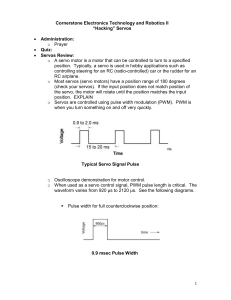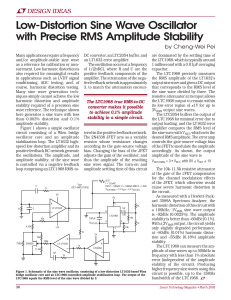
Low-Distortion Sine Wave Oscillator with Precise RMS Amplitude
... the LTC1968, which is typically around 1 millisecond with a 0.01µF averaging capacitor. The LTC1968 precisely measures the RMS amplitude of the LT1632’s output sine wave and gives a DC output that corresponds to the RMS level of the sine wave divided by three. The resistive attenuator at its input a ...
... the LTC1968, which is typically around 1 millisecond with a 0.01µF averaging capacitor. The LTC1968 precisely measures the RMS amplitude of the LT1632’s output sine wave and gives a DC output that corresponds to the RMS level of the sine wave divided by three. The resistive attenuator at its input a ...
555 Timer.ppt - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... • The phase comparator (phase detector) can be as simple as an exclusive-or gate (digital signals) or is a mixer (non-linear device - frequency multiplier) for analog signals. ...
... • The phase comparator (phase detector) can be as simple as an exclusive-or gate (digital signals) or is a mixer (non-linear device - frequency multiplier) for analog signals. ...
Pulse Input Adapters (Part # S-UCC-M00x and S-UCD
... To verify proper operation of the Pulse Input Adapter, connect the adapter to a logger and launch the logger. For the S-UCDM00x model, enter a known number of pulses (for example, if using a tipping-bucket rain gauge, tip the bucket several times). Then read out the logger and verify that the number ...
... To verify proper operation of the Pulse Input Adapter, connect the adapter to a logger and launch the logger. For the S-UCDM00x model, enter a known number of pulses (for example, if using a tipping-bucket rain gauge, tip the bucket several times). Then read out the logger and verify that the number ...
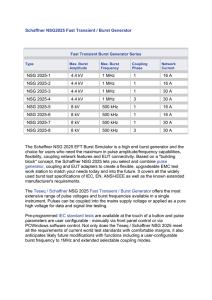
Schaffner NSG2025 Fast Transient / Burst Generator NSG 2025
... 110/115 V and 220/240 V, and country-specific power-line sockets for the EUT are interchangeable so full compliance and volume production tests can be run on finished products and systems destined for different markets. Built-in safety Every component in the NSG 2025 that carries a high voltage is des ...
... 110/115 V and 220/240 V, and country-specific power-line sockets for the EUT are interchangeable so full compliance and volume production tests can be run on finished products and systems destined for different markets. Built-in safety Every component in the NSG 2025 that carries a high voltage is des ...
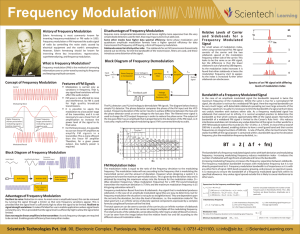
frequency modulation
... complex. With the proliferation of ICs, complex circuitry used in FM has all but disappeared. ICs are inexpensive and easy to use. FM and PM have become the most widely used modulation method in electronic communication today. ...
... complex. With the proliferation of ICs, complex circuitry used in FM has all but disappeared. ICs are inexpensive and easy to use. FM and PM have become the most widely used modulation method in electronic communication today. ...
A Compact High Voltage Nanosecond Pulse Generator
... fresh lime and orange juices with respect to the unpulsed juice (control). Conditions 1 and 2 correspond to 10 minutes and 20 minutes of pulse applications respectively. A 0.4cm electrode gap was used for this measurement. The applied voltage was 500V (corresponding to a electric field intensity of ...
... fresh lime and orange juices with respect to the unpulsed juice (control). Conditions 1 and 2 correspond to 10 minutes and 20 minutes of pulse applications respectively. A 0.4cm electrode gap was used for this measurement. The applied voltage was 500V (corresponding to a electric field intensity of ...
a survey and study of different types of pwm
... Fig-1: S ymmetric and Asymmetric PWM Signals Fig.-1 shows two types of PWM signals, symmetric and asymmetric. The pulses of a symmetric PWM signal are always symmetric with respect to the center of each PWM period. The pulses of an asymmetric PWM signal always have the same side aligned with one end ...
... Fig-1: S ymmetric and Asymmetric PWM Signals Fig.-1 shows two types of PWM signals, symmetric and asymmetric. The pulses of a symmetric PWM signal are always symmetric with respect to the center of each PWM period. The pulses of an asymmetric PWM signal always have the same side aligned with one end ...
Design and Analysis of an Efficient Counter Using Pulse
... the number of transistors stacked in the discharging path and also reduces the overall switching delay. This enhanced pulse triggered low-power flip flop (EPTLFF) avoids unnecessary internal node transitions to improve the power consumption as compared to previously designed circuits. A 4-bit counte ...
... the number of transistors stacked in the discharging path and also reduces the overall switching delay. This enhanced pulse triggered low-power flip flop (EPTLFF) avoids unnecessary internal node transitions to improve the power consumption as compared to previously designed circuits. A 4-bit counte ...
CF8000 - Ortec
... To compensate for varying rise-times requires a further elaboration of the timing system. The elaboration is to modify the delay time of the non-attenuated, non-inverted signal shown in Fig. 1(c) to a value less than the shortest rise-time that will be encountered. Fig. 3 illustrates the result for ...
... To compensate for varying rise-times requires a further elaboration of the timing system. The elaboration is to modify the delay time of the non-attenuated, non-inverted signal shown in Fig. 1(c) to a value less than the shortest rise-time that will be encountered. Fig. 3 illustrates the result for ...
7.0 - Radio Signals and Measurements
... E4B10 -- Which of the following describes a method to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically re ...
... E4B10 -- Which of the following describes a method to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically re ...
Amateur Extra License Class - Wabash Valley Amateur Radio Asso
... E4B10 -- Which of the following describes a method to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically re ...
... E4B10 -- Which of the following describes a method to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically re ...
History of Frequency Modulation - Hik
... FM wave is not affected to noise and interference. So FM is used for high quality broadcast transmissions. ...
... FM wave is not affected to noise and interference. So FM is used for high quality broadcast transmissions. ...
Chirp compression

The chirp pulse compression process transforms a long duration frequency-coded pulse into a narrow pulse of greatly increased amplitude. It is a technique used in radar and sonar systems because it is a method whereby a narrow pulse with high peak power can be derived from a long duration pulse with low peak power. Furthermore, the process offers good range resolution because the half-power beam width of the compressed pulse is consistent with the system bandwidth.The basics of the method for radar applications were developed in the late 1940s and early 1950s, but it was not until 1960, following declassification of the subject matter, that a detailed article on the topic appeared the public domain. Thereafter, the number of published articles grew quickly, as demonstrated by the comprehensive selection of papers to be found in a compilation by Barton.Briefly, the basic pulse compression properties can be related as follows. For a chirp waveform that sweeps over a frequency range F1 to F2 in a time period T, the nominal bandwidth of the pulse is B, where B = F2 – F1, and the pulse has a time-bandwidth product of T×B . Following pulse compression, a narrow pulse of duration τ is obtained, where τ ≈ 1/B, together with a peak voltage amplification of √(T×B).