Antimicrobial efficacy of the Clave® Connector using silver
... Intravenous (IV) therapy is the primary route for therapeutic regimens in the acute care setting. Nearly all hospitalized patients have some type of vascular access device inserted to support their treatment. As reliance on the IV pathway has increased, the potential for accidental needlestick injur ...
... Intravenous (IV) therapy is the primary route for therapeutic regimens in the acute care setting. Nearly all hospitalized patients have some type of vascular access device inserted to support their treatment. As reliance on the IV pathway has increased, the potential for accidental needlestick injur ...
LAB 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques II I. Differential Stains: Gram
... commonly used in the microbiology laboratory that differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure. Most bacteria can be divided into two groups based on the composition of their cell wall: 1) Gram-positive cell walls have a thick peptidoglycan layer beyond the plasma membrane. Char ...
... commonly used in the microbiology laboratory that differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure. Most bacteria can be divided into two groups based on the composition of their cell wall: 1) Gram-positive cell walls have a thick peptidoglycan layer beyond the plasma membrane. Char ...
An Analysis of Human Pathogens Found in Horse/Mule Manure
... proportion of different organisms was unique to each sample. In addition, within a given stretch of 10 miles, manure samples with different morphologic characteristics and of different ages were collected. Finally, it is possible that because of extreme heat, cold, and intense sunlight, certain path ...
... proportion of different organisms was unique to each sample. In addition, within a given stretch of 10 miles, manure samples with different morphologic characteristics and of different ages were collected. Finally, it is possible that because of extreme heat, cold, and intense sunlight, certain path ...
Ch. 16 Presentation
... circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which replicate independently of the chromosome. ...
... circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which replicate independently of the chromosome. ...
UV toothbrush sterilizer
... The UV toothbrush sterilizer reduces your exposure to harmful bacteria and viruses, by sterilizing one of the most common breeding grounds: your toothbrush. Harmful bacteria and viruses living on your toothbrush are transferred to your mouth every time you brush your teeth. This can trigger a range ...
... The UV toothbrush sterilizer reduces your exposure to harmful bacteria and viruses, by sterilizing one of the most common breeding grounds: your toothbrush. Harmful bacteria and viruses living on your toothbrush are transferred to your mouth every time you brush your teeth. This can trigger a range ...
Document
... The abundance of lactose in the medium compared to glucose allows for differentiation of fermentation of one sugar against that of both sugars. Since lactose is a disaccharide (glucose and galactose) if lactose is fermented then glucose must be fermented too. Thus distinction is made between fermen ...
... The abundance of lactose in the medium compared to glucose allows for differentiation of fermentation of one sugar against that of both sugars. Since lactose is a disaccharide (glucose and galactose) if lactose is fermented then glucose must be fermented too. Thus distinction is made between fermen ...
General Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease
... evaluation, testing, and grading policies; expectations; BlackBoard structure. ...
... evaluation, testing, and grading policies; expectations; BlackBoard structure. ...
Document
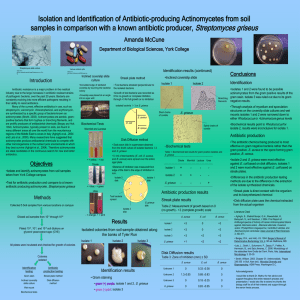
... Antibiotic resistance is a major problem in the medical industry due to the large increases in antibiotic resistant strains of pathogenic bacteria, over the past 20 years. Bacteria are constantly evolving into more efficient pathogens resulting in their ability to resist antibiotics. Many of the cur ...
... Antibiotic resistance is a major problem in the medical industry due to the large increases in antibiotic resistant strains of pathogenic bacteria, over the past 20 years. Bacteria are constantly evolving into more efficient pathogens resulting in their ability to resist antibiotics. Many of the cur ...
Future Microbiology
... NADPH oxidase produces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which reacts with Cu(I) and Fe(II) to generate hydroxyl radical (·OH) and hydroxyl anion (OH -), which are highly toxic for bacteria. Cu(I) flux into cell occurs through the Ctr1 plasma membrane protein with consecutive binding to copper chaperone Ato ...
... NADPH oxidase produces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which reacts with Cu(I) and Fe(II) to generate hydroxyl radical (·OH) and hydroxyl anion (OH -), which are highly toxic for bacteria. Cu(I) flux into cell occurs through the Ctr1 plasma membrane protein with consecutive binding to copper chaperone Ato ...
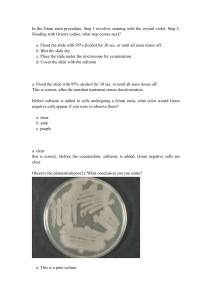
staining-streaking
... This is correct. This is not a pure culture as a variety of colony morphologies can be seen. Methylene blue, crystal violet, and safranin are all basic dyes. What color would each stain the Gram positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus? a. Staphylococcus aureus is Gram positive, it would stain purpl ...
... This is correct. This is not a pure culture as a variety of colony morphologies can be seen. Methylene blue, crystal violet, and safranin are all basic dyes. What color would each stain the Gram positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus? a. Staphylococcus aureus is Gram positive, it would stain purpl ...
Clinical Oral Microbiology
... ◦ capsule is hard to see in a microscope but can be visualized by the exclusion of India ink ...
... ◦ capsule is hard to see in a microscope but can be visualized by the exclusion of India ink ...
staph_Lowy
... distinguish S. aureus from other staphylococcal species. Biology: There are a large number of surface components as well as secreted products of staphylococci. These are summarized below. Structural components: The cell envelope of staphylococci is composed of a microcapsule and a cell wall consisti ...
... distinguish S. aureus from other staphylococcal species. Biology: There are a large number of surface components as well as secreted products of staphylococci. These are summarized below. Structural components: The cell envelope of staphylococci is composed of a microcapsule and a cell wall consisti ...
Indicator Microorganisms
... Coliphages: viruses (bacteriophages) infecting E. coli and perhaps other coliforms; attach directly to cell wall (somatic) heterogeneous group; may not be feces-specific; hostdependent detection Male-specific (F+) coliphages: coliphages infecting "male" strains of E. coli (posses pili); may be feces ...
... Coliphages: viruses (bacteriophages) infecting E. coli and perhaps other coliforms; attach directly to cell wall (somatic) heterogeneous group; may not be feces-specific; hostdependent detection Male-specific (F+) coliphages: coliphages infecting "male" strains of E. coli (posses pili); may be feces ...
- Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
... surface and evasion of phagocytosis.36 Factor H and its splice variant FH-like protein 1 (FHL1) are central fluid-phase regulators of the alternative complement pathway, functioning to accelerate the decay of the C3bBb C3 convertase and acting as cofactors for FImediated degradation of C3b.37 The ce ...
... surface and evasion of phagocytosis.36 Factor H and its splice variant FH-like protein 1 (FHL1) are central fluid-phase regulators of the alternative complement pathway, functioning to accelerate the decay of the C3bBb C3 convertase and acting as cofactors for FImediated degradation of C3b.37 The ce ...
Antibiotics lectureSKD
... • Weakens cell wall, causes lysis • Poorly absorbed from intestinal tract, usually administered via IV except for intestinal infections • Important for treating Gram-positives resistant to β-lactam drugs; also used for severe C. difficile • Often drug of last resort; resistance increasingly a pr ...
... • Weakens cell wall, causes lysis • Poorly absorbed from intestinal tract, usually administered via IV except for intestinal infections • Important for treating Gram-positives resistant to β-lactam drugs; also used for severe C. difficile • Often drug of last resort; resistance increasingly a pr ...
Introduction to Biochemical tests
... coagulase, which causes the fibrin of blood plasma to clot. Organisms that produce Coagulase can form protective barriers of fibrin around themselves, making themselves highly resistant to phagocytosis, other immune responses, and some other antimicrobial agents. ...
... coagulase, which causes the fibrin of blood plasma to clot. Organisms that produce Coagulase can form protective barriers of fibrin around themselves, making themselves highly resistant to phagocytosis, other immune responses, and some other antimicrobial agents. ...
File
... Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety of shapes The three most common shapes are spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety of shapes The three most common shapes are spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 27 Power Point
... Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety of shapes The three most common shapes are spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety of shapes The three most common shapes are spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
27_Lecture_Presentation
... adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Earth’s first organisms were likely prokaryotes Most prokaryotes are unicellular, although some species form colonies Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety o ...
... adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Earth’s first organisms were likely prokaryotes Most prokaryotes are unicellular, although some species form colonies Most prokaryotic cells are 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm of many eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells have a variety o ...
Most Probable Number Method
... • The theory behind the MPN method is central to the commonly used D-value determination by fraction-negative method, and a variant of this method has been suggested for trending of environmental monitoring data from the aseptic core. • MPN can be adjusted to provide a sensitive method to determine ...
... • The theory behind the MPN method is central to the commonly used D-value determination by fraction-negative method, and a variant of this method has been suggested for trending of environmental monitoring data from the aseptic core. • MPN can be adjusted to provide a sensitive method to determine ...
Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone
... (Fuqua & Winans, 1996). The second one is a regulatory protein (LuxR and/or LuxR homologues) which promotes (in most cases) transcription of target genes, when bound with AHL (Fuqua et al., 1994). AHL binding requires three-dimensional changes of the regulatory protein and in turn allows its interac ...
... (Fuqua & Winans, 1996). The second one is a regulatory protein (LuxR and/or LuxR homologues) which promotes (in most cases) transcription of target genes, when bound with AHL (Fuqua et al., 1994). AHL binding requires three-dimensional changes of the regulatory protein and in turn allows its interac ...
Bacteriophage
... What are Bacteriophages Viruses that attack bacteria were observed by Twort and d'Herelle in 1915 and 1917. They observed that broth cultures of certain intestinal bacteria could be dissolved by addition of a bacteria-free filtrate obtained from ...
... What are Bacteriophages Viruses that attack bacteria were observed by Twort and d'Herelle in 1915 and 1917. They observed that broth cultures of certain intestinal bacteria could be dissolved by addition of a bacteria-free filtrate obtained from ...
Get PDF - IOS Press
... the bulk components of biofilm [3]. Of the estimated 700 oral bacteria identified by DNA, only around 50% have been cultured [4]. Many are “unculturable” probably because they cannot survive in isolation, but need other species for attachment and/or nutrients [2]. This is a common feature of biofilm ...
... the bulk components of biofilm [3]. Of the estimated 700 oral bacteria identified by DNA, only around 50% have been cultured [4]. Many are “unculturable” probably because they cannot survive in isolation, but need other species for attachment and/or nutrients [2]. This is a common feature of biofilm ...
Bacterial cell structure
Bacteria, despite their simplicity, contain a well-developed cell structure which is responsible for many of their unique biological structures. Many structural features are unique to bacteria and are not found among archaea or eukaryotes. Because of the simplicity of bacteria relative to larger organisms and the ease with which they can be manipulated experimentally, the cell structure of bacteria has been well studied, revealing many biochemical principles that have been subsequently applied to other organisms.