Viruses & Bacteria
... • By the way they move. • By the way they obtain energy. – Most are Heterotrophes which obtain energy by ...
... • By the way they move. • By the way they obtain energy. – Most are Heterotrophes which obtain energy by ...
Family Enterobacteriaceae
... to nitrite, although exceptions exist (e.g. Photorhabdus). Unlike most similar bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae generally lack cytochrome C oxidase, although there are exceptions (e.g. Plesiomonas shigelloides). Most have many flagella used to move about, but a few genera are non-motile. They are non-sp ...
... to nitrite, although exceptions exist (e.g. Photorhabdus). Unlike most similar bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae generally lack cytochrome C oxidase, although there are exceptions (e.g. Plesiomonas shigelloides). Most have many flagella used to move about, but a few genera are non-motile. They are non-sp ...
Final Microbial Physiology
... grows in an anaerobic mode -- can tolerate oxygen and grow in its presence even though they cannot ...
... grows in an anaerobic mode -- can tolerate oxygen and grow in its presence even though they cannot ...
Bacteria Webquest
... Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm http://whyfiles.org/038badbugs/mechanism.html http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/endospores.html 19. What is penicillin? How does it work? 20. What is a plasmid? How does this allow for antibiotic resistance? 21. How can some ...
... Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm http://whyfiles.org/038badbugs/mechanism.html http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/endospores.html 19. What is penicillin? How does it work? 20. What is a plasmid? How does this allow for antibiotic resistance? 21. How can some ...
2.4 Bacteria - gooyers3cbiology
... Bacteria that cause tuberculosis are aerobic organisms. Other bacteria are anaerobic and can only grow in the absence of oxygen. Organisms causing gangrene, tetanus, and botulism are anaerobic organisms. Many bacteria can survive and grow with or without oxygen. E. coli, the bacterium in Figure 4, i ...
... Bacteria that cause tuberculosis are aerobic organisms. Other bacteria are anaerobic and can only grow in the absence of oxygen. Organisms causing gangrene, tetanus, and botulism are anaerobic organisms. Many bacteria can survive and grow with or without oxygen. E. coli, the bacterium in Figure 4, i ...
01 Role of microbiology in the dentist`sl practice
... Heterotroph – must obtain carbon in an organic form made by other living organisms such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids Autotroph - an organism that uses CO2, an inorganic gas as its carbon source ...
... Heterotroph – must obtain carbon in an organic form made by other living organisms such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids Autotroph - an organism that uses CO2, an inorganic gas as its carbon source ...
Test #2 Results by Next Week Chapter 10: Biological Productivity
... – Many of the elements in seawater are utilized by marine organisms for growth. – Salinity tolerance is also important in limiting distribution. ...
... – Many of the elements in seawater are utilized by marine organisms for growth. – Salinity tolerance is also important in limiting distribution. ...
Outline
... B. Other conditions (table 11.1, page 337) 1. Temperature 2. Pressure 3. Salinity 4. Dissolved oxygen C. The abyssal plain vs. trenches ...
... B. Other conditions (table 11.1, page 337) 1. Temperature 2. Pressure 3. Salinity 4. Dissolved oxygen C. The abyssal plain vs. trenches ...
Cell Organelles and Biotechnology
... cell at some time in the distant past. The larger cell would have gained the ability to make its own food, and have a greater ability to break down foods by cellular respiration. The smaller bacterial cells would have gained the food-gathering ability of the larger cells. We have some evidence for t ...
... cell at some time in the distant past. The larger cell would have gained the ability to make its own food, and have a greater ability to break down foods by cellular respiration. The smaller bacterial cells would have gained the food-gathering ability of the larger cells. We have some evidence for t ...
Hydrothermal Vent Fast Facts
... The first hydrothermal vent (long suspected to exist) was discovered in 1977 when scientists used Alvin to descend 2.5 km below sea level near the Galapagos Islands. The high abundance of life found at the vents was surprising to scientists. Photosynthesis is not the only way that food is produced i ...
... The first hydrothermal vent (long suspected to exist) was discovered in 1977 when scientists used Alvin to descend 2.5 km below sea level near the Galapagos Islands. The high abundance of life found at the vents was surprising to scientists. Photosynthesis is not the only way that food is produced i ...
Microbes SLOs - Miss Jan`s Science Wikispace
... explain the characteristic S-shaped curve for population growth of bacteria Lesson 3 – Culturing Bacteria describe the process used to culture bacteria describe the safety conditions needed when culturing bacteria describe the conditions that bacteria grow best in explain why the incubated ...
... explain the characteristic S-shaped curve for population growth of bacteria Lesson 3 – Culturing Bacteria describe the process used to culture bacteria describe the safety conditions needed when culturing bacteria describe the conditions that bacteria grow best in explain why the incubated ...
MICROBIOLOGY
... describes clustered arrangement of cells and golden yellow color of colonies Escherichia coli Honors the discoverer, Theodor Escherich and describes its habitat, the colon. After the first use, scientific names may be abbreviated with the first letter of the genus and full species epithet. (Ex: E. c ...
... describes clustered arrangement of cells and golden yellow color of colonies Escherichia coli Honors the discoverer, Theodor Escherich and describes its habitat, the colon. After the first use, scientific names may be abbreviated with the first letter of the genus and full species epithet. (Ex: E. c ...
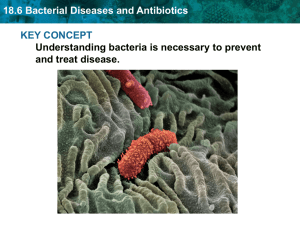
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics KEY CONCEPT
... 18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics Bacteria can evolve resistance to antibiotics. • Bacteria are gaining resistance to antibiotics. A bacterium carries – overuse genes for antibiotic resistance on a plasmid. – underuse – misuse A copy of the plasmid is ...
... 18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics Bacteria can evolve resistance to antibiotics. • Bacteria are gaining resistance to antibiotics. A bacterium carries – overuse genes for antibiotic resistance on a plasmid. – underuse – misuse A copy of the plasmid is ...
Science Introduction
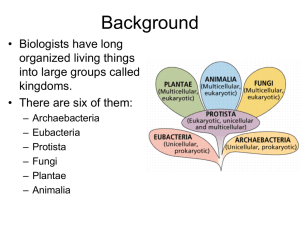
... 2. Relate the levels of classification to the relationships between organisms. 3. List characteristics used to classify organism into groups, including domains and kingdoms. 2-2 Classifying Organisms A. Why do Scientists Classify? There are more than 1 million species of organisms identified – sti ...
... 2. Relate the levels of classification to the relationships between organisms. 3. List characteristics used to classify organism into groups, including domains and kingdoms. 2-2 Classifying Organisms A. Why do Scientists Classify? There are more than 1 million species of organisms identified – sti ...
Bacteria and Archaea
... Chapter 27 • Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms • Most prokaryotes are microscopic, but what they lack in size they make up for in numbers • There are more in a handful of fertile soil than the number of people who have eve ...
... Chapter 27 • Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms • Most prokaryotes are microscopic, but what they lack in size they make up for in numbers • There are more in a handful of fertile soil than the number of people who have eve ...
Section 2-Bacteria
... Decomposers are organisms that break down large organisms into small chemicals. They are known as nature’s ...
... Decomposers are organisms that break down large organisms into small chemicals. They are known as nature’s ...
Document
... Binary Fission is like mitosis but produce a COMPLETELY new organism! (Not just a new part of an organism) Can reproduce and grow very quickly – thousands of new bacteria within ...
... Binary Fission is like mitosis but produce a COMPLETELY new organism! (Not just a new part of an organism) Can reproduce and grow very quickly – thousands of new bacteria within ...
Growing, growing, gone…
... Obligate aerobes- completely dependent on atmospheric O2 for growth. Facultative anaerobes- do not require O2 for growth, but grow better in its presence. Aerotolerant anaerobes- grow equally well in the presence or absence of O2. Strict anaerobes- do not tolerate O2 at all and die it its presence. ...
... Obligate aerobes- completely dependent on atmospheric O2 for growth. Facultative anaerobes- do not require O2 for growth, but grow better in its presence. Aerotolerant anaerobes- grow equally well in the presence or absence of O2. Strict anaerobes- do not tolerate O2 at all and die it its presence. ...
Archae and Bacteria ppt
... geysers. Hot springs are pools of hot water that have moved toward earth's surface. The source of their heat is the hot magma beneath and they can reach temperatures as high as 400 degrees Fahrenheit ...
... geysers. Hot springs are pools of hot water that have moved toward earth's surface. The source of their heat is the hot magma beneath and they can reach temperatures as high as 400 degrees Fahrenheit ...
General Microbiology 130 Fall 2007
... 3) Reproduce quickly (some 20 minutes), can be used for gene transfer Scientists have achieved great success in understanding life processes, and disease control by studying microbes ...
... 3) Reproduce quickly (some 20 minutes), can be used for gene transfer Scientists have achieved great success in understanding life processes, and disease control by studying microbes ...
What barriers exist to prevent infection by viruses/bacteria/other
... binds to and colonizes the gastrointestinal tract causing diarrhea. ...
... binds to and colonizes the gastrointestinal tract causing diarrhea. ...
Slide 1
... microbial diversity and habitats • habitat diversity – unique C and E sources – metabolic strategies •fermentation respiration • heterotrophy phototrophy •symbioses – ruminants – mycorrhizae – extreme environments •pH •temperature •salinity •pressure ...
... microbial diversity and habitats • habitat diversity – unique C and E sources – metabolic strategies •fermentation respiration • heterotrophy phototrophy •symbioses – ruminants – mycorrhizae – extreme environments •pH •temperature •salinity •pressure ...