First Order Linear Differential Equations16
... Eq. (3.4-11) can be expressed in terms of the real functions by using the Euler’s identity eimx = cos(mx) + isin(mx) , and e-imx = cos(mx) - isin(mx) y = A1(cos(mx) + isin(mx)) + A2(cos(mx) - isin(mx)) y = (A1 + A2)cos(mx) + i(A1 - A2)sin(mx) y = C1cos(mx) + C2sin(mx) ...
... Eq. (3.4-11) can be expressed in terms of the real functions by using the Euler’s identity eimx = cos(mx) + isin(mx) , and e-imx = cos(mx) - isin(mx) y = A1(cos(mx) + isin(mx)) + A2(cos(mx) - isin(mx)) y = (A1 + A2)cos(mx) + i(A1 - A2)sin(mx) y = C1cos(mx) + C2sin(mx) ...
Linear Equations
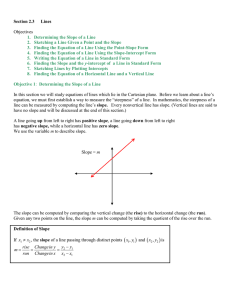
... The slope and y-intercept of a linear function The slope or gradient of a graph can be measured looking at the increase in y that results when x increases by one unit. When given a linear function in the form y = ax + c, the slope or gradient is a. If a is positive the graph slopes upwards from left ...
... The slope and y-intercept of a linear function The slope or gradient of a graph can be measured looking at the increase in y that results when x increases by one unit. When given a linear function in the form y = ax + c, the slope or gradient is a. If a is positive the graph slopes upwards from left ...
PX408: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... are described in terms of a mathematical theory of great beauty and power.” This statement is certainly true of the Dirac equation. From the simple requirement that we need a first-order relativistically invariant quantum-mechanical equation, we find that the solutions must be 4 component spinors, w ...
... are described in terms of a mathematical theory of great beauty and power.” This statement is certainly true of the Dirac equation. From the simple requirement that we need a first-order relativistically invariant quantum-mechanical equation, we find that the solutions must be 4 component spinors, w ...
Notes on Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
... We set each factor equal to 0 and solve for x. 4x + 3 = 0 or x + 2 = 0 4x = –3 or x = –2 x = –¾ or x = –2 So the x-intercepts are the points (–¾, 0) and (–2, 0). ...
... We set each factor equal to 0 and solve for x. 4x + 3 = 0 or x + 2 = 0 4x = –3 or x = –2 x = –¾ or x = –2 So the x-intercepts are the points (–¾, 0) and (–2, 0). ...
A) B - ISD 622
... B) Graph the equation in the graphing calculator and see if your (hint: enter equation (y = mx + b) go equation is correct. to table and match ordered pairs.) ...
... B) Graph the equation in the graphing calculator and see if your (hint: enter equation (y = mx + b) go equation is correct. to table and match ordered pairs.) ...
3-1 Study Guide and Intervention Solving Systems of Equations
... same variables. You can solve a system of linear equations by using a table or by graphing the equations on the same coordinate plane. If the lines intersect, the solution is that intersection point. The following chart summarizes the possibilities for graphs of two linear equations in two variables ...
... same variables. You can solve a system of linear equations by using a table or by graphing the equations on the same coordinate plane. If the lines intersect, the solution is that intersection point. The following chart summarizes the possibilities for graphs of two linear equations in two variables ...
Differential Equations 2280 Name
... 4. (Laplace Theory) (a) [40%] The solution of x000 + x0 = 0, x(0) = 1, x0 (0) = 0, x00 (0) = 0 is x(t) = 1. Show the details in Laplace’s Method for obtaining this answer. ...
... 4. (Laplace Theory) (a) [40%] The solution of x000 + x0 = 0, x(0) = 1, x0 (0) = 0, x00 (0) = 0 is x(t) = 1. Show the details in Laplace’s Method for obtaining this answer. ...