] and hard to approximate [20, 34, 2]. Our results can be thought of as a generalization to the densest ...
A Mathematical Structure of Processes for Generating Rankings
... In this subsection, the mathematical properties of each element in ranking vector r M(II) are given. As is mentioned in Property 5, the matrix M(II) has a period 2. Therefore, we cannot have the characteristics of each element in r M(II) by the transition of successive potential in applying the powe ...
... In this subsection, the mathematical properties of each element in ranking vector r M(II) are given. As is mentioned in Property 5, the matrix M(II) has a period 2. Therefore, we cannot have the characteristics of each element in r M(II) by the transition of successive potential in applying the powe ...
for twoside printing - Institute for Statistics and Mathematics
... In this course we will have to solve many problems. For this task the reader may use any theorem that have already been proved up to this point. Missing definitions could be found in the handouts for the course Mathematische Methoden. However, one must not use any results or theorems from these hand ...
... In this course we will have to solve many problems. For this task the reader may use any theorem that have already been proved up to this point. Missing definitions could be found in the handouts for the course Mathematische Methoden. However, one must not use any results or theorems from these hand ...
Notes
... matrices U ∈ O (n) with det(U ) = −1. Exercise 1.10. Describe both components of O (2). Because O (n) sits inside of the Euclidean matrix space Mn (R) (with the HilbertSchmidt inner product), it has a Riemannian metric that it inherits from the Euclidean metric. Here’s how that works: a Riemannian m ...
... matrices U ∈ O (n) with det(U ) = −1. Exercise 1.10. Describe both components of O (2). Because O (n) sits inside of the Euclidean matrix space Mn (R) (with the HilbertSchmidt inner product), it has a Riemannian metric that it inherits from the Euclidean metric. Here’s how that works: a Riemannian m ...
Non-negative matrix factorization

NMF redirects here. For the bridge convention, see new minor forcing.Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), also non-negative matrix approximation is a group of algorithms in multivariate analysis and linear algebra where a matrix V is factorized into (usually) two matrices W and H, with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements. This non-negativity makes the resulting matrices easier to inspect. Also, in applications such as processing of audio spectrograms non-negativity is inherent to the data being considered. Since the problem is not exactly solvable in general, it is commonly approximated numerically.NMF finds applications in such fields as computer vision, document clustering, chemometrics, audio signal processing and recommender systems.