Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... The red emission nebula, glowing with the characteristic light of hot hydrogen gas, hides a young star cluster near its center. The dust lanes appear dark because they obscure visible light, and are thus seen in silhouette against the brighter, glowing, hydrogen gas. Surrounding the red nebula is a ...
... The red emission nebula, glowing with the characteristic light of hot hydrogen gas, hides a young star cluster near its center. The dust lanes appear dark because they obscure visible light, and are thus seen in silhouette against the brighter, glowing, hydrogen gas. Surrounding the red nebula is a ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Then star is either circumpolar or below the horizon Example – at latitude 45oN, cos(L)=0.707, the star Capella (declination = 46o) just becomes circumpolar Then cos(Rz) is just slightly greater than 1. ...
... Then star is either circumpolar or below the horizon Example – at latitude 45oN, cos(L)=0.707, the star Capella (declination = 46o) just becomes circumpolar Then cos(Rz) is just slightly greater than 1. ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... Binaries that are able to survive in the dense environment of star cluster (in particular GCs) are so close that even the HST is not able to resolve the single components… So, light coming from each star will combine, and the binary system will appear as a single point-like source… when indicating w ...
... Binaries that are able to survive in the dense environment of star cluster (in particular GCs) are so close that even the HST is not able to resolve the single components… So, light coming from each star will combine, and the binary system will appear as a single point-like source… when indicating w ...
File
... The Constellation and Stars According to seasky.org the constellation Aries is located at 2.66 hours right ascension and 20.09 degrees declination ("December Constellations"). However as found on table #1 below the brightest star in Aries (Hamal) is located at about 2 hours RA and 23 degrees DEC, ju ...
... The Constellation and Stars According to seasky.org the constellation Aries is located at 2.66 hours right ascension and 20.09 degrees declination ("December Constellations"). However as found on table #1 below the brightest star in Aries (Hamal) is located at about 2 hours RA and 23 degrees DEC, ju ...
astronomy webquest…… explore the universe
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/stars/lifecycle/ http://btc.montana.edu/ceres/html/LifeCycle/starsbackground.htm http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Nebula.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Strange.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link= ...
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/stars/lifecycle/ http://btc.montana.edu/ceres/html/LifeCycle/starsbackground.htm http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Nebula.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Strange.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link= ...
Sample Final - IUPUI Physics
... 2. The core of the sun is primarily powered by: A) the burning of chemical fuel B) gravitational energy C) nuclear fusion D) all of the above 3. What is about the expected lifetime of a 0.8 solar mass star? • A) 6 billion years • B) 10 billion years • C) 16 billion years • D) a 0.8 solar mass star d ...
... 2. The core of the sun is primarily powered by: A) the burning of chemical fuel B) gravitational energy C) nuclear fusion D) all of the above 3. What is about the expected lifetime of a 0.8 solar mass star? • A) 6 billion years • B) 10 billion years • C) 16 billion years • D) a 0.8 solar mass star d ...
AST101_lect_12
... • This is analogous to determining how often you have to refill the gas tank in your car. Time remaining is the amount of fuel you have (the size of the tank) by your ...
... • This is analogous to determining how often you have to refill the gas tank in your car. Time remaining is the amount of fuel you have (the size of the tank) by your ...
ASTRO 1050 The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
... (a) Using the globular cluster data above, make a histogram of the data, drawing the same type of graph that you used previously. ...
... (a) Using the globular cluster data above, make a histogram of the data, drawing the same type of graph that you used previously. ...
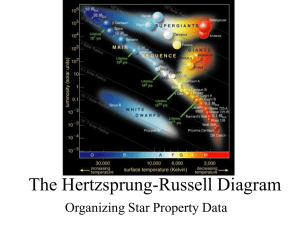
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: 1/16/07
... kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For this reason, astronomers use a different unit of measurement when they talk about distances between stars. ...
... kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For this reason, astronomers use a different unit of measurement when they talk about distances between stars. ...
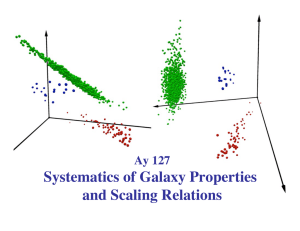
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... (not separated in the traditional Hubble sequence) ...
... (not separated in the traditional Hubble sequence) ...
At the Heart of the Matter: The Blue White Dwarf in M 57. Paul Temple
... comparison, the earth itself has an average density of only 5.4 x 103 kg/m3. That means a white dwarf is 200,000 times as dense! ...
... comparison, the earth itself has an average density of only 5.4 x 103 kg/m3. That means a white dwarf is 200,000 times as dense! ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 24 Galaxies
... The Hubble Law: There is a simple linear relationship between the distance from the Earth to a remote galaxy and the redshift of that galaxy (which is a measure of the speed with which it is receding from us). This relationship is the Hubble law, v = H0d. The value of the Hubble constant, H0, is not ...
... The Hubble Law: There is a simple linear relationship between the distance from the Earth to a remote galaxy and the redshift of that galaxy (which is a measure of the speed with which it is receding from us). This relationship is the Hubble law, v = H0d. The value of the Hubble constant, H0, is not ...
D109-08x
... apart as it races at 4.5 million miles per hour through the heart of a distant cluster of galaxies. The images, taken over several wavelengths, provide evidence of the "galactic assault and battery," namely, gas being stripped from the doomed galaxy, called C153. The composite photograph at left was ...
... apart as it races at 4.5 million miles per hour through the heart of a distant cluster of galaxies. The images, taken over several wavelengths, provide evidence of the "galactic assault and battery," namely, gas being stripped from the doomed galaxy, called C153. The composite photograph at left was ...
Electromagnetic Radiation from the Sun
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are ...
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are ...
Fingerprints in Starlight: Spectroscopy of Stars Inquiry Questions
... net photon release: 6 gamma rays (neutrinos interact so weakly that they fly out of the sun immediately) The mass of one helium nucleus is less than the total mass of the four hydrogen nuclei that fuse to form it. The mass difference is converted into the tremendous amount of energy that fuels the s ...
... net photon release: 6 gamma rays (neutrinos interact so weakly that they fly out of the sun immediately) The mass of one helium nucleus is less than the total mass of the four hydrogen nuclei that fuse to form it. The mass difference is converted into the tremendous amount of energy that fuels the s ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.