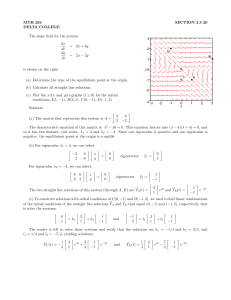
power series solution of non-linear first order differential equation
... AMODIO P, MAZZIA F, Numerical solution of differential-algebraic equations and Computation of consistent initial/boundary conditions. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. 87, 135-146,1997. 2 ASCHER U.M., PETZOLD L.R., Computer Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations and Differential ...
... AMODIO P, MAZZIA F, Numerical solution of differential-algebraic equations and Computation of consistent initial/boundary conditions. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. 87, 135-146,1997. 2 ASCHER U.M., PETZOLD L.R., Computer Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations and Differential ...
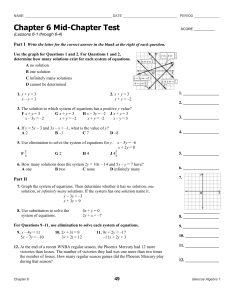
Elimination using the Multiplication Method
... 2. Multiply one or both equations by an appropriate factor so that the new coefficients of x or y have the same absolute value. 3. Add or subtract the equations and solve for the remaining variable. 4. Substitute the value for that variable into one of the equations and solve for the value of the ot ...
... 2. Multiply one or both equations by an appropriate factor so that the new coefficients of x or y have the same absolute value. 3. Add or subtract the equations and solve for the remaining variable. 4. Substitute the value for that variable into one of the equations and solve for the value of the ot ...
Dear Parents
... that cannot be written as the ratio of two integers. Leg: Either of the two shorter sides of a right triangle. The two legs form the right angle of the triangle. Pythagorean Theorem: A theorem that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle: The sum of the squares of the lengths of the leg ...
... that cannot be written as the ratio of two integers. Leg: Either of the two shorter sides of a right triangle. The two legs form the right angle of the triangle. Pythagorean Theorem: A theorem that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle: The sum of the squares of the lengths of the leg ...