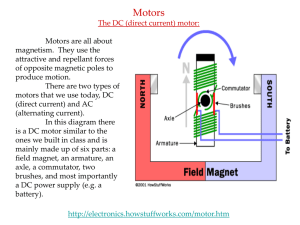
dc motor
... Dc motor is most used electrical machine. Converts electrical to mechanical energy. The mechanical movement produced due to torque. A Dc motor should never be started without load. Starters are essential for starting all motors. Dc motor is simply converse of a Dc Generator. ...
... Dc motor is most used electrical machine. Converts electrical to mechanical energy. The mechanical movement produced due to torque. A Dc motor should never be started without load. Starters are essential for starting all motors. Dc motor is simply converse of a Dc Generator. ...
because it rotates. 17.3 Electric motors In a working electric motor
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
Series DC Motors
... • Generator action: An emf (voltage) is induced in a conductor if it moves through a magnetic field. • Motor action: A force is induced in a conductor that has a current going through it and placed in a magnetic field • Any DC machine can act either as a generator or as a motor. ...
... • Generator action: An emf (voltage) is induced in a conductor if it moves through a magnetic field. • Motor action: A force is induced in a conductor that has a current going through it and placed in a magnetic field • Any DC machine can act either as a generator or as a motor. ...
Electric Motors
... cobalt). This magnetic effect comes from a special alignment of the atomic structure of the material. All magnets have two poles, a north pole and a south pole. It is impossible to have a singular magnetic pole; they always come in pairs. Magnets follow the rule that opposite poles attract and like ...
... cobalt). This magnetic effect comes from a special alignment of the atomic structure of the material. All magnets have two poles, a north pole and a south pole. It is impossible to have a singular magnetic pole; they always come in pairs. Magnets follow the rule that opposite poles attract and like ...
How Motors Operate Presented by John Freeland
... connection determines if the motor runs clockwise or counterclockwise If both ends of the starting and running windings are accessible, the motor can be reversed “Induction” in a split phase induction motor means a current and therefore a magnetic field is induced in the rotor by the stator magnetic ...
... connection determines if the motor runs clockwise or counterclockwise If both ends of the starting and running windings are accessible, the motor can be reversed “Induction” in a split phase induction motor means a current and therefore a magnetic field is induced in the rotor by the stator magnetic ...
5-Motors
... if we change the direction of the flow of electrons by reversing the battery connections. This “flips” the electric field of the electromagnet causing another repulsion and attraction between the poles of the two magnets, pushing the nail around again to complete the circle. ...
... if we change the direction of the flow of electrons by reversing the battery connections. This “flips” the electric field of the electromagnet causing another repulsion and attraction between the poles of the two magnets, pushing the nail around again to complete the circle. ...
LAB TECHNICIAN POSITION: Responsible for building and testing
... providing analytical evaluation. Will gather technical information, procure motor components, operate various measurement and electrical test equipment, present professional reports, and provide input regarding motor performance and troubleshooting. REQUIREMENTS: Position requires a minimum 2 year t ...
... providing analytical evaluation. Will gather technical information, procure motor components, operate various measurement and electrical test equipment, present professional reports, and provide input regarding motor performance and troubleshooting. REQUIREMENTS: Position requires a minimum 2 year t ...
Presentation by Yongguo
... • Not consider PDA here • Concentrated on the speed control of motors to save energy ...
... • Not consider PDA here • Concentrated on the speed control of motors to save energy ...
bee-material-new-microsoft-office-powerpoint
... 4. The emf generated in a dc motor is called back emf because. a) It is generated in the armature. b) it opposes the direction of rotation of the motor. c) it is in a direction opposite to that of the applied voltage a) none of these. ...
... 4. The emf generated in a dc motor is called back emf because. a) It is generated in the armature. b) it opposes the direction of rotation of the motor. c) it is in a direction opposite to that of the applied voltage a) none of these. ...
Fluid Dynamics: Thrust Lesson 9 Dr. Aaron P. Wemhoff
... Simple: run current through a loop of wire in a magnetic field Current switches direction based on what side of the loop it is on Results in a pair of forces which cause torque The loop will align with the magnets but will not spin ...
... Simple: run current through a loop of wire in a magnetic field Current switches direction based on what side of the loop it is on Results in a pair of forces which cause torque The loop will align with the magnets but will not spin ...
Electric motor

An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The reverse of this would be the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy and is done by an electric generator.In normal motoring mode, most electric motors operate through the interaction between an electric motor's magnetic field and winding currents to generate force within the motor. In certain applications, such as in the transportation industry with traction motors, electric motors can operate in both motoring and generating or braking modes to also produce electrical energy from mechanical energy.Found in applications as diverse as industrial fans, blowers and pumps, machine tools, household appliances, power tools, and disk drives, electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, motor vehicles or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as from the power grid, inverters or generators. Small motors may be found in electric watches. General-purpose motors with highly standardized dimensions and characteristics provide convenient mechanical power for industrial use. The largest of electric motors are used for ship propulsion, pipeline compression and pumped-storage applications with ratings reaching 100 megawatts. Electric motors may be classified by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.Electric motors are used to produce linear or rotary force (torque), and should be distinguished from devices such as magnetic solenoids and loudspeakers that convert electricity into motion but do not generate usable mechanical powers, which are respectively referred to as actuators and transducers.