WFIRST-2.4: What Every Astronomer Should Know
... would be able to survey hundreds of nearby stars, enabling the characterization of dozens of known cool Jupiter-mass companions, the discovery and characterization of a similar number of cool Jupiter and Neptune companions, and the detection and characterization of debris disks in systems containin ...
... would be able to survey hundreds of nearby stars, enabling the characterization of dozens of known cool Jupiter-mass companions, the discovery and characterization of a similar number of cool Jupiter and Neptune companions, and the detection and characterization of debris disks in systems containin ...
ES Chapter 30
... – A binary star is two stars that are gravitationally bound together and that orbit a common center of mass. – More than half of the stars in the sky are either binary stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through ...
... – A binary star is two stars that are gravitationally bound together and that orbit a common center of mass. – More than half of the stars in the sky are either binary stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • very long, billions of years, because it is a fixed shell of interstellar matter being illuminated by a white dwarf star whose age is this long. • very short, about 100 years, because it represents the rapidly expanding shell of an exploding star, or supernova. • relatively short, about 50,000 yea ...
... • very long, billions of years, because it is a fixed shell of interstellar matter being illuminated by a white dwarf star whose age is this long. • very short, about 100 years, because it represents the rapidly expanding shell of an exploding star, or supernova. • relatively short, about 50,000 yea ...
Document
... Io and Europa are mostly rocky but Ganymede and Callisto have more ices; Densities: 3.6, 3.0, 1.9, 1.8 g/cc respectively. ...
... Io and Europa are mostly rocky but Ganymede and Callisto have more ices; Densities: 3.6, 3.0, 1.9, 1.8 g/cc respectively. ...
Today: Magnitude Terminology Photometry Applications Reading
... Calibrated Magnitude: physically meaningful brightness of a star calibrated relative to the known flux standard (e.g. Vega); typically obtained by calculating differential magnitude w.r.t. a known standard star. ...
... Calibrated Magnitude: physically meaningful brightness of a star calibrated relative to the known flux standard (e.g. Vega); typically obtained by calculating differential magnitude w.r.t. a known standard star. ...
10 - Keele Astrophysics Group
... This classification scheme was based simply on the appearance of the spectra and the physical reason underlying these properties was not understood until the 1930s. Even though there are some genuine differences in chemical composition between stars, the main property that determines the observed sp ...
... This classification scheme was based simply on the appearance of the spectra and the physical reason underlying these properties was not understood until the 1930s. Even though there are some genuine differences in chemical composition between stars, the main property that determines the observed sp ...
Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2012
... aren’t defined, if important steps of explanation are missing, etc. If the answer is written down without *any* context whatsoever, take off 1/3 of the points. One point off per question for inappropriately high precision (which usually means more than 2 significant figures in this homework). No mor ...
... aren’t defined, if important steps of explanation are missing, etc. If the answer is written down without *any* context whatsoever, take off 1/3 of the points. One point off per question for inappropriately high precision (which usually means more than 2 significant figures in this homework). No mor ...
The evolution of stars - School of Physics
... underlying physical link between these properties. What is this link? For example, consider an alien scientist constructing a similar diagram ...
... underlying physical link between these properties. What is this link? For example, consider an alien scientist constructing a similar diagram ...
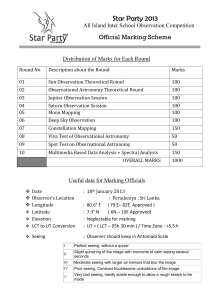
Marking Scheme of Observational Sessions
... constellation of “Orion”) in his/her constellation mapping drawing. But drawing Orion nebula IS NOT ACCEPTABLE ! Maximum Minus marks that can be given for each report is (-2 ) Observers should make a Relative apparent magnitude scale and show it on at least one observation report. IF it missing (– 3 ...
... constellation of “Orion”) in his/her constellation mapping drawing. But drawing Orion nebula IS NOT ACCEPTABLE ! Maximum Minus marks that can be given for each report is (-2 ) Observers should make a Relative apparent magnitude scale and show it on at least one observation report. IF it missing (– 3 ...
What units are used in astronomical photometry?
... Astrometry: Technological advances (including the Hubble Space Telescope) have improved parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 10 12 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations mad ...
... Astrometry: Technological advances (including the Hubble Space Telescope) have improved parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 10 12 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations mad ...
The Royal Arch of the Heavens
... On a band of sky which lies roughly 8 either side of the Ecliptic is where we find the constellations of the zodiac circle of animals. This thin band of sky is divided into twelve segments of 30 each, with one constellation contained, or at least mostly contained, within each segment. As far as we ...
... On a band of sky which lies roughly 8 either side of the Ecliptic is where we find the constellations of the zodiac circle of animals. This thin band of sky is divided into twelve segments of 30 each, with one constellation contained, or at least mostly contained, within each segment. As far as we ...
STELLAR FORMATION AND EVOLUTION
... did this with a large number of stars and noticed there were distinct groups. Hot stars inhabit the left hand side of the diagram, cool stars the right hand side. Bright stars at the top, faint stars at the bottom. Our Sun is a fairly average star and sits near the middle. Most of the stars in the d ...
... did this with a large number of stars and noticed there were distinct groups. Hot stars inhabit the left hand side of the diagram, cool stars the right hand side. Bright stars at the top, faint stars at the bottom. Our Sun is a fairly average star and sits near the middle. Most of the stars in the d ...
What, and Why, is the International Astronomical Union?
... The formal structure evolved in Brussels and signed into effect in Rome consisted of Standing Committees “for the study of various branches of astronomy, encouragement of collective investigations, and discussion of questions requiring international agreement or standardization.” The word in the Fre ...
... The formal structure evolved in Brussels and signed into effect in Rome consisted of Standing Committees “for the study of various branches of astronomy, encouragement of collective investigations, and discussion of questions requiring international agreement or standardization.” The word in the Fre ...
Chapter 14
... These objects are very close to the galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
... These objects are very close to the galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
1 - ESO
... Dusty Circumstellar Disks: From IRAS to Spitzer • Collaborators: • Joseph Rhee, Inseok Song (Gemini Observatory), • Michael McElwain, Eric Becklin (UCLA) • Alycia Weinberger (Carnegie Institution) ...
... Dusty Circumstellar Disks: From IRAS to Spitzer • Collaborators: • Joseph Rhee, Inseok Song (Gemini Observatory), • Michael McElwain, Eric Becklin (UCLA) • Alycia Weinberger (Carnegie Institution) ...
Constraining the star formation histories of spiral bulges
... GonzaÂlez 1992; Davies et al. 1993; Gorgas et al. 1997; Greggio 1997). This Mg2 excess is interpreted as indicating [Mg/Fe] greater than solar (Davies et al. 1993). High [Mg/Fe] ratios can be achieved by star formation times of &1 Gyr; in accordance with the short time-scales of gas inflow in both m ...
... GonzaÂlez 1992; Davies et al. 1993; Gorgas et al. 1997; Greggio 1997). This Mg2 excess is interpreted as indicating [Mg/Fe] greater than solar (Davies et al. 1993). High [Mg/Fe] ratios can be achieved by star formation times of &1 Gyr; in accordance with the short time-scales of gas inflow in both m ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.