February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... Lyrae and is the 5th star in Lyra. In the chart above it can be found just north (above) the brightest star α (Vega). The two pairs of the double double are labelled as ε1 and ε2 and are separated by 208″. In turn each pair is separated by just 2″, about 160 AU (1 AU = Earth / Sun distance). The fou ...
... Lyrae and is the 5th star in Lyra. In the chart above it can be found just north (above) the brightest star α (Vega). The two pairs of the double double are labelled as ε1 and ε2 and are separated by 208″. In turn each pair is separated by just 2″, about 160 AU (1 AU = Earth / Sun distance). The fou ...
HR Diagram - Geneva 304
... 39. Name the star with the greatest proper motion and tell how fast it moves across the celestial sphere. 40. Name and describe the two components in space velocity, and tell how we to determine each. ...
... 39. Name the star with the greatest proper motion and tell how fast it moves across the celestial sphere. 40. Name and describe the two components in space velocity, and tell how we to determine each. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... – Star begins to shrink; outer core of hydrogen begins to fuse • Star gets bigger ...
... – Star begins to shrink; outer core of hydrogen begins to fuse • Star gets bigger ...
Lecture 1 - University of Maryland Astronomy
... less certain about the virus. However, as we’ll discuss when we go over possible origins of life, there are reasons to think that some clays have properties similar to primitive life, and snowflakes also fit some of the definitions (although I’d have a tough time assigning life to a snowflake). Wha ...
... less certain about the virus. However, as we’ll discuss when we go over possible origins of life, there are reasons to think that some clays have properties similar to primitive life, and snowflakes also fit some of the definitions (although I’d have a tough time assigning life to a snowflake). Wha ...
Distances farther out
... K giants (more luminous) – Subgiants (class IV) – Dwarfs (less luminous) Subgiants (stars above MS, but not really giants), 4/5 solar radius. Appear to be evolving from MS upwards into true lum class III). In this region above MS get many T Tauri stars: odd in nature: emission lines, vary irregula ...
... K giants (more luminous) – Subgiants (class IV) – Dwarfs (less luminous) Subgiants (stars above MS, but not really giants), 4/5 solar radius. Appear to be evolving from MS upwards into true lum class III). In this region above MS get many T Tauri stars: odd in nature: emission lines, vary irregula ...
Astrowheel activity for Wednesday Feb 16
... which will do many of the things a globe can do, at least for one latitude value. Such a device, called the Astrowheel, will be constructed in this exercise. PROCEDURE: a) The Polar Star Wheel (PSW) Your instructor will provide a polar projection map (polar star wheel) of the equatorial coordinate s ...
... which will do many of the things a globe can do, at least for one latitude value. Such a device, called the Astrowheel, will be constructed in this exercise. PROCEDURE: a) The Polar Star Wheel (PSW) Your instructor will provide a polar projection map (polar star wheel) of the equatorial coordinate s ...
A Study of the Spiral Galaxy M101 Elizabeth City State University
... filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. The Image Reduction and Analysis Facility (IRAF) is the software that was used for the image reducti ...
... filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. The Image Reduction and Analysis Facility (IRAF) is the software that was used for the image reducti ...
Stars on the HR Diagram
... what kinds of stars are most populous throughout the universe. Astronomers call the plot of stars from the upper left to the lower right of the HR diagram, the “main sequence” and 90% of all stars plot along this curve. Comparing the physical aspects of a number of stars is much like an alien visiti ...
... what kinds of stars are most populous throughout the universe. Astronomers call the plot of stars from the upper left to the lower right of the HR diagram, the “main sequence” and 90% of all stars plot along this curve. Comparing the physical aspects of a number of stars is much like an alien visiti ...
Star Life Cycle Review 1. What is the first stage of star creation? A
... B. A star requires a continual supply of material from other stars in order to survive for long periods of time. C. ...
... B. A star requires a continual supply of material from other stars in order to survive for long periods of time. C. ...
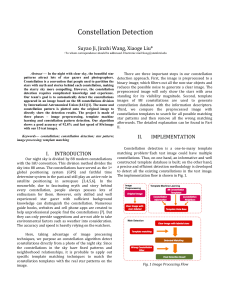
Constellation Detection
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... Sun, Stars, HR Diagram Base your answers to questions 18through 20 on the diagram below, which shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space. ...
... Sun, Stars, HR Diagram Base your answers to questions 18through 20 on the diagram below, which shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space. ...
Properties of Stars in general
... • Most stars are seen to lie on the Main Sequence. – This is because stars spend the major part of their life in the region of the main sequence – During this period they are burning Hydrogen into Helium in their cores. – Their position in the main sequence is dependant on their mass (more massive a ...
... • Most stars are seen to lie on the Main Sequence. – This is because stars spend the major part of their life in the region of the main sequence – During this period they are burning Hydrogen into Helium in their cores. – Their position in the main sequence is dependant on their mass (more massive a ...
CASPEC Observations of the Most Metal-Deficient Main
... Herbig AelBe star. Strom et al. (1972) give a list of 12 Galactic stars of this type with known distances. If we place these stars in the SMC, their V magnitudes will range from 17 to 22. The brightest one, HD 200775, assumed to lie at 440 pc from the Sun (Whitcomb et al., 1981), may be fainter than ...
... Herbig AelBe star. Strom et al. (1972) give a list of 12 Galactic stars of this type with known distances. If we place these stars in the SMC, their V magnitudes will range from 17 to 22. The brightest one, HD 200775, assumed to lie at 440 pc from the Sun (Whitcomb et al., 1981), may be fainter than ...
Fixed Stars
... The foundation for astrology is emanation, transmission and reception of energies, along the lines of affinity, triangles and old relations, in cyclic movements, between entities Who rule the spherical bodies in space. Isn’t it joyful and meaningful that the Universe is not a random “Big Bang”? Even ...
... The foundation for astrology is emanation, transmission and reception of energies, along the lines of affinity, triangles and old relations, in cyclic movements, between entities Who rule the spherical bodies in space. Isn’t it joyful and meaningful that the Universe is not a random “Big Bang”? Even ...
HR Diagram Lab
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.