ISA_lecture01 - School of Physics
... A “planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. A “dwarf planet” is a celestial bo ...
... A “planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. A “dwarf planet” is a celestial bo ...
Document
... between yearly epochs at the 5 level with the CFHT Legacy Survey optical catalog. • Rule out sources with optical hosts with the colors and morphology of a star or quasar. • Follow up galaxy hosts that do not have an hard X-ray detection with optical spectroscopy to look for signs of an AGN. • Trig ...
... between yearly epochs at the 5 level with the CFHT Legacy Survey optical catalog. • Rule out sources with optical hosts with the colors and morphology of a star or quasar. • Follow up galaxy hosts that do not have an hard X-ray detection with optical spectroscopy to look for signs of an AGN. • Trig ...
3.2 Spectra and Spectral Classification
... Harvard Observatory College (1913): A. J. Cannon and her team of Ladies at Harvard working for years on the classification of steller spectra. In 1897 Cannon was hired by Pickering to classify the spectra of stars of the southern hemisphere. Cannon and her team classified stars at an average rate of ...
... Harvard Observatory College (1913): A. J. Cannon and her team of Ladies at Harvard working for years on the classification of steller spectra. In 1897 Cannon was hired by Pickering to classify the spectra of stars of the southern hemisphere. Cannon and her team classified stars at an average rate of ...
The Korean 1592--1593 Record of a Guest Star: Animpostor`of the
... recorded in history books of East Asian and/or European countries: SN 1006, 1054, 1181, 1572, and 1604 (Stephenson & Green 2002). Each of them was visible to the naked eye in the night sky over a period longer than six months, and their supernova remnants (SNRs) are now observable as beautiful nebul ...
... recorded in history books of East Asian and/or European countries: SN 1006, 1054, 1181, 1572, and 1604 (Stephenson & Green 2002). Each of them was visible to the naked eye in the night sky over a period longer than six months, and their supernova remnants (SNRs) are now observable as beautiful nebul ...
Kepler Mission: The Search for Earth-sized Planets
... For which of these star(s) will Kepler be able to detect transiting planets? ...
... For which of these star(s) will Kepler be able to detect transiting planets? ...
Sky Watcher - Boise Astronomical Society
... and fainter Mercury lower in the northwest. Mercury and Jupiter will be the brightest two stars between the west and northwest. There’s a possible new meteor shower in the offing! The reason is that Comet LINEAR 209P, which an automated telescope discovered in 2004, is passing through the inner sola ...
... and fainter Mercury lower in the northwest. Mercury and Jupiter will be the brightest two stars between the west and northwest. There’s a possible new meteor shower in the offing! The reason is that Comet LINEAR 209P, which an automated telescope discovered in 2004, is passing through the inner sola ...
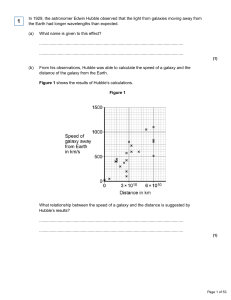
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from
... The observations made by Hubble support the idea that the Universe is expanding. This means that galaxies are continually moving away from each other and from the Earth. Figure 2 shows a student using a balloon to model the idea of an expanding Universe. Some dots, which represent galaxies, were ma ...
... The observations made by Hubble support the idea that the Universe is expanding. This means that galaxies are continually moving away from each other and from the Earth. Figure 2 shows a student using a balloon to model the idea of an expanding Universe. Some dots, which represent galaxies, were ma ...
Starwalk Manual En
... The Search feature allows you to switch between the following categories: • Stars and constellations • Solar system - includes planets, the Moon, the Sun, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets • Deep space – includes clusters, nebulas, galaxies, clouds • Satellites Each category has a lis ...
... The Search feature allows you to switch between the following categories: • Stars and constellations • Solar system - includes planets, the Moon, the Sun, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets • Deep space – includes clusters, nebulas, galaxies, clouds • Satellites Each category has a lis ...
August, 2005 Observer - Fort Bend Astronomy Club
... of its orbit), 357,393 km (222,074 miles) from Earth. That makes today's Full Moon the 2nd closest of the year. Tonight the Moon rises in ESE about 25 minutes after sunset, as seen from southern Michigan. When the Moon is rising or setting, regardless of its distance, it always seems much larger tha ...
... of its orbit), 357,393 km (222,074 miles) from Earth. That makes today's Full Moon the 2nd closest of the year. Tonight the Moon rises in ESE about 25 minutes after sunset, as seen from southern Michigan. When the Moon is rising or setting, regardless of its distance, it always seems much larger tha ...
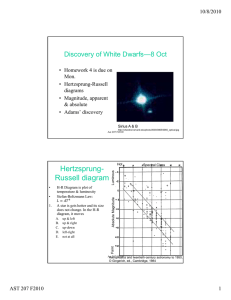
Discovery of White Dwarfs—8 Oct
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram of nearby stars 1. Stars in region X are A. Dwarfs B. Giants C. White dwarfs ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram of nearby stars 1. Stars in region X are A. Dwarfs B. Giants C. White dwarfs ...
Did the division of the year by the Babylonians into twelve months
... unchanged following such an event, and finishing with the story of ‘Amphos’, a thousand years after the event: ...
... unchanged following such an event, and finishing with the story of ‘Amphos’, a thousand years after the event: ...
Surface Gravity as a Diagnostic ... Youth Cameron Higby-Naquin Advisor: Eric Jensen
... Knowing the age of a star is only the first step to understanding stellar evolution and completely describing how stars change with time. In short, different stars take different amounts of time to form, and to fully grasp the formation process, physical properties of the star must be determined. A ...
... Knowing the age of a star is only the first step to understanding stellar evolution and completely describing how stars change with time. In short, different stars take different amounts of time to form, and to fully grasp the formation process, physical properties of the star must be determined. A ...
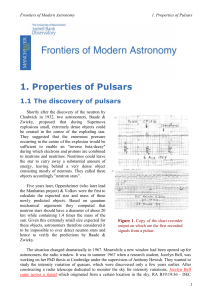
1: Properties of Pulsars
... The question about the true nature of pulsars was finally settled, when a pulsar was discovered in the centre of the Crab Nebula supernova remnant. The Crab Nebula (Figure 2; also called M1 as it was the first object in Messier's famous list) is the visible remnant of a supernova explosion witnessed ...
... The question about the true nature of pulsars was finally settled, when a pulsar was discovered in the centre of the Crab Nebula supernova remnant. The Crab Nebula (Figure 2; also called M1 as it was the first object in Messier's famous list) is the visible remnant of a supernova explosion witnessed ...
júpiter, king of the moon
... 2,258 miles. It orbits Jupiter once every 42, 5 hours. Its orbit is affected by the magnetic field of Jupiter and the proximity to Europe and Ganymede. It is rocky and permanently maintains intense volcanic eruptions, is the most volcanically active body in the Solar System. The massive volcanic eru ...
... 2,258 miles. It orbits Jupiter once every 42, 5 hours. Its orbit is affected by the magnetic field of Jupiter and the proximity to Europe and Ganymede. It is rocky and permanently maintains intense volcanic eruptions, is the most volcanically active body in the Solar System. The massive volcanic eru ...
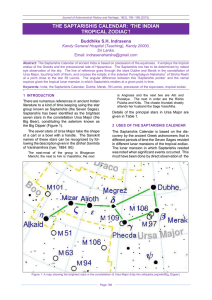
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.