Marginal utility
... Sociologists and anthropologists have argued that social factors such as culture, customs, and religion are very important in explaining the choices consumers make. Economists have traditionally seen such factors as being relatively unimportant, if they take them into consideration at all. ...
... Sociologists and anthropologists have argued that social factors such as culture, customs, and religion are very important in explaining the choices consumers make. Economists have traditionally seen such factors as being relatively unimportant, if they take them into consideration at all. ...
IB Economics SL Unit 1: Microeconomics
... A shift in a demand or supply curve occurs when a good's quantity demanded or supplied changes even though price remains the same. For instance, if the price for a bottle of beer was $2 and the quantity of beer demanded increased from Q1 to Q2, then there would be a shift in the demand for beer. Shi ...
... A shift in a demand or supply curve occurs when a good's quantity demanded or supplied changes even though price remains the same. For instance, if the price for a bottle of beer was $2 and the quantity of beer demanded increased from Q1 to Q2, then there would be a shift in the demand for beer. Shi ...
HO3e_ch14 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... 14.4 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Use a graph to illustrate how a monopoly affects economic ...
... 14.4 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Use a graph to illustrate how a monopoly affects economic ...
Pre-Test Chapter 19 ed17
... B. marginal utility of extra soft drink cans or bottles declines slowly, particularly because they are storable and can be consumed later. C. marginal utility of extra soft drink cans or bottles declines quite rapidly. D. opportunity cost of additional cans or bottles of soft drink increase very slo ...
... B. marginal utility of extra soft drink cans or bottles declines slowly, particularly because they are storable and can be consumed later. C. marginal utility of extra soft drink cans or bottles declines quite rapidly. D. opportunity cost of additional cans or bottles of soft drink increase very slo ...
chapter overview
... (Drug addiction comes to mind.) Reason with students how this would ultimately result in a consumer spending all of his/her income on this one good. Emphasize that this is fortunately not consistent with most consumer behavior. This helps support the law of diminishing marginal utility and the proce ...
... (Drug addiction comes to mind.) Reason with students how this would ultimately result in a consumer spending all of his/her income on this one good. Emphasize that this is fortunately not consistent with most consumer behavior. This helps support the law of diminishing marginal utility and the proce ...
Chapter 6
... 12. In Exhibit 4, assume the Multiplex tickets cost $6 each, video rentals cost $2 each, and bags of popcorn cost $1 each. Suppose the consumer has $12 per week to spend on multiplex tickets, video rentals, and popcorn. In consumer equilibrium, what is the marginal utility per dollar for each of th ...
... 12. In Exhibit 4, assume the Multiplex tickets cost $6 each, video rentals cost $2 each, and bags of popcorn cost $1 each. Suppose the consumer has $12 per week to spend on multiplex tickets, video rentals, and popcorn. In consumer equilibrium, what is the marginal utility per dollar for each of th ...
Document
... This means that the model is an ‘optimising’ model: the firm attempts to achieve the best possible performance, rather than simply seeking “feasible” performance which meets some set of ...
... This means that the model is an ‘optimising’ model: the firm attempts to achieve the best possible performance, rather than simply seeking “feasible” performance which meets some set of ...
The Price System, Demand and Supply, and Elasticity
... below which exchange is not permitted. • The most common example of a price ...
... below which exchange is not permitted. • The most common example of a price ...
The Price System, Demand and Supply, and Elasticity
... below which exchange is not permitted. • The most common example of a price ...
... below which exchange is not permitted. • The most common example of a price ...
B. When the marginal utility of two goods is the same, the consumer
... A. First compute the marginal utility for each item. Second, divide the price for each item into the MU of each item. Third, the consumer purchases items according to the highest MU/$1. The result in order of purchase is 1 bag of popcorn, 1 video rental, 1 movie ticket, 1 bag of popcorn and 1 video ...
... A. First compute the marginal utility for each item. Second, divide the price for each item into the MU of each item. Third, the consumer purchases items according to the highest MU/$1. The result in order of purchase is 1 bag of popcorn, 1 video rental, 1 movie ticket, 1 bag of popcorn and 1 video ...
Chapter 3
... change in price making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods that are substitutes. Income effect The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the effect of a change in the good’s price on consumer purchasing power. © 2006 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Economi ...
... change in price making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods that are substitutes. Income effect The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the effect of a change in the good’s price on consumer purchasing power. © 2006 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Economi ...
Working paper 4 - University of South Australia
... being unambiguously positive. That is, when the costs of gambling activities (such as family breakdowns and job absenteeism) are compared with the benefits of gambling (which includes the entertainment derived from engaging in gambling activities), the findings of the draft report suggested that Aus ...
... being unambiguously positive. That is, when the costs of gambling activities (such as family breakdowns and job absenteeism) are compared with the benefits of gambling (which includes the entertainment derived from engaging in gambling activities), the findings of the draft report suggested that Aus ...
Second Degree Price Discrimination
... First try: Sell the maximum quantity the consumer will purchase, at a price equal to all the area under the individual consumer’s demand curve. For Type B consumers this means a quantity of 1000 and a price of (10 x 1000)/2 = $5,000. For Type A consumers, this means a quantity of 500 at a price of ( ...
... First try: Sell the maximum quantity the consumer will purchase, at a price equal to all the area under the individual consumer’s demand curve. For Type B consumers this means a quantity of 1000 and a price of (10 x 1000)/2 = $5,000. For Type A consumers, this means a quantity of 500 at a price of ( ...
Document
... Chapter 6 Consumer Choice Theory • Key Concepts • Summary • Practice Quiz • Internet Exercises ©2002 South-Western College Publishing ...
... Chapter 6 Consumer Choice Theory • Key Concepts • Summary • Practice Quiz • Internet Exercises ©2002 South-Western College Publishing ...
What is Marginal Utility? - Choose your book for Principles of
... Are White Rats Rational Consumers? There is evidence that lab rats make consumer choices based on MU/P. • Economists Battalio and Kagel found that white lab rats respond to price and income changes in a manner consistent with economic theory. ...
... Are White Rats Rational Consumers? There is evidence that lab rats make consumer choices based on MU/P. • Economists Battalio and Kagel found that white lab rats respond to price and income changes in a manner consistent with economic theory. ...
Principles of Economics Third Edition by Fred Gottheil
... Are White Rats Rational Consumers? There is evidence that lab rats make consumer choices based on MU/P. • Economists Battalio and Kagel found that white lab rats respond to price and income changes in a manner consistent with economic theory. ...
... Are White Rats Rational Consumers? There is evidence that lab rats make consumer choices based on MU/P. • Economists Battalio and Kagel found that white lab rats respond to price and income changes in a manner consistent with economic theory. ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,8e
... to the industry, producing virtually identical products and in which no firm is large enough to have any control over prices. In perfectly competitive industries, new competitors can freely enter and exit the market. homogeneous products Undifferentiated products; products that are identical to, or ...
... to the industry, producing virtually identical products and in which no firm is large enough to have any control over prices. In perfectly competitive industries, new competitors can freely enter and exit the market. homogeneous products Undifferentiated products; products that are identical to, or ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MANUFACTURER LIABILITY FOR HARMS Bruce Hay
... consumer heterogeneity. Importantly, the representative consumer' s inverse demand curve P (q) can be easily reinterpreted as representing a continuum of consumers who differ in the value they place on consuming a single unit of the good. ...
... consumer heterogeneity. Importantly, the representative consumer' s inverse demand curve P (q) can be easily reinterpreted as representing a continuum of consumers who differ in the value they place on consuming a single unit of the good. ...
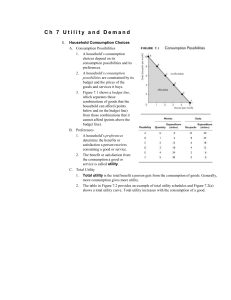
utlity and demand 1 Ch 7 Utility and Demand I. Household
... utility from movies by more than it decreases the total utility from soda, so total utility increases. b) Similarly, if MUS/PS > MUM/PM,then moving a dollar from movies to soda increases the total utility from soda by more than it decreases the total utility from movies, so total utility increases. ...
... utility from movies by more than it decreases the total utility from soda, so total utility increases. b) Similarly, if MUS/PS > MUM/PM,then moving a dollar from movies to soda increases the total utility from soda by more than it decreases the total utility from movies, so total utility increases. ...
26 Writing it up, writing it down: being reflexive in accounts of
... Notes: Standpoint theory is probably one of the most controversial theories in feminist studies I summarize below some of the issues raised by Harding (2004).Its origins can be traced to a period when women felt that they had been treated primarily as the object and not the subject of knowledge proj ...
... Notes: Standpoint theory is probably one of the most controversial theories in feminist studies I summarize below some of the issues raised by Harding (2004).Its origins can be traced to a period when women felt that they had been treated primarily as the object and not the subject of knowledge proj ...
Regulatory Equilibrium - The Center for Regulatory Effectiveness
... This content downloaded from 98.169.114.155 on Sun, 27 Mar 2016 19:58:37 UTC All use subject to http://about.jstor.org/terms ...
... This content downloaded from 98.169.114.155 on Sun, 27 Mar 2016 19:58:37 UTC All use subject to http://about.jstor.org/terms ...
The Relationship between Consumer Price and Producer Price
... relationship, there is a bidirectional relationship, there is a unidirectional relationship from PPI to CPI, and there is a unidirectional relationship from CPI to PPI. All these four possibilities are shown in the previous studies Akcay, 2011 and Tiwari, 2012). On the other hand, the unidirectional ...
... relationship, there is a bidirectional relationship, there is a unidirectional relationship from PPI to CPI, and there is a unidirectional relationship from CPI to PPI. All these four possibilities are shown in the previous studies Akcay, 2011 and Tiwari, 2012). On the other hand, the unidirectional ...
Topic 4. Utility and consumer choice
... Utility is a measure of the benefit or satisfaction that consumers get from a good or service. (19th century concept) Total utility (TU): the benefit or satisfaction that consumer gets from consuming a particular quantity of a good or service Marginal utility (MU): the increase in total utility obta ...
... Utility is a measure of the benefit or satisfaction that consumers get from a good or service. (19th century concept) Total utility (TU): the benefit or satisfaction that consumer gets from consuming a particular quantity of a good or service Marginal utility (MU): the increase in total utility obta ...