September 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... To build a map of the Milky Way, the scientists used the SDSS Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Explorer (APOGEE) spectrograph to observe 100,000 stars during a four-year campaign. The key to creating and interpreting this map is measuring the elements in the atmosphere of each star. “From ...
... To build a map of the Milky Way, the scientists used the SDSS Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Explorer (APOGEE) spectrograph to observe 100,000 stars during a four-year campaign. The key to creating and interpreting this map is measuring the elements in the atmosphere of each star. “From ...
Astrophysics 11 - HR Diagram
... • But AQA seem to prefer the absolute magnitude scale going from -15 to 10. ...
... • But AQA seem to prefer the absolute magnitude scale going from -15 to 10. ...
MS Word
... luminosity). Familiarize yourself with Figure 1 which is an empty H-R diagram. Along the bottom of the diagram are the common spectral types (we have left off O type stars since there are no O stars anywhere near the Sun). Recall that each letter category is also broken into ten subcatagories. Thus ...
... luminosity). Familiarize yourself with Figure 1 which is an empty H-R diagram. Along the bottom of the diagram are the common spectral types (we have left off O type stars since there are no O stars anywhere near the Sun). Recall that each letter category is also broken into ten subcatagories. Thus ...
Parallax - High Point University
... A comparison of two EIT images almost two years apart illustrates how the level of solar activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 ...
... A comparison of two EIT images almost two years apart illustrates how the level of solar activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 ...
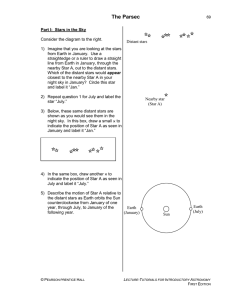
The Parsec
... even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles are measured in “arcseconds” where an arcsecond is 1/3600 of 1 degree. To describe the distances to stars, astronomers use a unit of length called the parsec. 1 parsec is defined as the distanc ...
... even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles are measured in “arcseconds” where an arcsecond is 1/3600 of 1 degree. To describe the distances to stars, astronomers use a unit of length called the parsec. 1 parsec is defined as the distanc ...
Written In The Sky
... There is a deeper, more fascinating meaning in the signs of the zodiac than you will ever find in the daily horoscope column. Each of these astrological signs, in one way or another, talks about a mighty Person who is going to come, triumph over a great enemy, take away sin and its terrible conseque ...
... There is a deeper, more fascinating meaning in the signs of the zodiac than you will ever find in the daily horoscope column. Each of these astrological signs, in one way or another, talks about a mighty Person who is going to come, triumph over a great enemy, take away sin and its terrible conseque ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... The spectral lines of a star can be seen to be moving to shorter wavelengths and also to longer wavelengths ...
... The spectral lines of a star can be seen to be moving to shorter wavelengths and also to longer wavelengths ...
Star in a Box Worksheet - Beginning with solutions
... 2. When will the Sun be at its brightest? During the Asymptotic Giant Branch, when it is about 10,205.16 billion years old. 3. When will the Sun be at its hottest? During the Thermally-pulsing Asymptotic Giant Branch at 10209.76 billion years old. 4. In which stage of its life does the Sun spend t ...
... 2. When will the Sun be at its brightest? During the Asymptotic Giant Branch, when it is about 10,205.16 billion years old. 3. When will the Sun be at its hottest? During the Thermally-pulsing Asymptotic Giant Branch at 10209.76 billion years old. 4. In which stage of its life does the Sun spend t ...
Epsilon Aurigae Mystery and Opportunity
... The History of the Mystery • Johann Fritsch was the first to note the variability of epsilon Aurigae in early 1821, when the star was likely in the midst of a deep eclipse. • The German astronomers Argelander and Heis both began "regular" observing once every few years around 1842-1843, and the data ...
... The History of the Mystery • Johann Fritsch was the first to note the variability of epsilon Aurigae in early 1821, when the star was likely in the midst of a deep eclipse. • The German astronomers Argelander and Heis both began "regular" observing once every few years around 1842-1843, and the data ...
Document
... Students should be able to understand the basic physics underlying complex stellar evolution models Students will learn how to interpret observational characteristics of stars in terms of the underlying physical parameters You should gain an understanding of how stars of different mass evolve, and w ...
... Students should be able to understand the basic physics underlying complex stellar evolution models Students will learn how to interpret observational characteristics of stars in terms of the underlying physical parameters You should gain an understanding of how stars of different mass evolve, and w ...
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder
... • Multiple measurements of nearest 60 F-, G-, and K- stars. • Directly test rocky planet formation ...
... • Multiple measurements of nearest 60 F-, G-, and K- stars. • Directly test rocky planet formation ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... 5. Circle the group of ten stars above the main sequence. 6. Label these stars as the “red giant stars.” 7. Circle the group of five stars below the main sequence. 8. Label these stars as the “white dwarf stars.” ...
... 5. Circle the group of ten stars above the main sequence. 6. Label these stars as the “red giant stars.” 7. Circle the group of five stars below the main sequence. 8. Label these stars as the “white dwarf stars.” ...
AyC10 Fall 2007: Midterm 2 Review Sheet
... have enough mutual gravitational attraction to stay together for a long time as a star cluster, but eventually they will drift apart. Additionally, some stars form in binary pairs (and binary pairs are still in clusters with other stars when they form). Binary stars usually orbit each other for thei ...
... have enough mutual gravitational attraction to stay together for a long time as a star cluster, but eventually they will drift apart. Additionally, some stars form in binary pairs (and binary pairs are still in clusters with other stars when they form). Binary stars usually orbit each other for thei ...
Lecture 22 - Seattle Central
... What are the main stages in a high mass star’s life? What happens in the core of a high mass star at the end of its life? Why does fusion stop at Iron in high mass stars? Where do elements heavier than Iron come from? What are the two possibilities when the electron degeneracy pressure in a high mas ...
... What are the main stages in a high mass star’s life? What happens in the core of a high mass star at the end of its life? Why does fusion stop at Iron in high mass stars? Where do elements heavier than Iron come from? What are the two possibilities when the electron degeneracy pressure in a high mas ...
celestial sphere
... star chart mounted in such a fashion that it can be oriented to represent the true aspect of the sky as seen by an observer at any point on the earth at any time. Since the surface is spherical, the distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the conste ...
... star chart mounted in such a fashion that it can be oriented to represent the true aspect of the sky as seen by an observer at any point on the earth at any time. Since the surface is spherical, the distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the conste ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.