Drosophila Immunity: Analysis of PGRP-SB1 Expression, Enzymatic Activity and Function
... after injection of the Gram-negative bacteria Erwinia carotovora, Gram-positive Listeria monocytogenes or Gram-positive M. luteus. PGRP-SB1 expression was strongly induced 4 h after infection with E. carotovora or L. monocytogenes, both of which contain DAP-type PGN, and remained sustained during th ...
... after injection of the Gram-negative bacteria Erwinia carotovora, Gram-positive Listeria monocytogenes or Gram-positive M. luteus. PGRP-SB1 expression was strongly induced 4 h after infection with E. carotovora or L. monocytogenes, both of which contain DAP-type PGN, and remained sustained during th ...
Microbiology
... Adhere to complementary receptors on the host cells. Adhesins can be part of: Glycocalyx: e.g.Streptococcus mutans Fimbriae (also pili and flagella): e.g.E. coli Host cell receptors are most commonly sugars (e.g. mannose for E. coli Biofilms provide attachment and resistance to antimicrobial age ...
... Adhere to complementary receptors on the host cells. Adhesins can be part of: Glycocalyx: e.g.Streptococcus mutans Fimbriae (also pili and flagella): e.g.E. coli Host cell receptors are most commonly sugars (e.g. mannose for E. coli Biofilms provide attachment and resistance to antimicrobial age ...
FLUID, PLEURAL FLUID AND SYNOVIAL FLUID AT KENYATTA
... suppresses their multiplication or growth. Antibiotic susceptibility is the inhibition of growth or killing of bacteria by use of antibiotics. Acquisition of Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is resistance of a microorganism to an antimicrobial agent to which it was originally sensitive. Resistant orga ...
... suppresses their multiplication or growth. Antibiotic susceptibility is the inhibition of growth or killing of bacteria by use of antibiotics. Acquisition of Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is resistance of a microorganism to an antimicrobial agent to which it was originally sensitive. Resistant orga ...
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
... Adhere to complementary receptors on the host cells. Adhesins can be part of: Glycocalyx: e.g.Streptococcus mutans Fimbriae (also pili and flagella): e.g.E. coli Host cell receptors are most commonly sugars (e.g. mannose for E. coli Biofilms provide attachment and resistance to antimicrobial age ...
... Adhere to complementary receptors on the host cells. Adhesins can be part of: Glycocalyx: e.g.Streptococcus mutans Fimbriae (also pili and flagella): e.g.E. coli Host cell receptors are most commonly sugars (e.g. mannose for E. coli Biofilms provide attachment and resistance to antimicrobial age ...
MS Word - Nano
... applications in cancer treatment, and silver nanoparticles are found to have antimicrobial properties. Though there is a serious lack of information to describe the mechanism in which the silver nanoparticles actually prevent bacterial growth, most research points to interactions with the bacterial ...
... applications in cancer treatment, and silver nanoparticles are found to have antimicrobial properties. Though there is a serious lack of information to describe the mechanism in which the silver nanoparticles actually prevent bacterial growth, most research points to interactions with the bacterial ...
asexual reproduction teacher copy
... -- all individuals can produce offspring directly -- can occur rapidly; rapid exploitation of resources -- saves energy and resources (no gonads or gametes, no finding mates, no courtship, no STDs, no males) 2. disadvantages -- no genetic variability in offspring (except for random mutations) -- lim ...
... -- all individuals can produce offspring directly -- can occur rapidly; rapid exploitation of resources -- saves energy and resources (no gonads or gametes, no finding mates, no courtship, no STDs, no males) 2. disadvantages -- no genetic variability in offspring (except for random mutations) -- lim ...
Succession of bacterivorous protists on laboratory
... low food abundances found there (Caron, 1991). Ciliates appeared later in time, probably because they need high abundances of bacterial or flagellate prey. Therefore, they may play a pivotal role in structuring the detrital communities, because, as previously suggested by other authors (Silver etal. ...
... low food abundances found there (Caron, 1991). Ciliates appeared later in time, probably because they need high abundances of bacterial or flagellate prey. Therefore, they may play a pivotal role in structuring the detrital communities, because, as previously suggested by other authors (Silver etal. ...
asexual reproduction teacher copy
... -- all individuals can produce offspring directly -- can occur rapidly; rapid exploitation of resources -- saves energy and resources (no gonads or gametes, no finding mates, no courtship, no STDs, no males) 2. disadvantages -- no genetic variability in offspring (except for random mutations) -- lim ...
... -- all individuals can produce offspring directly -- can occur rapidly; rapid exploitation of resources -- saves energy and resources (no gonads or gametes, no finding mates, no courtship, no STDs, no males) 2. disadvantages -- no genetic variability in offspring (except for random mutations) -- lim ...
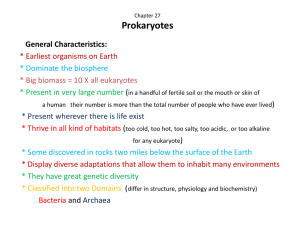
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes
... • Outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria makes them more resistant to antibiotics, than gram-positive species • The outer membrane impedes entry of the drugs • Many antibiotics, including penicillin, inhibit the synthesis of cross-links in peptidoglycans, preventing the formation of a functional w ...
... • Outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria makes them more resistant to antibiotics, than gram-positive species • The outer membrane impedes entry of the drugs • Many antibiotics, including penicillin, inhibit the synthesis of cross-links in peptidoglycans, preventing the formation of a functional w ...
The Prokaryotes
... medium and incubation for 24–48 h, cultures are streaked out on solid JNFb medium containing 20 mg of yeast extract per liter and three times the bromothymol blue concentration of the JNFb medium. Herbaspirillum seropedicae and H. rubrisubalbicans form small moist white colonies with a green or dark ...
... medium and incubation for 24–48 h, cultures are streaked out on solid JNFb medium containing 20 mg of yeast extract per liter and three times the bromothymol blue concentration of the JNFb medium. Herbaspirillum seropedicae and H. rubrisubalbicans form small moist white colonies with a green or dark ...
Slide 1 - UAB School of Optometry
... We will use the same format as before in terms of talking about the organisms and their characteristics, the epidemiology of their diseases, how they produce diseases, and how we detect and identify them. Slide 3 The first one we are going to talk about is Haemophilus, which means “blood-loving.” It ...
... We will use the same format as before in terms of talking about the organisms and their characteristics, the epidemiology of their diseases, how they produce diseases, and how we detect and identify them. Slide 3 The first one we are going to talk about is Haemophilus, which means “blood-loving.” It ...
Simocephalus serrulatus
... group. Due to the short span of the experiment and the use of a cultured specimen that is not directly representative of the population, the data cannot say conclusively that E. coli negatively affects the reproduction of Simocephalus serrulatus. With these errors, results of both graphs indicated t ...
... group. Due to the short span of the experiment and the use of a cultured specimen that is not directly representative of the population, the data cannot say conclusively that E. coli negatively affects the reproduction of Simocephalus serrulatus. With these errors, results of both graphs indicated t ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... bona fide tubular infection threads that disseminate them fur- ...
... bona fide tubular infection threads that disseminate them fur- ...
09 anaerobic bacteria
... 8. Discuss antimicrobial susceptibility testing of anaerobes including methods and antimicrobial agents to be tested. 9. Describe the major approaches to treat anaerobicassociated diseases either medical or surgical. ...
... 8. Discuss antimicrobial susceptibility testing of anaerobes including methods and antimicrobial agents to be tested. 9. Describe the major approaches to treat anaerobicassociated diseases either medical or surgical. ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... Aminoglycosides are compounds that are characterised by the presences of an aminocyclitol ring linked to amino-sugars in their structure. Those that are derived from bacteria of the Streptomyces genus are named with the suffix –mycin (e.g streptomycin, neomycin, tobramycin etc), whereas those that a ...
... Aminoglycosides are compounds that are characterised by the presences of an aminocyclitol ring linked to amino-sugars in their structure. Those that are derived from bacteria of the Streptomyces genus are named with the suffix –mycin (e.g streptomycin, neomycin, tobramycin etc), whereas those that a ...
Boils - British Association of Dermatologists
... Yes. Infections caused by S. aureus settle with treatment. Sometimes severe or recurrent boils are caused by a type of bacteria called PVL staphylococcus which may need different antibiotics – please ask your doctor about this type of infection (see Patient Information Leaflet on PVL Staphylococcus ...
... Yes. Infections caused by S. aureus settle with treatment. Sometimes severe or recurrent boils are caused by a type of bacteria called PVL staphylococcus which may need different antibiotics – please ask your doctor about this type of infection (see Patient Information Leaflet on PVL Staphylococcus ...
Assessment Report - Nexus Research Group
... exhibit smooth colony morphology. Also, without knowing the temperature of incubation, or the type of agar being used, deducing the type of organism in colony C would be very difficult without making wrong assumptions such as those above. By the statement in the assessment schedule this would have d ...
... exhibit smooth colony morphology. Also, without knowing the temperature of incubation, or the type of agar being used, deducing the type of organism in colony C would be very difficult without making wrong assumptions such as those above. By the statement in the assessment schedule this would have d ...
UExcel® Official Content Guide for Microbiology
... sample the entire content of the exam and are not intended to serve as an entire practice test. ...
... sample the entire content of the exam and are not intended to serve as an entire practice test. ...
Antimicrobial resistance
... mechanism which governs a higher minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) than the original or wild bacteria – epidemiological definition: any group of bacterial strains which can be distinguished from the normal (Gauss) distribution of MICs to an antibiotic. Bacterial resistance to a particular antib ...
... mechanism which governs a higher minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) than the original or wild bacteria – epidemiological definition: any group of bacterial strains which can be distinguished from the normal (Gauss) distribution of MICs to an antibiotic. Bacterial resistance to a particular antib ...
Limitations of phage therapy
... There is an urgent need to develop new classes of antibiotics to tackle the increase in resistance in many common bacterial pathogens. Pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis, which are each capable of causing severe and even fatal infections , hav ...
... There is an urgent need to develop new classes of antibiotics to tackle the increase in resistance in many common bacterial pathogens. Pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis, which are each capable of causing severe and even fatal infections , hav ...
antimicrobial drug discovery through bacteriophage genomics
... There is an urgent need to develop new classes of antibiotics to tackle the increase in resistance in many common bacterial pathogens. Pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis, which are each capable of causing severe and even fatal infections , hav ...
... There is an urgent need to develop new classes of antibiotics to tackle the increase in resistance in many common bacterial pathogens. Pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis, which are each capable of causing severe and even fatal infections , hav ...
Microbial Growth PowerPoint
... duplicates all its genetic material B) DNA copies move to opposite ends of parent and attach to a section of the cell membrane as it begins to pinch together at the center ...
... duplicates all its genetic material B) DNA copies move to opposite ends of parent and attach to a section of the cell membrane as it begins to pinch together at the center ...
Medical Microbiology Syllabus (2010)
... The aim of Medical Microbiology course is to introduce basic principles and application relevance of clinical disease for students who are in preparation for physicians. The content of rigorous course includes many etiological agents responsible for global infectious diseases. It covers all biology ...
... The aim of Medical Microbiology course is to introduce basic principles and application relevance of clinical disease for students who are in preparation for physicians. The content of rigorous course includes many etiological agents responsible for global infectious diseases. It covers all biology ...
PHYSICAL AGENTS TO CONTROL MICROORGANISMS
... a. The term disinfectant is used for an agent used to disinfect inanimate objects or surfaces but is generally to toxic to use on human tissues. b. The term antiseptic refers to an agent that kills or inhibits growth of microbes but is safe to use on human tissue. c. The term sanitizer describes an ...
... a. The term disinfectant is used for an agent used to disinfect inanimate objects or surfaces but is generally to toxic to use on human tissues. b. The term antiseptic refers to an agent that kills or inhibits growth of microbes but is safe to use on human tissue. c. The term sanitizer describes an ...
Thermal Lysis of Bacterial Membranes and Its
... chloramphenicol, Streptococcus faecalis incorporates [14C]glycineinto the free amino acid pool only and this compound is retained when the organisms are incubated in buffer at 0" or 37" (Brock & Moo-Penn, 1962). Whole bacteria containing r4C]glycine in their pools can thus be used to study the effec ...
... chloramphenicol, Streptococcus faecalis incorporates [14C]glycineinto the free amino acid pool only and this compound is retained when the organisms are incubated in buffer at 0" or 37" (Brock & Moo-Penn, 1962). Whole bacteria containing r4C]glycine in their pools can thus be used to study the effec ...