
Biology 20 Diversity of Life PowerPoint part 2.pps
... 3. In what ways are cilia and flagella similar? How are they different? - Cilia and flagella are both used for movement in protists. Both are formed from the cell membrane and are permanent structures. However, cilia are shorter and more hair like and can be in rows or clusters that cover parts of a ...
... 3. In what ways are cilia and flagella similar? How are they different? - Cilia and flagella are both used for movement in protists. Both are formed from the cell membrane and are permanent structures. However, cilia are shorter and more hair like and can be in rows or clusters that cover parts of a ...
m L
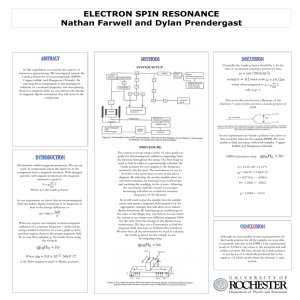
... For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the direction of the internal field, Bint. The state with ms aligned with Bint has a lower energy than ms anti-aligned (ms = spin magnetic dipole mo ...
... For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the direction of the internal field, Bint. The state with ms aligned with Bint has a lower energy than ms anti-aligned (ms = spin magnetic dipole mo ...
Poster: ESR
... Lande g-factor for our samples is the frequency emitted by the klystron. The instrument we use to find this is the wavemeter as seen in the above diagram. By adjusting the nearby tunable short we can find resonance, by hooking in an oscilloscope and watching the readings, in the system. Adjusting th ...
... Lande g-factor for our samples is the frequency emitted by the klystron. The instrument we use to find this is the wavemeter as seen in the above diagram. By adjusting the nearby tunable short we can find resonance, by hooking in an oscilloscope and watching the readings, in the system. Adjusting th ...
Lesson 16 - Magnetic Fields III
... By choosing the zero potential energy reference point when the fields are perpendicular, we have that the potential energy for a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field is ...
... By choosing the zero potential energy reference point when the fields are perpendicular, we have that the potential energy for a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field is ...
Magnetism - Physical Science
... – 2. Magnetic domains—groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles. • A) In a magnet, the like poles of all the domains point in the same direction. • B) Permanent magnets are made by placing a magnetic material in a strong magnetic field, forcing a large number of magnetic domains to line up. ...
... – 2. Magnetic domains—groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles. • A) In a magnet, the like poles of all the domains point in the same direction. • B) Permanent magnets are made by placing a magnetic material in a strong magnetic field, forcing a large number of magnetic domains to line up. ...
Chapter 12: Magnetism and Magnetic Circuits
... The Nature of a Magnetic Field • Magnetism – Force of attraction or repulsion that acts between magnets and other magnetic materials ...
... The Nature of a Magnetic Field • Magnetism – Force of attraction or repulsion that acts between magnets and other magnetic materials ...
Chapter 4 - Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... C. Diagnostic Scheme -- Medically Important Bacteria An adaptation of the phenotypic scheme – Bacteria are identified by morphology, arrangement, differential and structural staining, colony characteristics, biochemical analysis, serological typing and genetic and molecular identification methods. D ...
... C. Diagnostic Scheme -- Medically Important Bacteria An adaptation of the phenotypic scheme – Bacteria are identified by morphology, arrangement, differential and structural staining, colony characteristics, biochemical analysis, serological typing and genetic and molecular identification methods. D ...
Microbial Growth CHAPTER 6 MICROBIAL GROWTH
... – In amino acids, proteins – Most bacteria decompose proteins – Some bacteria use NH4+ or NO3− – A few bacteria use N2 in nitrogen fixation ...
... – In amino acids, proteins – Most bacteria decompose proteins – Some bacteria use NH4+ or NO3− – A few bacteria use N2 in nitrogen fixation ...
M - BIAC – Duke
... • NMR measures magnetization of atomic nuclei in the presence of magnetic fields • Magnetization can be manipulated by manipulating the magnetic fields (this is how we get images) • Static magnetic fields don’t change (< 0.1 ppm / hr): The main field is static and (nearly) homogeneous • RF (radio fr ...
... • NMR measures magnetization of atomic nuclei in the presence of magnetic fields • Magnetization can be manipulated by manipulating the magnetic fields (this is how we get images) • Static magnetic fields don’t change (< 0.1 ppm / hr): The main field is static and (nearly) homogeneous • RF (radio fr ...
Unit 14* Magnetic Induction
... of induced voltage are: a. the number of turns of wire. b. the strength of the magnetic field. c. the speed of the magnetic flux cutting ...
... of induced voltage are: a. the number of turns of wire. b. the strength of the magnetic field. c. the speed of the magnetic flux cutting ...
Magnetism Review
... when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
... when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
chapter24b
... Charged particles in the solar wind can collide with particles in Earth's atmosphere, especially near the north and south magnetic poles. When they do, they excite atoms which then return to ground state, emitting light. We see the eerie streaming flows of color that result. They are called the auro ...
... Charged particles in the solar wind can collide with particles in Earth's atmosphere, especially near the north and south magnetic poles. When they do, they excite atoms which then return to ground state, emitting light. We see the eerie streaming flows of color that result. They are called the auro ...
lecture 27 magnetic fields
... If there are multiple sources of magnetic field, the magnetic field at a particular location is the superposition of magnetic field due to each source. ! Since magnetic field is a vector quantity, you need to add magnetic field vectorially. ...
... If there are multiple sources of magnetic field, the magnetic field at a particular location is the superposition of magnetic field due to each source. ! Since magnetic field is a vector quantity, you need to add magnetic field vectorially. ...
Spore Forming and Non-Spore Forming Gram
... • Small/Short, G+,peritrichous flagella, rod. Grow on Mueller-Hinton agar (better in sheep bloodsmall zone of haemolysis); facultative anaerobe, motile at room temp, catalase + • Listeriosis results from ingestion of contaminated food such as cheese and vegie; primarily affects pregnant women, newbo ...
... • Small/Short, G+,peritrichous flagella, rod. Grow on Mueller-Hinton agar (better in sheep bloodsmall zone of haemolysis); facultative anaerobe, motile at room temp, catalase + • Listeriosis results from ingestion of contaminated food such as cheese and vegie; primarily affects pregnant women, newbo ...
Center of trifold poster
... from particle motion in the magnetosphere is very available magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) difficult. code to move a number of charged particles • Electronic equipment, such as on satellites and while neglecting their own fields, energy orbiting telescopes, can be damaged by depositions, and relativisti ...
... from particle motion in the magnetosphere is very available magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) difficult. code to move a number of charged particles • Electronic equipment, such as on satellites and while neglecting their own fields, energy orbiting telescopes, can be damaged by depositions, and relativisti ...
ch-6 [Magnetism]
... Magnetism • Magnetism was known from long times ago • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magneti ...
... Magnetism • Magnetism was known from long times ago • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magneti ...
classification of magnetic mate
... temperature and applied field. If the applied magnetic energy is greater than the thermal energy, the magnetic moment of the material is finite and large. The number of orientations of orbital and spin magnetic moments be such that the vector sum of magnetic moments is not zero and there is a resul ...
... temperature and applied field. If the applied magnetic energy is greater than the thermal energy, the magnetic moment of the material is finite and large. The number of orientations of orbital and spin magnetic moments be such that the vector sum of magnetic moments is not zero and there is a resul ...
PHYS_3342_111511
... produces uniform longitudinal field in the interior and almost no field outside For the path in an ideal solenoid: BL 0nIL B 0nI (n turns of the coil per unit length) ...
... produces uniform longitudinal field in the interior and almost no field outside For the path in an ideal solenoid: BL 0nIL B 0nI (n turns of the coil per unit length) ...




















![ch-6 [Magnetism]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366853_1-cbc1ce7a74752c20e1a6e456bd1e46ed-300x300.png)

