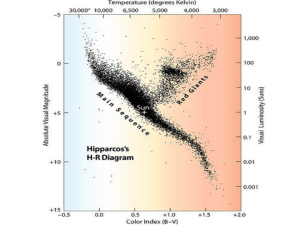
H-R Diagram
... In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the S ...
... In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the S ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... usually cold (100O K or -300O F) usually almost perfect vacuum with 1 atom/cm3 (1 g water = 1023 atoms) Local concentrations: compressed by gravity and form stars. Called Giant Molecular Clouds as molecules have been observed. Need about 1,000,000 times the mass of the Sun in 100 LY volume to initia ...
... usually cold (100O K or -300O F) usually almost perfect vacuum with 1 atom/cm3 (1 g water = 1023 atoms) Local concentrations: compressed by gravity and form stars. Called Giant Molecular Clouds as molecules have been observed. Need about 1,000,000 times the mass of the Sun in 100 LY volume to initia ...
Cosmic Dawn A Hunting for the First Stars in the Universe
... of these secondary elements backwards in time, we can infer the existence of generations of stars that have long since disappeared, in much the same way that an archeologist peels back geological strata to map the fossil record of extinct species. What astronomers call the “pollution” of the univer ...
... of these secondary elements backwards in time, we can infer the existence of generations of stars that have long since disappeared, in much the same way that an archeologist peels back geological strata to map the fossil record of extinct species. What astronomers call the “pollution” of the univer ...
J: Chapter 4: Stars and Galaxies
... Figure 2. Notice how the front two stars of the Big Dipper point almost directly at the North Star, Polaris, which is located at the end of the Little Dipper in the constellation Ursa Minor. Polaris is positioned almost directly over Earth’s north pole. ...
... Figure 2. Notice how the front two stars of the Big Dipper point almost directly at the North Star, Polaris, which is located at the end of the Little Dipper in the constellation Ursa Minor. Polaris is positioned almost directly over Earth’s north pole. ...
Determining the Sizes & Distances of Stars Using the H
... A star's radius is simply half the star's diameter. Stars are simply large balls of gas held together by gravity, and they are approximately spherical in shape. Radii of stars can be measured in meters, but because stars are so very large that its much more convenient to measure stellar radii in uni ...
... A star's radius is simply half the star's diameter. Stars are simply large balls of gas held together by gravity, and they are approximately spherical in shape. Radii of stars can be measured in meters, but because stars are so very large that its much more convenient to measure stellar radii in uni ...
Lecture 14: Star Formation
... Ignite p-p chain fusion in the core Settles slowly onto the main sequence ...
... Ignite p-p chain fusion in the core Settles slowly onto the main sequence ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... The purpose of this research was to study the LIRGs (Luminous Infrared Galaxies) and see if they follow the Tully-Fisher relation. The LIRGs are different to normal galaxies in the fact that they emit 90% of their light i in infrared. The TullyFisher relation states that the bigger the galaxy is, th ...
... The purpose of this research was to study the LIRGs (Luminous Infrared Galaxies) and see if they follow the Tully-Fisher relation. The LIRGs are different to normal galaxies in the fact that they emit 90% of their light i in infrared. The TullyFisher relation states that the bigger the galaxy is, th ...
Zodiac Calendar History
... predicates later Babylonian and Egyptian zodiacs. Astrological signs are the ancient mathematical interpretations that measure time. Entire pictures decorated minds and artwork long ago. Astronomical constellations are the modern approach that purely references scientific observation. Many star chart ...
... predicates later Babylonian and Egyptian zodiacs. Astrological signs are the ancient mathematical interpretations that measure time. Entire pictures decorated minds and artwork long ago. Astronomical constellations are the modern approach that purely references scientific observation. Many star chart ...
Weighing a Galaxy—11 Nov Ast 207 F2005 Nov-09 • Schedule
... Use Doppler effect • Kepler’s Law needs modification since period of sun’s motion around Milky Way is 200 Myr. Mass = R3 / T2 = R (R/ T)2 Mass = R v2 (w/o constants) Mass = 233 R v2 Msun (v in km/s and R in pc) • Doppler effect for measuring speed. – No need to wait to see motion. – Speed is imprint ...
... Use Doppler effect • Kepler’s Law needs modification since period of sun’s motion around Milky Way is 200 Myr. Mass = R3 / T2 = R (R/ T)2 Mass = R v2 (w/o constants) Mass = 233 R v2 Msun (v in km/s and R in pc) • Doppler effect for measuring speed. – No need to wait to see motion. – Speed is imprint ...
Zodiac Party Game - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... o DAY--The period of time required for the Earth to TURN AROUND ONCE on its axis. o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if a ...
... o DAY--The period of time required for the Earth to TURN AROUND ONCE on its axis. o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if a ...
Constants and Equations
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
L10 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
Carolina Kehrig
... There is still a lack of understanding of narrow HeII emitters even at low redshift WR features are not seen whenever narrow HeII is observed IFS spatial offset between nebular HeII-emitting zone and WR stars can be a possible explanation for the non-detection of WR features in some galaxy s ...
... There is still a lack of understanding of narrow HeII emitters even at low redshift WR features are not seen whenever narrow HeII is observed IFS spatial offset between nebular HeII-emitting zone and WR stars can be a possible explanation for the non-detection of WR features in some galaxy s ...
Lecture 02
... Question : The celestial equator is ? A The path of the Sun compared to the stars. B The path of the Moon compared to the stars. C Always directly overhead at the Earth's equator. D The average path of planets on a star chart. E Always along the horizon for people on Earth's equator. ...
... Question : The celestial equator is ? A The path of the Sun compared to the stars. B The path of the Moon compared to the stars. C Always directly overhead at the Earth's equator. D The average path of planets on a star chart. E Always along the horizon for people on Earth's equator. ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.