Mysteries of Space
... • The mass discovered by scientists for this galaxy used the estimated mass to estimate the speed of various stars movement and discovered that they are moving much faster than predicted. The way scientists have explained this phenomenon is that there must be 90 times more matter that is not visible ...
... • The mass discovered by scientists for this galaxy used the estimated mass to estimate the speed of various stars movement and discovered that they are moving much faster than predicted. The way scientists have explained this phenomenon is that there must be 90 times more matter that is not visible ...
The Early Universe and the Big Bang
... Stars can make Lithium in nuclear reactions but most stars actually DESTROY lithium. Why? 1. It gets fused into other elements 2. No energy is released by the fusion of lithium 3. Lots of energy is released by the fusion of lithium 4. Lithium reacts chemically to make molecules 5. Stars hate l ...
... Stars can make Lithium in nuclear reactions but most stars actually DESTROY lithium. Why? 1. It gets fused into other elements 2. No energy is released by the fusion of lithium 3. Lots of energy is released by the fusion of lithium 4. Lithium reacts chemically to make molecules 5. Stars hate l ...
creation of a cosmology: big bang theory _eng
... Around the same time the Dutch astronomer Willem deSitter used Einstein's general theory of relativity to develop his own model of the Universe. His model was unique in that it did not take into consideration the existence of matter in the Universe. However it did go beyond Einstein's model in that ...
... Around the same time the Dutch astronomer Willem deSitter used Einstein's general theory of relativity to develop his own model of the Universe. His model was unique in that it did not take into consideration the existence of matter in the Universe. However it did go beyond Einstein's model in that ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are displaced toward shorter wavelengths, this is called a ______________shift. 21. Which shift suggests ...
... 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are displaced toward shorter wavelengths, this is called a ______________shift. 21. Which shift suggests ...
Measuring Distances: Mph (miles per hour): miles traveled per hour
... universe, and is supported by observa;onal evidence. A Belgian priest named Georges Lemaitre first suggested the Big Bang Theory when he theorized that the universe began from a single atom. Suppor;ng ...
... universe, and is supported by observa;onal evidence. A Belgian priest named Georges Lemaitre first suggested the Big Bang Theory when he theorized that the universe began from a single atom. Suppor;ng ...
Studying Space Chapter 26 Notes
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
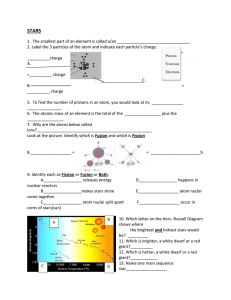
Name____________________________________________
... S6E1 Where do we live in the Universe, Milky Way, and our Solar System? 1. Between 15-20 billion years ago the Universe began expanding out of an enormous explosion scientist called the Big Bang theory. 2. From largest to smallest, order the following (1 is largest -4 is smallest): __4___ The Sun __ ...
... S6E1 Where do we live in the Universe, Milky Way, and our Solar System? 1. Between 15-20 billion years ago the Universe began expanding out of an enormous explosion scientist called the Big Bang theory. 2. From largest to smallest, order the following (1 is largest -4 is smallest): __4___ The Sun __ ...
The measure of Cosmological distances
... H0 = Hubble’s constant = 70 (km/s) / Mpc Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): II. 1929 - Discovery of distance - velocity relation in galaxies ...
... H0 = Hubble’s constant = 70 (km/s) / Mpc Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): II. 1929 - Discovery of distance - velocity relation in galaxies ...
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester
... A) They combined in groups to make protons, neutrons, and their antiparticles. B) They froze out of the soup of particles at the end of the era. C) They evaporated. D) They combined in groups to make electrons and neutrinos. 24) Why do we expect the cosmic background radiation to be almost, but not ...
... A) They combined in groups to make protons, neutrons, and their antiparticles. B) They froze out of the soup of particles at the end of the era. C) They evaporated. D) They combined in groups to make electrons and neutrinos. 24) Why do we expect the cosmic background radiation to be almost, but not ...
Introduction to the Earth
... from the center of the Universe because the Universe is expanding. The existence of RED SHIFT and the ...
... from the center of the Universe because the Universe is expanding. The existence of RED SHIFT and the ...
Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... Review Questions: (Give answers in your own words) A Sense of the Universe 1. What was the universe like for ancient/medieval astronomers? 2. How did Astronomy relate to religious beliefs? 3. Why has the understandings and discoveries in the field of Astronomy increased so much over the last 30 year ...
... Review Questions: (Give answers in your own words) A Sense of the Universe 1. What was the universe like for ancient/medieval astronomers? 2. How did Astronomy relate to religious beliefs? 3. Why has the understandings and discoveries in the field of Astronomy increased so much over the last 30 year ...
How big is the Universe? - Contemporary Science Issues
... • Using the cards, match the evidence to the theories they support. (Some cards might go to more than one theory) • Why do you think the Ancient Greeks thought the Universe was “Static” or unchanging? • Which theory do you think is most likely? • Which of Friedmann’s Universes do you think is right? ...
... • Using the cards, match the evidence to the theories they support. (Some cards might go to more than one theory) • Why do you think the Ancient Greeks thought the Universe was “Static” or unchanging? • Which theory do you think is most likely? • Which of Friedmann’s Universes do you think is right? ...
The measure of Cosmological distances
... Velocity = Distance H0 H0 = Hubble’s constant = 70 (km/s) / Mpc Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): II. 1929 - Discovery of distance - velocity relation in galaxies ...
... Velocity = Distance H0 H0 = Hubble’s constant = 70 (km/s) / Mpc Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): II. 1929 - Discovery of distance - velocity relation in galaxies ...
OCN 201 Origin of the Universe
... Star shines for billions of years until most of hydrogen used up ...
... Star shines for billions of years until most of hydrogen used up ...
Document
... The English chemist William Hyde Wollaston was in 1802 the first person to note the appearance of a number of dark features in the solar spectrum. In 1814, Fraunhofer independently rediscovered the lines and began a systematic study and careful measurement of the wavelength of these features. In all ...
... The English chemist William Hyde Wollaston was in 1802 the first person to note the appearance of a number of dark features in the solar spectrum. In 1814, Fraunhofer independently rediscovered the lines and began a systematic study and careful measurement of the wavelength of these features. In all ...
Astronomy
... 10-15 billion years old (Earth is 4.6 billion years old) Where do we think the universe came from/how did it form? ...
... 10-15 billion years old (Earth is 4.6 billion years old) Where do we think the universe came from/how did it form? ...
Science Curriculum Map
... (C) relate position of the Moon and Sun to their effect on ocean tides. 8.8 Earth and space. The student knows characteristics of the universe. The student is expected to: (A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Herztsprung-Russell ...
... (C) relate position of the Moon and Sun to their effect on ocean tides. 8.8 Earth and space. The student knows characteristics of the universe. The student is expected to: (A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Herztsprung-Russell ...
Where do we come from?
... t=0: The Big Bang How do we know that this happened? Universe was denser in the past; if we daringly extrapolate backward to infinite density, that was a finite time ago. ...
... t=0: The Big Bang How do we know that this happened? Universe was denser in the past; if we daringly extrapolate backward to infinite density, that was a finite time ago. ...
1 - UCSC Physics - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Einstein Passes New Tests Sky & Telescope, March 3, 2005, by Robert Naeye A binary pulsar system provides an excellent laboratory for testing some of the most bizarre predictions of general relativity. The two pulsars in the J0737-3039 system are actually very far apart compared to their sizes. In ...
... Einstein Passes New Tests Sky & Telescope, March 3, 2005, by Robert Naeye A binary pulsar system provides an excellent laboratory for testing some of the most bizarre predictions of general relativity. The two pulsars in the J0737-3039 system are actually very far apart compared to their sizes. In ...
1 Dark Matter as a consequence of electric charge non
... charge non-conservation. On top of that we assume that due to a specific coupling with the gravitational field to be described below neutral particles survived inflation. These “early” neutral particles constitute what appears at present dark matter. For the sake of concreteness (cf. below) we will ...
... charge non-conservation. On top of that we assume that due to a specific coupling with the gravitational field to be described below neutral particles survived inflation. These “early” neutral particles constitute what appears at present dark matter. For the sake of concreteness (cf. below) we will ...
CosmologyL1
... satellite, shows the furthest light we can see. It is also the oldest: The light was emitted shortly after the Big Bang, and has been traveling through space for 13.7 billion years to us. In this "baby picture" of the universe, the red and yellow patches are regions that are just a few millionths of ...
... satellite, shows the furthest light we can see. It is also the oldest: The light was emitted shortly after the Big Bang, and has been traveling through space for 13.7 billion years to us. In this "baby picture" of the universe, the red and yellow patches are regions that are just a few millionths of ...
Chapter 34: Cosmology FYI 1. Radar Ranging 2. Triangulation idea
... the universe began with an incredibly dense concentration of mass energy in the process of rapid expansion and cooling matter was formed point-like particles (electrons, quarks, photons, etc.) nucleons (protons and neutrons) simple nuclei (hydrogen and helium) more complex nuclei, atoms, and molecul ...
... the universe began with an incredibly dense concentration of mass energy in the process of rapid expansion and cooling matter was formed point-like particles (electrons, quarks, photons, etc.) nucleons (protons and neutrons) simple nuclei (hydrogen and helium) more complex nuclei, atoms, and molecul ...
Cosmo: Student`s Workbook
... significant figure has enabled a more precise value ie 0.2 rather than 5. remain. In recent years the Universe The Cosmology story is unfinished. Many problems has been measured to be accelerating. This suggests that there is a force other than gravity that the so-called Big Bang. Where an ...
... significant figure has enabled a more precise value ie 0.2 rather than 5. remain. In recent years the Universe The Cosmology story is unfinished. Many problems has been measured to be accelerating. This suggests that there is a force other than gravity that the so-called Big Bang. Where an ...
Astro-2: History of the Universe
... The night sky is dark This implies that the emission of starlight in the universe must be finite, in space, time or both. This is fundamental test for any cosmological model The Big-bang explains Olbers’s paradox with the finiteness of the lifetime of the Universe and hence of its stars: The univers ...
... The night sky is dark This implies that the emission of starlight in the universe must be finite, in space, time or both. This is fundamental test for any cosmological model The Big-bang explains Olbers’s paradox with the finiteness of the lifetime of the Universe and hence of its stars: The univers ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.